Key Public Health Concerns in Today’s Urban Environments
Key Public Health Concerns in Today’s Urban Environments
Do you ever feel like you’re swimming against the current in the bustling city?
Well, when it comes to public health, there are several key concerns that are like strong currents in today’s urban environments.
Take air pollution, for example. It’s like a thick smog that clogs your lungs and affects your respiratory health.
And let’s not forget about the inadequate access to healthcare services, which is like hitting a roadblock when you need medical assistance.
The rise of chronic diseases in urban populations is another pressing issue, like a ticking time bomb waiting to explode.
Mental health challenges in urban environments are like shadows that follow you everywhere, affecting your well-being.
And the impact of noise pollution on public health is like a constant bombardment that disrupts your peace.
Lastly, urbanization has led to a decline in physical activity levels, making it harder for you to stay fit and healthy.
These are just a few of the key public health concerns that require attention in today’s urban environments.
Key Takeaways
– Breathing polluted air in urban environments can lead to respiratory problems and increase the risk of respiratory conditions and diseases.
– Limited availability and high costs of healthcare services in urban areas hinder access to necessary medical care, particularly for low-income individuals and underserved neighborhoods.
– Unhealthy lifestyles and urban infrastructure contribute to the rise of chronic diseases in urban populations, emphasizing the need for prevention strategies and investments in infrastructure maintenance and access to healthcare services.
– Urban environments pose mental health challenges, including high stress levels, social isolation, noise pollution, and limited access to green spaces, which require recognition and action for improvement.
Air Pollution and Respiratory Health
Breathing polluted air can significantly impact your respiratory health. When you’re exposed to air pollution, your lungs can become irritated, leading to respiratory problems such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5), which consists of tiny particles suspended in the air, can penetrate deep into your lungs and even enter your bloodstream, causing inflammation and damage to your respiratory system.
Exposure to air pollution has been linked to the development and worsening of respiratory conditions such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can also increase the risk of respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis, particularly in children and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Furthermore, long-term exposure to air pollution can lead to the progressive decline of lung function and the development of respiratory diseases later in life. Research has shown that individuals living in areas with high levels of air pollution have an increased risk of developing lung cancer and other respiratory diseases.
To protect your respiratory health, it’s important to be aware of the air quality in your surroundings and take necessary precautions. Limiting your exposure to polluted air by staying indoors on days with poor air quality, using air purifiers, and wearing masks when necessary can help reduce the impact of air pollution on your respiratory system.
Inadequate Access to Healthcare Services
To ensure the well-being of your respiratory health, it’s crucial to address the key public health concern of inadequate access to healthcare services in urban environments. In densely populated cities, access to healthcare services can be a significant challenge for many individuals. Limited availability of healthcare facilities, long wait times, and high costs can prevent people from receiving timely and necessary medical care.
One of the main issues contributing to inadequate access to healthcare services is the shortage of healthcare providers in urban areas. The growing population and increased demand for healthcare have strained the existing healthcare infrastructure, leading to overcrowded hospitals and clinics. As a result, individuals may have difficulty scheduling appointments, and emergencies may not be promptly addressed.
Furthermore, economic factors can also hinder access to healthcare services. Many urban dwellers face financial constraints that prevent them from seeking appropriate medical care. High healthcare costs, including insurance premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses, can be a significant barrier. This financial burden often forces individuals to forgo necessary medical treatments or delay seeking care until their condition worsens.
Inadequate access to healthcare services in urban environments disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, including low-income individuals, racial and ethnic minorities, and those living in underserved neighborhoods. These disparities in access to healthcare can result in poorer health outcomes and exacerbate existing health inequalities.
To address this public health concern, it’s essential for policymakers to prioritize the expansion of healthcare services in urban areas. This includes increasing the number of healthcare providers, improving the distribution of healthcare facilities, and implementing measures to reduce healthcare costs. Additionally, initiatives to raise awareness about available healthcare resources and promote preventive care can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their respiratory health.
Rise of Chronic Diseases in Urban Populations
You are living in an urban environment where the rise of chronic diseases is becoming a major concern. The choices you make in your lifestyle can greatly impact your risk of developing these diseases.
It’s important to recognize that the urban infrastructure, such as air pollution and lack of green spaces, can also contribute to the prevalence of chronic illnesses.
To combat this issue, prevention strategies need to be implemented to promote healthier lifestyles and improve the urban environment.
Lifestyle and Chronic Diseases
As you navigate the challenges of urban living, it’s essential to acknowledge the role that lifestyle choices play in the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases among urban populations.
