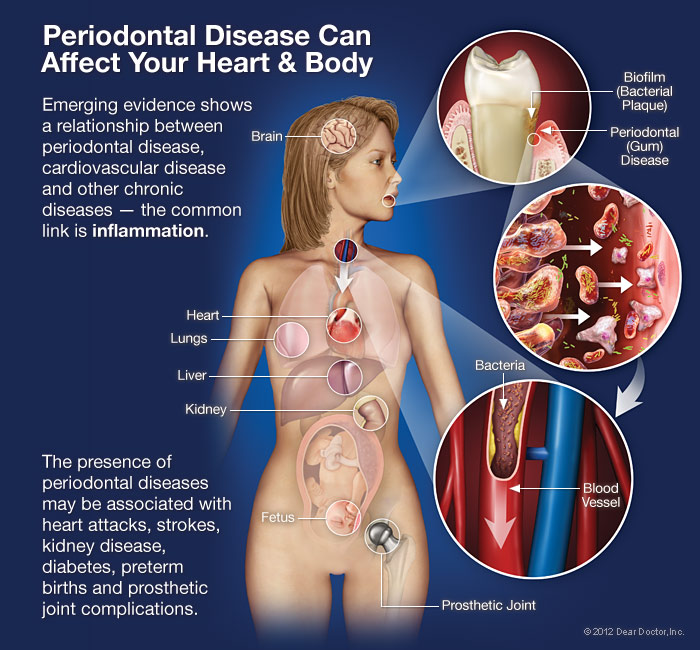
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Overall Health
They say, ‘An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.’ And when it comes to your health, this adage couldn’t be more true.
But did you know that taking care of your oral health could have a significant impact on your overall well-being? Periodontal disease, a common dental condition, has been linked to a range of health issues beyond just your teeth and gums.
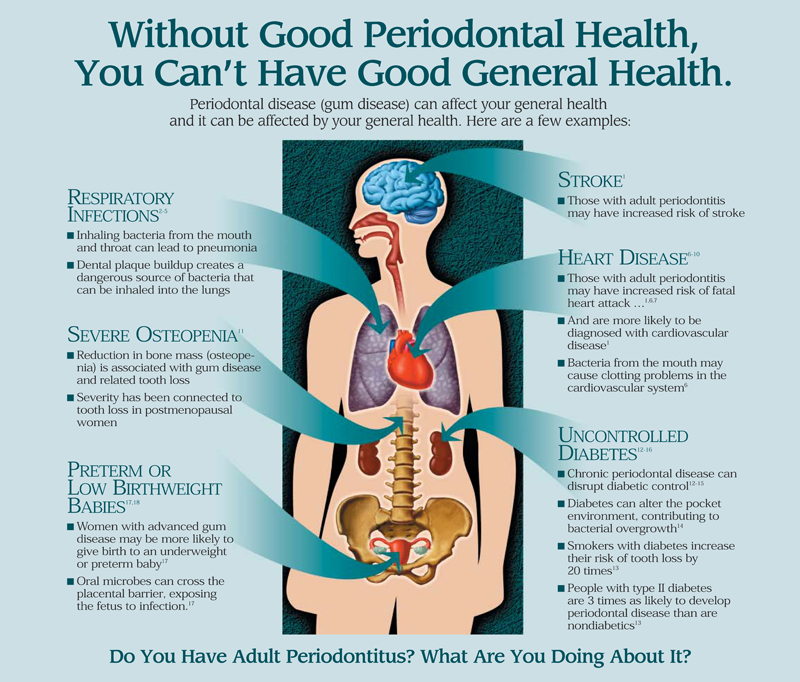
From cardiovascular health to respiratory health, diabetes to pregnancy complications, the connection between periodontal disease and overall health is undeniable.
So, how exactly does your oral health affect the rest of your body? Let’s explore the fascinating link and discover why maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for your overall well-being.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Understanding periodontal disease is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. It’s caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to serious complications such as tooth loss and increased risk of other health problems.
The first stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If not treated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. This infection can then spread to the bones and tissues supporting the teeth, causing them to weaken and eventually leading to tooth loss.
Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing and managing periodontal disease. Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria from your mouth. Additionally, quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy diet can also contribute to better oral health.
The Oral-Systemic Connection
Maintaining good oral health isn’t only important for your teeth and gums, but it also has a significant impact on your overall health. The connection between oral health and systemic health is known as the oral-systemic connection. Research has shown that the health of your mouth can affect your body in various ways.
