

Maximise your business potential with Professional SEO Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with Parramatta WordPress developers Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Technical SEO Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Best SEO Agency Parramatta Australia.Maximise your business potential with SEO for trades Parramatta We deliver impactful strategies designed to boost your brand awareness, improve online visibility, and generate a steady flow of qualified leads in Parramatta
Choose excellence in digital marketing with Mobile-friendly web design Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Experience outstanding online performance through Lead generation Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Effective Web Design Parramatta Sydney.Experience outstanding online performance through Parramatta SEO packages Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Take your digital presence further with On-page SEO Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Experience outstanding online performance through SEO and web design Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Best Local SEO Parramatta.

Choose excellence in digital marketing with SEO content writing Parramatta Our proven approaches drive website traffic, enhance customer engagement, and significantly improve conversion rates, supporting long-term business success in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with Parramatta branding and web design Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Experience outstanding online performance through Website optimisation Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
range of SEO Packages Parramatta Sydney.Take your digital presence further with SEO strategy Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Experience outstanding online performance through Local business SEO Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with Google Ads and SEO Parramatta Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Top Digital Marketing Parramatta NSW.

Transform your business growth with SEO for local services Parramatta Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Transform your business growth with Parramatta UI UX design Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today
Take your digital presence further with Conversion-focused web design Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Take your digital presence further with Fast-loading websites Parramatta We develop custom strategies aimed at increasing your online visibility, improving search engine rankings, and achieving sustainable growth for your Parramatta-based business
Experience outstanding online performance through SEO landing pages Parramatta Our expert team specialises in delivering solutions that improve rankings, drive engagement, and generate valuable leads for consistent business growth in Parramatta
Transform your business growth with Parramatta SEO marketing Our strategies enhance visibility, attract targeted traffic, and maximise conversions for sustained success Partner with us for measurable digital marketing outcomes today

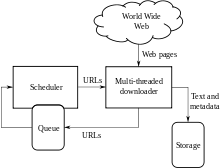
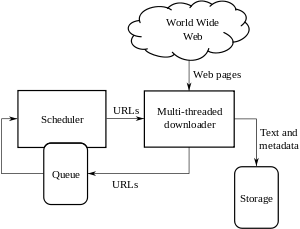
A Web crawler, sometimes called a spider or spiderbot and often shortened to crawler, is an Internet bot that systematically browses the World Wide Web and that is typically operated by search engines for the purpose of Web indexing (web spidering).[1]
Web search engines and some other websites use Web crawling or spidering software to update their web content or indices of other sites' web content. Web crawlers copy pages for processing by a search engine, which indexes the downloaded pages so that users can search more efficiently.
Crawlers consume resources on visited systems and often visit sites unprompted. Issues of schedule, load, and "politeness" come into play when large collections of pages are accessed. Mechanisms exist for public sites not wishing to be crawled to make this known to the crawling agent. For example, including a robots.txt file can request bots to index only parts of a website, or nothing at all.
The number of Internet pages is extremely large; even the largest crawlers fall short of making a complete index. For this reason, search engines struggled to give relevant search results in the early years of the World Wide Web, before 2000. Today, relevant results are given almost instantly.
Crawlers can validate hyperlinks and HTML code. They can also be used for web scraping and data-driven programming.
A web crawler is also known as a spider,[2] an ant, an automatic indexer,[3] or (in the FOAF software context) a Web scutter.[4]
A Web crawler starts with a list of URLs to visit. Those first URLs are called the seeds. As the crawler visits these URLs, by communicating with web servers that respond to those URLs, it identifies all the hyperlinks in the retrieved web pages and adds them to the list of URLs to visit, called the crawl frontier. URLs from the frontier are recursively visited according to a set of policies. If the crawler is performing archiving of websites (or web archiving), it copies and saves the information as it goes. The archives are usually stored in such a way they can be viewed, read and navigated as if they were on the live web, but are preserved as 'snapshots'.[5]
The archive is known as the repository and is designed to store and manage the collection of web pages. The repository only stores HTML pages and these pages are stored as distinct files. A repository is similar to any other system that stores data, like a modern-day database. The only difference is that a repository does not need all the functionality offered by a database system. The repository stores the most recent version of the web page retrieved by the crawler.[citation needed]
The large volume implies the crawler can only download a limited number of the Web pages within a given time, so it needs to prioritize its downloads. The high rate of change can imply the pages might have already been updated or even deleted.