The rise of chronic diseases in urban areas is closely linked to unhealthy lifestyles, including poor diet, lack of physical activity, and high stress levels. In urban environments, convenience often takes precedence over health, leading to a reliance on fast food and sedentary behaviors. These lifestyle choices contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Additionally, the fast-paced urban lifestyle often leaves little time for self-care, further exacerbating the problem. To address this issue, urban dwellers must prioritize their health and make conscious choices to adopt healthier lifestyles, including regular exercise, balanced diets, and stress management techniques.
Urban Infrastructure Impact
The deteriorating condition of urban infrastructure directly contributes to the rise of chronic diseases in urban populations. Here are four key ways in which this impact occurs:
1. Lack of access to clean water and sanitation facilities can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera and dysentery.
2. Poorly maintained roads and sidewalks can discourage physical activity, contributing to sedentary lifestyles and an increased risk of obesity and related conditions.
3. Inadequate waste management systems can lead to the accumulation of garbage and the breeding of disease-carrying vectors like mosquitoes and rats.
4. Limited access to healthcare facilities in underserved urban areas can result in delayed or inadequate treatment for chronic conditions, leading to poorer health outcomes.
To address these issues, it’s crucial for urban planners and policymakers to prioritize investments in infrastructure maintenance, improve access to clean water and sanitation, promote active transportation options, and ensure equitable access to healthcare services.
Prevention Strategies Needed
To effectively address the rise of chronic diseases in urban populations, it’s imperative to implement proactive prevention strategies. With the rapid urbanization and lifestyle changes, chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity have become prevalent in urban areas.
To combat this issue, cities must prioritize prevention through various strategies. Encouraging physical activity by creating safe and accessible green spaces and implementing infrastructure that promotes walking and cycling can help combat sedentary lifestyles.
Additionally, public education campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of healthy eating and the dangers of tobacco and alcohol consumption. Investing in healthcare facilities and services that provide early detection and treatment of chronic diseases is also crucial to prevent their progression.
Mental Health Challenges in Urban Environments
In urban environments, you face significant mental health challenges. The fast-paced, crowded, and often isolating nature of city life can take a toll on your mental well-being. It’s important to recognize and address these challenges to maintain a healthy mind and body.
Here are four key mental health challenges commonly experienced in urban environments:
1. High levels of stress: The constant hustle and bustle of city life can lead to chronic stress, which can have detrimental effects on your mental health. Long work hours, traffic congestion, and the pressure to succeed can all contribute to elevated stress levels.
2. Social isolation: Despite being surrounded by people, urban environments can be incredibly lonely. The lack of meaningful social connections and a sense of community can leave you feeling isolated and disconnected, which can negatively impact your mental health.
3. Noise pollution: Cities are notorious for their noise levels, with honking horns, construction sites, and loud music permeating the urban landscape. Excessive noise can lead to irritability, sleep disturbances, and heightened anxiety levels, all of which can contribute to mental health challenges.
4. Limited access to green spaces: Urban environments often lack sufficient green spaces, such as parks and gardens, which are known to have positive effects on mental well-being. The absence of nature can deprive you of opportunities for relaxation, stress reduction, and rejuvenation.
Recognizing these mental health challenges is the first step towards addressing them. Urban planners, policymakers, and individuals must work together to create healthier urban environments that prioritize mental well-being.
Impact of Noise Pollution on Public Health
Excessive noise in urban environments significantly affects your overall public health, specifically impacting your mental well-being and physical health. The constant exposure to high levels of noise can lead to a variety of mental health challenges, such as stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. The incessant noise from traffic, construction, and other urban activities can disrupt your ability to relax and concentrate, causing chronic stress that can further lead to cardiovascular issues, including increased blood pressure and heart disease.
Moreover, noise pollution can have a detrimental effect on your physical health. Prolonged exposure to loud noises can damage your hearing, leading to hearing loss and other auditory problems. The constant barrage of noise can also disrupt your sleep patterns, resulting in fatigue, decreased cognitive function, and impaired immune system response. Additionally, noise pollution has been linked to an increased risk of obesity, as it can disrupt healthy eating habits and hinder physical activity.
To mitigate the negative impact of noise pollution on public health, urban planners and policymakers should prioritize noise reduction measures, such as the implementation of noise barriers, stricter noise regulations, and the promotion of quieter urban designs. Individuals can also take steps to protect themselves by using earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones and seeking out quieter, green spaces for relaxation and rejuvenation.
Urbanization and Its Effects on Physical Activity Levels
Urbanization has led to a sedentary lifestyle for many individuals, with people spending more time sitting and engaging in less physical activity.
The lack of green spaces in urban areas further compounds this issue, as there are limited opportunities for outdoor exercise and recreation.