One of the most prominent links in the oral-systemic connection is between periodontal disease and several systemic conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory illnesses. Periodontal disease is a chronic infection of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth, which can result in tooth loss if left untreated. The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation in other parts of the body, contributing to the development or worsening of these systemic conditions.
Furthermore, the inflammation caused by periodontal disease can also affect pregnancy outcomes. Pregnant women with periodontal disease are at a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight babies. It’s believed that the inflammation and immune response triggered by the oral infection can disrupt the normal development of the fetus.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
The impact of periodontal disease on overall health extends to cardiovascular health as well, with research showing a significant connection between gum disease and the development or worsening of heart conditions. It turns out that the bacteria from gum infections can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, including the heart. Once there, these bacteria can cause inflammation and damage to the blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Studies have found that individuals with periodontal disease are more likely to have heart disease compared to those with healthy gums. In fact, one study discovered that the presence of gum disease was a stronger predictor of heart disease than high cholesterol levels. The link between periodontal disease and cardiovascular health is thought to be due to the chronic inflammation caused by the infection. This inflammation can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, narrowing the blood vessels and restricting blood flow to the heart.
Furthermore, gum disease has also been associated with other risk factors for heart disease, such as diabetes and smoking. People with diabetes are more susceptible to gum disease, and the presence of both conditions can make each one worse. Smoking, a known risk factor for heart disease, can also increase the likelihood of developing periodontal disease.
Diabetes and Gum Disease
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gum disease. Diabetes affects the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels, which can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including gum disease. When blood sugar levels are high, it creates an ideal environment for bacteria to grow and multiply in the mouth, leading to the formation of plaque and tartar. This can then irritate and inflame the gums, causing gingivitis and eventually progressing to periodontitis if left untreated.
Moreover, gum disease can also have a negative impact on diabetes management. The inflammation caused by gum disease can make it more difficult for individuals with diabetes to control their blood sugar levels. It can also increase insulin resistance, making it harder for the body to use insulin effectively. This creates a vicious cycle, as uncontrolled diabetes can worsen gum disease, and gum disease can make it harder to control diabetes.
To reduce the risk of gum disease, individuals with diabetes should prioritize good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and visiting their dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. It’s also important for individuals with diabetes to maintain good blood sugar control to minimize the risk of developing gum disease and its complications.
Respiratory Health and Periodontal Disease
Did you know that periodontal disease can affect your respiratory health?
One of the risks associated with periodontal disease is an increased risk of lung infections. When you have gum disease, the oral bacteria can travel to your lungs, potentially causing respiratory issues.
It’s important to take care of your oral health to maintain a healthy respiratory system.
Lung Infection Risk
Regular dental care and good oral hygiene can help reduce the risk of lung infections associated with periodontal disease. When you have periodontal disease, bacteria from the infected gums can travel through your bloodstream and reach your lungs, causing infections like pneumonia. These bacteria can also worsen existing lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma.
By maintaining proper dental care, you can prevent the accumulation of harmful bacteria in your mouth and minimize the risk of these bacteria spreading to your lungs. Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups are essential steps in preventing periodontal disease and reducing the risk of lung infections.
Taking care of your oral health is crucial for maintaining your overall respiratory health.
Oral Bacteria Transmission
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing the transmission of oral bacteria and protecting your respiratory health from the risks associated with periodontal disease. The presence of periodontal disease can lead to the accumulation of harmful bacteria in your mouth, which can then be inhaled into your respiratory system. This can result in respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and exacerbation of existing conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The bacteria from your mouth can travel through your saliva, reaching your lungs and causing inflammation and infection. By practicing proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, you can reduce the likelihood of oral bacteria transmission and safeguard your respiratory health.
Pregnancy Complications and Gum Disease
Pregnancy complications can be linked to the presence of gum disease. Research has shown that expectant mothers with gum disease are more likely to experience certain complications during pregnancy. These complications include preterm birth, low birth weight, and preeclampsia.
The exact mechanism behind this link is still being studied, but it’s believed that the oral bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and affect the developing fetus. The inflammation caused by gum disease may also trigger an immune response that can lead to complications.
Preterm birth, defined as giving birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy, is a major concern for both mothers and babies. Babies born prematurely are at a higher risk of developmental issues and health problems. Low birth weight, which is often associated with preterm birth, can also have long-term effects on a child’s health.
Preeclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs, usually the liver and kidneys, during pregnancy. It can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby. Studies have shown that pregnant women with gum disease are more likely to develop preeclampsia compared to those with healthy gums.