The number of possible URLs crawled being generated by server-side software has also made it difficult for web crawlers to avoid retrieving duplicate content. Endless combinations of HTTP GET (URL-based) parameters exist, of which only a small selection will actually return unique content. For example, a simple online photo gallery may offer three options to users, as specified through HTTP GET parameters in the URL. If there exist four ways to sort images, three choices of thumbnail size, two file formats, and an option to disable user-provided content, then the same set of content can be accessed with 48 different URLs, all of which may be linked on the site. This mathematical combination creates a problem for crawlers, as they must sort through endless combinations of relatively minor scripted changes in order to retrieve unique content.
As Edwards et al. noted, "Given that the bandwidth for conducting crawls is neither infinite nor free, it is becoming essential to crawl the Web in not only a scalable, but efficient way, if some reasonable measure of quality or freshness is to be maintained."[6] A crawler must carefully choose at each step which pages to visit next.
The behavior of a Web crawler is the outcome of a combination of policies:[7]
Given the current size of the Web, even large search engines cover only a portion of the publicly available part. A 2009 study showed even large-scale search engines index no more than 40–70% of the indexable Web;[8] a previous study by Steve Lawrence and Lee Giles showed that no search engine indexed more than 16% of the Web in 1999.[9] As a crawler always downloads just a fraction of the Web pages, it is highly desirable for the downloaded fraction to contain the most relevant pages and not just a random sample of the Web.
This requires a metric of importance for prioritizing Web pages. The importance of a page is a function of its intrinsic quality, its popularity in terms of links or visits, and even of its URL (the latter is the case of vertical search engines restricted to a single top-level domain, or search engines restricted to a fixed Web site). Designing a good selection policy has an added difficulty: it must work with partial information, as the complete set of Web pages is not known during crawling.
Junghoo Cho et al. made the first study on policies for crawling scheduling. Their data set was a 180,000-pages crawl from the stanford.edu domain, in which a crawling simulation was done with different strategies.[10] The ordering metrics tested were breadth-first, backlink count and partial PageRank calculations. One of the conclusions was that if the crawler wants to download pages with high Pagerank early during the crawling process, then the partial Pagerank strategy is the better, followed by breadth-first and backlink-count. However, these results are for just a single domain. Cho also wrote his PhD dissertation at Stanford on web crawling.[11]
Najork and Wiener performed an actual crawl on 328 million pages, using breadth-first ordering.[12] They found that a breadth-first crawl captures pages with high Pagerank early in the crawl (but they did not compare this strategy against other strategies). The explanation given by the authors for this result is that "the most important pages have many links to them from numerous hosts, and those links will be found early, regardless of on which host or page the crawl originates."
Abiteboul designed a crawling strategy based on an algorithm called OPIC (On-line Page Importance Computation).[13] In OPIC, each page is given an initial sum of "cash" that is distributed equally among the pages it points to. It is similar to a PageRank computation, but it is faster and is only done in one step. An OPIC-driven crawler downloads first the pages in the crawling frontier with higher amounts of "cash". Experiments were carried in a 100,000-pages synthetic graph with a power-law distribution of in-links. However, there was no comparison with other strategies nor experiments in the real Web.
Boldi et al. used simulation on subsets of the Web of 40 million pages from the .it domain and 100 million pages from the WebBase crawl, testing breadth-first against depth-first, random ordering and an omniscient strategy. The comparison was based on how well PageRank computed on a partial crawl approximates the true PageRank value. Some visits that accumulate PageRank very quickly (most notably, breadth-first and the omniscient visit) provide very poor progressive approximations.[14][15]
Baeza-Yates et al. used simulation on two subsets of the Web of 3 million pages from the .gr and .cl domain, testing several crawling strategies.[16] They showed that both the OPIC strategy and a strategy that uses the length of the per-site queues are better than breadth-first crawling, and that it is also very effective to use a previous crawl, when it is available, to guide the current one.
Daneshpajouh et al. designed a community based algorithm for discovering good seeds.[17] Their method crawls web pages with high PageRank from different communities in less iteration in comparison with crawl starting from random seeds. One can extract good seed from a previously-crawled-Web graph using this new method. Using these seeds, a new crawl can be very effective.