Additionally, the transportation infrastructure and walkability of urban environments can also impact physical activity levels, with some cities lacking safe and accessible pedestrian pathways.
Sedentary Urban Lifestyle
With the rise of urbanization, physical activity levels among individuals living in cities have significantly decreased. This sedentary urban lifestyle poses several health concerns that need to be addressed:
1. Increased risk of chronic diseases: Lack of physical activity can lead to an increased risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
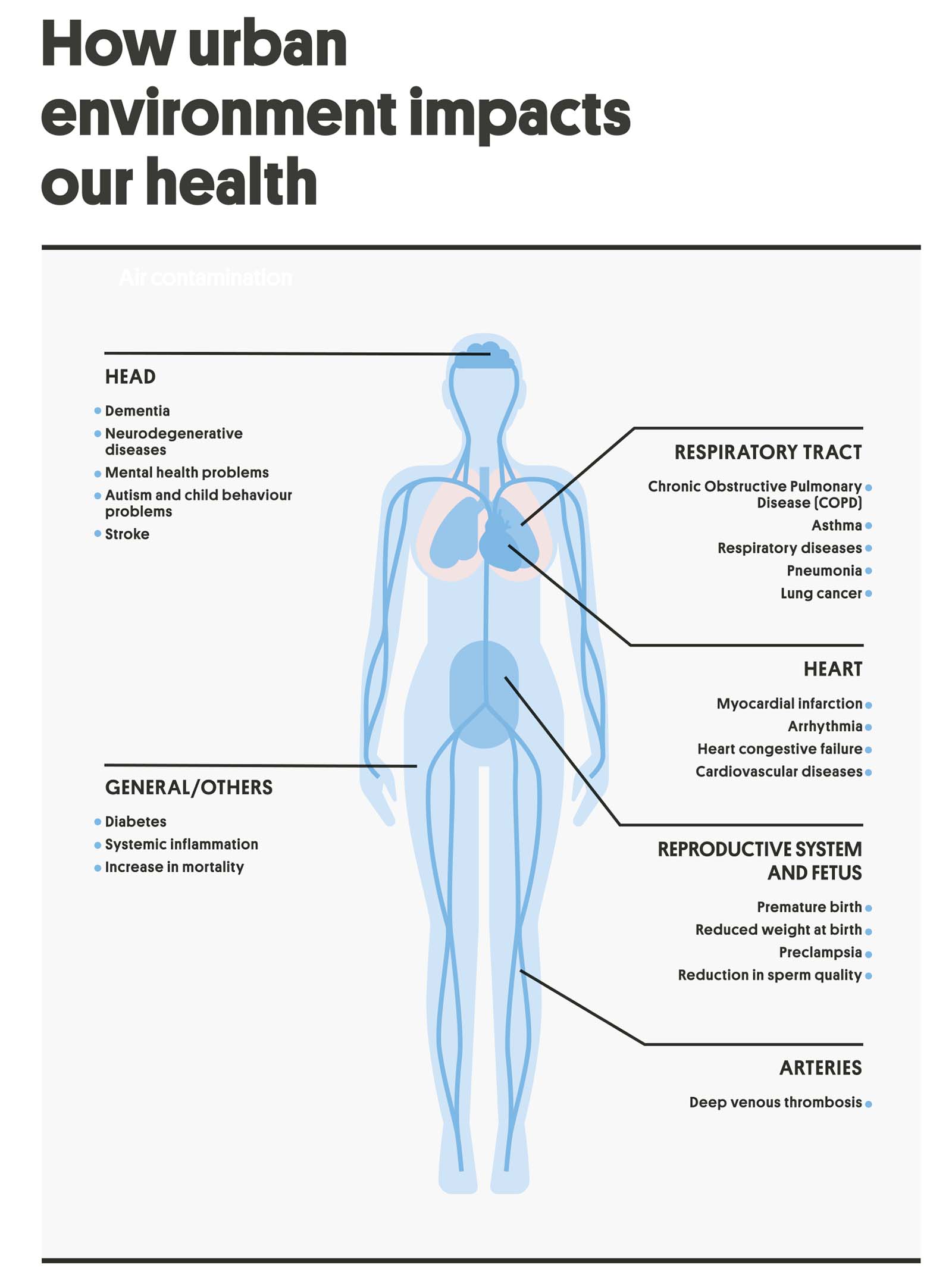
2. Mental health issues: Sedentary lifestyles can contribute to higher stress levels and mental health problems such as depression and anxiety.
3. Poor cardiovascular health: Reduced physical activity can negatively impact cardiovascular health, leading to higher rates of heart disease and stroke.