To minimize the risk of pregnancy complications, it’s important for expectant mothers to maintain good oral hygiene and seek regular dental care. This includes brushing and flossing daily, as well as scheduling dental check-ups during pregnancy. By taking care of their oral health, pregnant women can help reduce the chances of experiencing complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy for themselves and their babies.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
To maintain good oral hygiene, it’s important to pay attention to your brushing techniques and the importance of flossing.
When brushing your teeth, use short, gentle strokes and make sure to clean all surfaces, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces.
Additionally, don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
Brushing Techniques
Proper brushing techniques are essential for maintaining good oral hygiene. To ensure you’re brushing effectively, follow these steps:
– Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle against your gums.
– Use short, gentle strokes to clean each tooth’s outer surface.
– Be sure to reach the back teeth as well.
– Pay extra attention to the gumline where bacteria tend to accumulate.
– Brush the inner surfaces of your teeth using the same technique.
– Clean the chewing surfaces by moving the brush in a back-and-forth motion.
– Don’t forget to brush your tongue to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
– Brush for at least two minutes, twice a day, and replace your toothbrush every three to four months.
Flossing Importance
To maintain good oral hygiene and complement proper brushing techniques, it’s crucial to understand the importance of flossing.
While brushing cleans the surface of your teeth, flossing goes a step further by removing plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. These are areas that a toothbrush can’t reach effectively.
Flossing helps prevent the buildup of plaque, which can lead to gum disease and tooth decay. It also reduces the risk of developing periodontal disease, a serious gum infection that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting your teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Periodontal Disease Be Treated With Medication Alone, or Is Professional Dental Treatment Necessary?
Can periodontal disease be treated with medication alone, or is professional dental treatment necessary?
It’s important to understand that periodontal disease is a serious condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. While medication can help manage the symptoms and control the infection to some extent, it isn’t enough to fully treat the disease.
Professional dental treatment, such as deep cleaning and scaling, is necessary to remove the plaque and tartar buildup and restore oral health.
It’s best to consult with a dentist for a comprehensive treatment plan.
Is There a Link Between Periodontal Disease and Mental Health Conditions Such as Depression or Anxiety?
Yes, there’s a link between periodontal disease and mental health conditions like depression or anxiety. Studies have shown that individuals with periodontal disease are more likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety.
The exact cause of this link is still being investigated, but it’s believed that inflammation in the gums may contribute to the development of mental health issues.
It’s important to prioritize oral health and seek treatment for periodontal disease to potentially improve your overall mental well-being.
Can Poor Oral Hygiene Habits Contribute to the Development of Periodontal Disease?
Poor oral hygiene habits can indeed contribute to the development of periodontal disease. When you neglect to brush and floss regularly, plaque and bacteria can build up around your teeth and gums.
Over time, this can lead to inflammation and infection, causing the gums to recede and the teeth to become loose.
It’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice a day and flossing daily, to prevent the development of periodontal disease.
Are There Any Specific Dietary Changes That Can Help Prevent or Manage Periodontal Disease?
Making specific dietary changes can be helpful in preventing or managing periodontal disease. Incorporating more fruits and vegetables into your diet can provide essential vitamins and minerals that support oral health.
It’s also important to limit sugary and acidic foods and beverages, as they can contribute to tooth decay and gum inflammation.
Additionally, staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can help strengthen your immune system, which plays a role in fighting off gum infections.
Is It Possible to Prevent Periodontal Disease Entirely, or Is It Only Manageable Once It Develops?
It is possible to prevent periodontal disease entirely by practicing good oral hygiene. Regularly brushing and flossing your teeth, along with visiting the dentist for check-ups and cleanings, can help keep your gums healthy and prevent the development of periodontal disease.
However, if the disease does develop, it’s still manageable through various treatments and interventions. Early detection and prompt treatment are key in effectively managing periodontal disease and minimizing its impact on your overall health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s clear that there’s a strong link between periodontal disease and overall health. Research has shown that periodontal disease can have a negative impact on cardiovascular health, diabetes control, respiratory health, and even pregnancy outcomes.
Therefore, it’s crucial to mainta why not find out more in good oral hygiene and seek appropriate dental care to prevent and manage periodontal disease, ultimately contributing to better overall health.
Was this helpful?

Welcome to my website! I am Levi Halpern, a dedicated and passionate professional Cosmetic Dentist with extensive experience in Orthodontic Innovations, Periodontal Care, and Pediatric Dental Care. I am thrilled to have the opportunity to share my knowledge and expertise with you.