A crawler may only want to seek out HTML pages and avoid all other MIME types. In order to request only HTML resources, a crawler may make an HTTP HEAD request to determine a Web resource's MIME type before requesting the entire resource with a GET request. To avoid making numerous HEAD requests, a crawler may examine the URL and only request a resource if the URL ends with certain characters such as .html, .htm, .asp, .aspx, .php, .jsp, .jspx or a slash. This strategy may cause numerous HTML Web resources to be unintentionally skipped.
Some crawlers may also avoid requesting any resources that have a "?" in them (are dynamically produced) in order to avoid spider traps that may cause the crawler to download an infinite number of URLs from a Web site. This strategy is unreliable if the site uses URL rewriting to simplify its URLs.
Crawlers usually perform some type of URL normalization in order to avoid crawling the same resource more than once. The term URL normalization, also called URL canonicalization, refers to the process of modifying and standardizing a URL in a consistent manner. There are several types of normalization that may be performed including conversion of URLs to lowercase, removal of "." and ".." segments, and adding trailing slashes to the non-empty path component.[18]
Some crawlers intend to download/upload as many resources as possible from a particular web site. So path-ascending crawler was introduced that would ascend to every path in each URL that it intends to crawl.[19] For example, when given a seed URL of http://llama.org/hamster/monkey/page.html, it will attempt to crawl /hamster/monkey/, /hamster/, and /. Cothey found that a path-ascending crawler was very effective in finding isolated resources, or resources for which no inbound link would have been found in regular crawling.
The importance of a page for a crawler can also be expressed as a function of the similarity of a page to a given query. Web crawlers that attempt to download pages that are similar to each other are called focused crawler or topical crawlers. The concepts of topical and focused crawling were first introduced by Filippo Menczer[20][21] and by Soumen Chakrabarti et al.[22]
The main problem in focused crawling is that in the context of a Web crawler, we would like to be able to predict the similarity of the text of a given page to the query before actually downloading the page. A possible predictor is the anchor text of links; this was the approach taken by Pinkerton[23] in the first web crawler of the early days of the Web. Diligenti et al.[24] propose using the complete content of the pages already visited to infer the similarity between the driving query and the pages that have not been visited yet. The performance of a focused crawling depends mostly on the richness of links in the specific topic being searched, and a focused crawling usually relies on a general Web search engine for providing starting points.
An example of the focused crawlers are academic crawlers, which crawls free-access academic related documents, such as the citeseerxbot, which is the crawler of CiteSeerX search engine. Other academic search engines are Google Scholar and Microsoft Academic Search etc. Because most academic papers are published in PDF formats, such kind of crawler is particularly interested in crawling PDF, PostScript files, Microsoft Word including their zipped formats. Because of this, general open-source crawlers, such as Heritrix, must be customized to filter out other MIME types, or a middleware is used to extract these documents out and import them to the focused crawl database and repository.[25] Identifying whether these documents are academic or not is challenging and can add a significant overhead to the crawling process, so this is performed as a post crawling process using machine learning or regular expression algorithms. These academic documents are usually obtained from home pages of faculties and students or from publication page of research institutes. Because academic documents make up only a small fraction of all web pages, a good seed selection is important in boosting the efficiencies of these web crawlers.[26] Other academic crawlers may download plain text and HTML files, that contains metadata of academic papers, such as titles, papers, and abstracts. This increases the overall number of papers, but a significant fraction may not provide free PDF downloads.
Another type of focused crawlers is semantic focused crawler, which makes use of domain ontologies to represent topical maps and link Web pages with relevant ontological concepts for the selection and categorization purposes.[27] In addition, ontologies can be automatically updated in the crawling process. Dong et al.[28] introduced such an ontology-learning-based crawler using a support-vector machine to update the content of ontological concepts when crawling Web pages.
The Web has a very dynamic nature, and crawling a fraction of the Web can take weeks or months. By the time a Web crawler has finished its crawl, many events could have happened, including creations, updates, and deletions.