4. Decreased overall fitness: Sedentary urban lifestyles result in reduced muscle strength and endurance, leading to decreased overall fitness levels.
To combat these issues, it’s crucial to promote active transportation, create green spaces for physical activity, and encourage individuals to incorporate exercise into their daily routines.
Lack of Green Spaces
To combat the sedentary urban lifestyle and its associated health concerns, it’s essential to address the lack of green spaces and its impact on physical activity levels.
In today’s urban environments, the rapid pace of urbanization has resulted in the reduction of green spaces such as parks, gardens, and open areas. This lack of green spaces has significant consequences for physical activity levels.
Without accessible green spaces, individuals are less likely to engage in outdoor activities like walking, jogging, or playing sports. Instead, they’re confined to indoor settings, leading to a more sedentary lifestyle.
Studies have shown that exposure to green spaces is associated with increased physical activity and improved mental well-being.
Therefore, it’s crucial for city planners and policymakers to prioritize the development and maintenance of green spaces to encourage physical activity and combat the negative health effects of urbanization.
Transportation and Walkability
One of the key concerns in today’s urban environments is the impact of transportation and walkability on physical activity levels. The way transportation systems are designed and the availability of walkable spaces greatly influence the amount of physical activity individuals engage in.
Here are four important points to consider:
1. Access to public transportation: The availability and convenience of public transportation options can encourage people to use public transportation instead of relying on private vehicles, which promotes walking and physical activity.
2. Pedestrian infrastructure: Well-designed sidewalks, crosswalks, and pedestrian-friendly features such as benches and lighting can make walking more enjoyable and safer, encouraging people to choose walking as a mode of transportation.
3. Bike-friendly infrastructure: The presence of bike lanes, bike-sharing programs, and secure bike parking facilities can encourage individuals to use bicycles as a means of transportation, promoting physical activity.
4. Land use planning: Designing neighborhoods with mixed-use developments, where residential, commercial, and recreational areas are within close proximity, can reduce the need for long-distance travel, making walking or biking a more feasible option for daily activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Air Pollution Specifically Affect Respiratory Health in Urban Environments?
Air pollution in urban environments can have a significant impact on your respiratory health. Breathing in polluted air can irritate your lungs and airways, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
Long-term exposure to air pollution can also increase the risk of developing respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
It’s important to take steps to reduce your exposure to air pollution, such as avoiding heavily trafficked areas and using air purifiers indoors.
What Are the Main Reasons for Inadequate Access to Healthcare Services in Urban Areas?
Inadequate access to healthcare services in urban areas can be attributed to various factors.
Limited availability of healthcare facilities, long waiting times, and high costs of services are some key reasons.
Additionally, overcrowding and lack of transportation options can make it difficult for individuals to reach healthcare providers.
Language barriers and cultural differences may also hinder access to appropriate care.
These challenges contribute to disparities in healthcare access and can have negative impacts on the overall health of urban populations.
How Has the Rise of Chronic Diseases Impacted the Overall Health of Urban Populations?
The rise of chronic diseases has had a significant impact on your overall health in urban areas. These diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, have become more prevalent due to factors like sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, and environmental pollution.
They not only affect individuals but also strain healthcare systems and resources. It’s crucial for you to prioritize preventive measures like regular exercise, healthy eating, and access to quality healthcare to mitigate the detrimental effects of these chronic diseases.
What Are Some Common Mental Health Challenges Faced by Individuals Living in Urban Environments?
Living in urban environments can present various mental health challenges. The fast-paced lifestyle, high levels of stress, and social isolation can take a toll on your mental well-being. Common challenges include anxiety, depression, and substance abuse.
The constant noise, pollution, and lack of green spaces can also contribute to these issues. It’s important to prioritize self-care, seek support from friends or professionals, and find healthy coping mechanisms to maintain good mental health in urban settings.
What Are the Long-Term Health Effects of Exposure to High Levels of Noise Pollution in Urban Areas?
Exposure to high levels of noise pollution in urban areas can have significant long-term health effects on you. Studies have shown that constant exposure to loud noises can lead to increased stress levels, sleep disturbances, and even cardiovascular problems.
The noise can also negatively impact your mental health, causing anxiety, depression, and impaired cognitive function. It’s important to take steps to reduce noise pollution and protect your well-being in urban environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, living in urban environments poses significant public health concerns.
Air pollution and inadequate access to healthcare services contribute to respiratory health issues and hinder proper medical care.
The rise of chronic diseases and mental health challenges further exacerbate the situation.
Additionally, noise pollution and reduced physical activity levels due to urbanization also impact public health nega find this tively.
It’s crucial for policymakers and communities to address these concerns to ensure a healthier and more sustainable urban lifestyle.