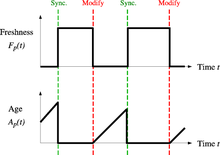
From the search engine's point of view, there is a cost associated with not detecting an event, and thus having an outdated copy of a resource. The most-used cost functions are freshness and age.[29]
Freshness: This is a binary measure that indicates whether the local copy is accurate or not. The freshness of a page p in the repository at time t is defined as:
Age: This is a measure that indicates how outdated the local copy is. The age of a page p in the repository, at time t is defined as:
Coffman et al. worked with a definition of the objective of a Web crawler that is equivalent to freshness, but use a different wording: they propose that a crawler must minimize the fraction of time pages remain outdated. They also noted that the problem of Web crawling can be modeled as a multiple-queue, single-server polling system, on which the Web crawler is the server and the Web sites are the queues. Page modifications are the arrival of the customers, and switch-over times are the interval between page accesses to a single Web site. Under this model, mean waiting time for a customer in the polling system is equivalent to the average age for the Web crawler.[30]
The objective of the crawler is to keep the average freshness of pages in its collection as high as possible, or to keep the average age of pages as low as possible. These objectives are not equivalent: in the first case, the crawler is just concerned with how many pages are outdated, while in the second case, the crawler is concerned with how old the local copies of pages are.
Two simple re-visiting policies were studied by Cho and Garcia-Molina:[31]
In both cases, the repeated crawling order of pages can be done either in a random or a fixed order.
Cho and Garcia-Molina proved the surprising result that, in terms of average freshness, the uniform policy outperforms the proportional policy in both a simulated Web and a real Web crawl. Intuitively, the reasoning is that, as web crawlers have a limit to how many pages they can crawl in a given time frame, (1) they will allocate too many new crawls to rapidly changing pages at the expense of less frequently updating pages, and (2) the freshness of rapidly changing pages lasts for shorter period than that of less frequently changing pages. In other words, a proportional policy allocates more resources to crawling frequently updating pages, but experiences less overall freshness time from them.
To improve freshness, the crawler should penalize the elements that change too often.[32] The optimal re-visiting policy is neither the uniform policy nor the proportional policy. The optimal method for keeping average freshness high includes ignoring the pages that change too often, and the optimal for keeping average age low is to use access frequencies that monotonically (and sub-linearly) increase with the rate of change of each page. In both cases, the optimal is closer to the uniform policy than to the proportional policy: as Coffman et al. note, "in order to minimize the expected obsolescence time, the accesses to any particular page should be kept as evenly spaced as possible".[30] Explicit formulas for the re-visit policy are not attainable in general, but they are obtained numerically, as they depend on the distribution of page changes. Cho and Garcia-Molina show that the exponential distribution is a good fit for describing page changes,[32] while Ipeirotis et al. show how to use statistical tools to discover parameters that affect this distribution.[33] The re-visiting policies considered here regard all pages as homogeneous in terms of quality ("all pages on the Web are worth the same"), something that is not a realistic scenario, so further information about the Web page quality should be included to achieve a better crawling policy.
Crawlers can retrieve data much quicker and in greater depth than human searchers, so they can have a crippling impact on the performance of a site. If a single crawler is performing multiple requests per second and/or downloading large files, a server can have a hard time keeping up with requests from multiple crawlers.
As noted by Koster, the use of Web crawlers is useful for a number of tasks, but comes with a price for the general community.[34] The costs of using Web crawlers include:
A partial solution to these problems is the robots exclusion protocol, also known as the robots.txt protocol that is a standard for administrators to indicate which parts of their Web servers should not be accessed by crawlers.[35] This standard does not include a suggestion for the interval of visits to the same server, even though this interval is the most effective way of avoiding server overload. Recently commercial search engines like Google, Ask Jeeves, MSN and Yahoo! Search are able to use an extra "Crawl-delay:" parameter in the robots.txt file to indicate the number of seconds to delay between requests.
The first proposed interval between successive pageloads was 60 seconds.[36] However, if pages were downloaded at this rate from a website with more than 100,000 pages over a perfect connection with zero latency and infinite bandwidth, it would take more than 2 months to download only that entire Web site; also, only a fraction of the resources from that Web server would be used.
Cho uses 10 seconds as an interval for accesses,[31] and the WIRE crawler uses 15 seconds as the default.[37] The MercatorWeb crawler follows an adaptive politeness policy: if it took t seconds to download a document from a given server, the crawler waits for 10t seconds before downloading the next page.[38] Dill et al. use 1 second.[39]
For those using Web crawlers for research purposes, a more detailed cost-benefit analysis is needed and ethical considerations should be taken into account when deciding where to crawl and how fast to crawl.[40]
Anecdotal evidence from access logs shows that access intervals from known crawlers vary between 20 seconds and 3–4 minutes. It is worth noticing that even when being very polite, and taking all the safeguards to avoid overloading Web servers, some complaints from Web server administrators are received. Sergey Brin and Larry Page noted in 1998, "... running a crawler which connects to more than half a million servers ... generates a fair amount of e-mail and phone calls. Because of the vast number of people coming on line, there are always those who do not know what a crawler is, because this is the first one they have seen."[41]
A parallel crawler is a crawler that runs multiple processes in parallel. The goal is to maximize the download rate while minimizing the overhead from parallelization and to avoid repeated downloads of the same page. To avoid downloading the same page more than once, the crawling system requires a policy for assigning the new URLs discovered during the crawling process, as the same URL can be found by two different crawling processes.
A crawler must not only have a good crawling strategy, as noted in the previous sections, but it should also have a highly optimized architecture.
Shkapenyuk and Suel noted that:[42]
While it is fairly easy to build a slow crawler that downloads a few pages per second for a short period of time, building a high-performance system that can download hundreds of millions of pages over several weeks presents a number of challenges in system design, I/O and network efficiency, and robustness and manageability.
Web crawlers are a central part of search engines, and details on their algorithms and architecture are kept as business secrets. When crawler designs are published, there is often an important lack of detail that prevents others from reproducing the work. There are also emerging concerns about "search engine spamming", which prevent major search engines from publishing their ranking algorithms.
While most of the website owners are keen to have their pages indexed as broadly as possible to have strong presence in search engines, web crawling can also have unintended consequences and lead to a compromise or data breach if a search engine indexes resources that should not be publicly available, or pages revealing potentially vulnerable versions of software.
Apart from standard web application security recommendations website owners can reduce their exposure to opportunistic hacking by only allowing search engines to index the public parts of their websites (with robots.txt) and explicitly blocking them from indexing transactional parts (login pages, private pages, etc.).
Web crawlers typically identify themselves to a Web server by using the User-agent field of an HTTP request. Web site administrators typically examine their Web servers' log and use the user agent field to determine which crawlers have visited the web server and how often. The user agent field may include a URL where the Web site administrator may find out more information about the crawler. Examining Web server log is tedious task, and therefore some administrators use tools to identify, track and verify Web crawlers. Spambots and other malicious Web crawlers are unlikely to place identifying information in the user agent field, or they may mask their identity as a browser or other well-known crawler.
Web site administrators prefer Web crawlers to identify themselves so that they can contact the owner if needed. In some cases, crawlers may be accidentally trapped in a crawler trap or they may be overloading a Web server with requests, and the owner needs to stop the crawler. Identification is also useful for administrators that are interested in knowing when they may expect their Web pages to be indexed by a particular search engine.
A vast amount of web pages lie in the deep or invisible web.[43] These pages are typically only accessible by submitting queries to a database, and regular crawlers are unable to find these pages if there are no links that point to them. Google's Sitemaps protocol and mod oai[44] are intended to allow discovery of these deep-Web resources.
Deep web crawling also multiplies the number of web links to be crawled. Some crawlers only take some of the URLs in <a href="URL"> form. In some cases, such as the Googlebot, Web crawling is done on all text contained inside the hypertext content, tags, or text.
Strategic approaches may be taken to target deep Web content. With a technique called screen scraping, specialized software may be customized to automatically and repeatedly query a given Web form with the intention of aggregating the resulting data. Such software can be used to span multiple Web forms across multiple Websites. Data extracted from the results of one Web form submission can be taken and applied as input to another Web form thus establishing continuity across the Deep Web in a way not possible with traditional web crawlers.[45]
Pages built on AJAX are among those causing problems to web crawlers. Google has proposed a format of AJAX calls that their bot can recognize and index.[46]
There are a number of "visual web scraper/crawler" products available on the web which will crawl pages and structure data into columns and rows based on the users requirements. One of the main difference between a classic and a visual crawler is the level of programming ability required to set up a crawler. The latest generation of "visual scrapers" remove the majority of the programming skill needed to be able to program and start a crawl to scrape web data.
The visual scraping/crawling method relies on the user "teaching" a piece of crawler technology, which then follows patterns in semi-structured data sources. The dominant method for teaching a visual crawler is by highlighting data in a browser and training columns and rows. While the technology is not new, for example it was the basis of Needlebase which has been bought by Google (as part of a larger acquisition of ITA Labs[47]), there is continued growth and investment in this area by investors and end-users.[citation needed]
The following is a list of published crawler architectures for general-purpose crawlers (excluding focused web crawlers), with a brief description that includes the names given to the different components and outstanding features:
The following web crawlers are available, for a price::
cite book: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)cite journal: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)cite journal: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)
Local search may refer to:
Parramatta (/ËŒpærəˈmætÉ™/; Dharuk: Burramatta) is a suburb and major commercial centre in Greater Western Sydney.[7][8] Parramatta is located approximately 24 kilometres (15 mi) west of the Sydney CBD, on the banks of the Parramatta River.[2] It is commonly regarded as the secondary central business district of metropolitan Sydney.
Parramatta is the municipal seat of the local government area of the City of Parramatta and is often regarded as one of the primary centres of the Greater Sydney metropolitan region, along with the Sydney CBD, Penrith, Campbelltown, and Liverpool.[9] Parramatta also has a long history as a second administrative centre in the Sydney metropolitan region, playing host to a number of government departments,[10] as well as state and federal courts. It is often colloquially referred to as "Parra".
Parramatta, which was founded as a British settlement in 1788, the same year as Sydney, is the oldest inland European settlement in Australia and serves as the economic centre of Greater Western Sydney.[11] Since 2000, state government agencies such as the New South Wales Police Force and Sydney Water[12] have relocated to Parramatta from Central Sydney. The 151st meridian east runs directly through the suburb.
Radiocarbon dating suggests human activity occurred in Parramatta from around 30,000 years ago.[13] The Darug people who lived in the area before European settlement regarded the area as rich in food from the river and forests. They named the area Baramada or Burramatta ('Parramatta') which means Eel ("Burra") Place ("matta"), with the resident Indigenous people being called the Burramattagal. Similar Darug words include Cabramatta (Grub place) and Wianamatta (Mother place).[14] Other references[which?] are derived from the words of Captain Watkin Tench, a white British man with a poor understanding of the Darug language, and are incorrect.[citation needed] To this day many eels and other sea creatures are attracted to nutrients that are concentrated where the saltwater of Port Jackson meets the freshwater of the Parramatta River. The Parramatta Eels rugby league club chose their symbol as a result of this phenomenon.



Parramatta was colonised by the British in 1788, the same year as Sydney. As such, Parramatta is the second oldest city in Australia, being only 10 months younger than Sydney. The British colonists, who had arrived in January 1788 on the First Fleet at Sydney Cove, had only enough food to support themselves for a short time and the soil around Sydney Cove proved too poor to grow the amount of food that 1,000 convicts, soldiers and administrators needed to survive. During 1788, Governor Arthur Phillip had reconnoitred several places before choosing Parramatta as the most likely place for a successful large farm.[15] Parramatta was the furthest navigable point inland on the Parramatta River (i.e. furthest from the thin, sandy coastal soil) and also the point at which the river became freshwater and therefore useful for farming.
On Sunday 2 November 1788, Governor Phillip took a detachment of marines along with a surveyor and, in boats, made his way upriver to a location that he called The Crescent, a defensible hill curved round a river bend, now in Parramatta Park. The Burramattagal were rapidly displaced with notable residents Maugoran, Boorong and Baludarri being forced from their lands.[16]
As a settlement developed, Governor Phillip gave it the name "Rose Hill" after British politician George Rose.[17] On 4 June 1791 Phillip changed the name of the township to Parramatta, approximating the term used by the local Aboriginal people.[18] A neighbouring suburb acquired the name "Rose Hill", which today is spelt "Rosehill".

In an attempt to deal with the food crisis, Phillip in 1789 granted a convict named James Ruse the land of Experiment Farm at Parramatta on the condition that he develop a viable agriculture. There, Ruse became the first European to successfully grow grain in Australia. The Parramatta area was also the site of the pioneering of the Australian wool industry by John Macarthur's Elizabeth Farm in the 1790s. Philip Gidley King's account of his visit to Parramatta on 9 April 1790 is one of the earliest descriptions of the area. Walking four miles with Governor Phillip to Prospect, he saw undulating grassland interspersed with magnificent trees and a great number of kangaroos and emus.[19]
The Battle of Parramatta, a major battle of the Australian frontier wars, occurred in March 1797 where Eora leader Pemulwuy led a group of Bidjigal warriors, estimated to be at least 100, in an attack on the town of Parramatta. The local garrison withdrew to their barracks and Pemulwuy held the town until he was eventually shot and wounded. A year later, a government farm at Toongabbie was attacked by Pemulwuy, who challenged the New South Wales Corps to a fight.[20][21]
Governor Arthur Phillip built a small house for himself on the hill of The Crescent. In 1799 this was replaced by a larger residence which, substantially improved by Governor Lachlan Macquarie from 1815 to 1818, has survived to the present day, making it the oldest surviving Government House anywhere in Australia. It was used as a retreat by Governors until the 1850s, with one Governor (Governor Brisbane) making it his principal home for a short period in the 1820s.
In 1803, another famous incident occurred in Parramatta, involving a convicted criminal named Joseph Samuel, originally from England. Samuel was convicted of murder and sentenced to death by hanging, but the rope broke. In the second attempt, the noose slipped off his neck. In the third attempt, the new rope broke. Governor King was summoned and pardoned Samuel, as the incident appeared to him to be divine intervention.[22]
In 1814, Macquarie opened a school for Aboriginal children at Parramatta as part of a policy of improving relations between Aboriginal and European communities. This school was later relocated to "Black Town".[23]
Parramatta was gazetted as a city on 19 November 1976, and later, a suburb on 10 June 1994.
The first significant skyscrapers began to emerge in Parramatta in the late 1990s and the suburb transformed into a major business and residential hub in the early 2000s. Since then, the suburb's growth has accelerated in the past decade.
On 20 December 2024, the first stage of the Parramatta Light Rail was completed.
Parramatta has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa) with mild to cool, somewhat short winters and warm to usually hot summers, alongside moderate rainfall spread throughout the year.
Summer maximum temperatures are quite variable, often reaching above 35 °C (95 °F), on average 13.1 days in the summer season, and sometimes remaining in the low 20s, especially after a cold front or a sea breeze, such as the southerly buster. Northwesterlies can occasionally bring hot winds from the desert that can raise temperatures higher than 40 °C (104 °F) mostly from November to February, and sometimes above 44 °C (111 °F) in January severe heatwaves. The record highest temperature (since 1967) was 47.0 °C (116.6 °F) on 4 January 2020. Parramatta is warmer than Sydney CBD in the summer due to the urban heat island effect and its inland location. In extreme cases though, it can be 5–10 °C (9–18 °F) warmer than Sydney, especially when sea breezes do not penetrate inland on hot summer and spring days. For example, on 28 November 2009, the city reached 29.3 °C (84.7 °F),[24] while Parramatta reached 39.0 °C (102.2 °F),[25] almost 10 °C (18 °F) higher. In the summer, Parramatta, among other places in western Sydney, can often be the hottest place in the world because of the Blue Mountains trapping hot air in the region, in addition to the UHI effect.[26]
Rainfall is slightly higher during the first three months of the year because the anticlockwise-rotating subtropical high is to the south of the country, thereby allowing moist easterlies from the Tasman Sea to penetrate the city.[27][28] The second half of the year tends to be drier (late winter/spring) since the subtropical high is to the north of the city, thus permitting dry westerlies from the interior to dominate.[29] Drier winters are also owed to its position on the leeward side of the Great Dividing Range, which block westerly cold fronts (that are more common in late winter) and thus would become foehn winds, whereby allowing decent amount of sunny days and relatively low precipitation in that period.[30] Thunderstorms are common in the months from early spring to early autumn, occasionally quite severe thunderstorms can occur. Snow is virtually unknown, having been recorded only in 1836 and 1896[31] Parrammatta gets 106.6 days of clear skies annually.
Depending on the wind direction, summer weather may be humid or dry, though the humidity is mostly in the comfortable range, with the late summer/autumn period having a higher average humidity than late winter/early spring.
| Climate data for Parramatta North (1991–2020 averages, 1967–present extremes) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 47.0 (116.6) |
44.5 (112.1) |
40.5 (104.9) |
37.0 (98.6) |
29.2 (84.6) |
25.5 (77.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
36.5 (97.7) |
40.1 (104.2) |
42.7 (108.9) |
44.0 (111.2) |
47.0 (116.6) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 40.1 (104.2) |
37.5 (99.5) |
33.9 (93.0) |
30.3 (86.5) |
26.2 (79.2) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
30.8 (87.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.6 (97.9) |
37.6 (99.7) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.1 (84.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
23.9 (75.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
18.2 (64.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
25.8 (78.4) |
27.7 (81.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 17.9 (64.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
15.9 (60.6) |
12.6 (54.7) |
9.6 (49.3) |
7.5 (45.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.0 (53.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
16.4 (61.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 12.9 (55.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
2.9 (37.2) |
1.7 (35.1) |
2.4 (36.3) |
4.5 (40.1) |
6.5 (43.7) |
8.6 (47.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 10.1 (50.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
6.8 (44.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
1.4 (34.5) |
0.8 (33.4) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
0.7 (33.3) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
4.0 (39.2) |
7.7 (45.9) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 89.9 (3.54) |
130.3 (5.13) |
99.1 (3.90) |
78.3 (3.08) |
61.3 (2.41) |
99.0 (3.90) |
48.0 (1.89) |
47.4 (1.87) |
48.5 (1.91) |
61.3 (2.41) |
82.0 (3.23) |
78.5 (3.09) |
923.6 (36.36) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 8.6 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 7.0 | 6.3 | 7.9 | 6.0 | 4.8 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 8.3 | 89.2 |
| Average afternoon relative humidity (%) | 56 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 59 | 58 | 55 | 45 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 55 | 54 |
| Average dew point °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
16.8 (62.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
7.6 (45.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.7 (45.9) |
9.9 (49.8) |
12.3 (54.1) |
14.3 (57.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology[32] | |||||||||||||

Church Street is home to many shops and restaurants. The northern end of Church Street, close to Lennox Bridge, features al fresco dining with a diverse range of cuisines. Immediately south of the CBD Church Street is known across Sydney as 'Auto Alley' for the many car dealerships lining both sides of the street as far as the M4 Motorway.[33]

Since 2000, Parramatta has seen the consolidation of its role as a government centre, with the relocation of agencies such as the New South Wales Police Force Headquarters and the Sydney Water Corporation[12] from Sydney CBD. At the same time, major construction work occurred around the railway station with the expansion of Westfield Shoppingtown and the creation of a new transport interchange. The western part of the Parramatta CBD is known as the Parramatta Justice Precinct and houses the corporate headquarters of the Department of Communities and Justice. Other legal offices include the Children's Court of New South Wales and the Sydney West Trial Courts, Legal Aid Commission of NSW, Office of Trustee and Guardian (formerly the Office of the Protective Commissioner), NSW Registry of Births, Deaths and Marriages, and the Office of the Director of Public Prosecutions. Nearby on Marsden Street is the Parramatta Courthouse and the Drug Court of New South Wales. The Garfield Barwick Commonwealth Law Courts Building (named in honour of Sir Garfield Barwick), houses courts of the Federal Magistrates Court and the Family Court of Australia. The NSW Government has also announced plans to secure up to 45,000 m2 of new A-grade leased office space in Parramatta to relocate a further 4,000 workers from the Sydney CBD.[34]

Parramatta Square (previously known as Civic Place) is a civic precinct located in the heart of the city, adjacent to Parramatta Town Hall. The Parramatta Square construction works included a redevelopment of the Parramatta Civic Centre, construction of a new culture and arts centre, and the construction of a new plaza. The designs of the first two projects, a 65-storey residential skyscraper and an office building were announced on 20 July 2012.[35] Concerns from CASA about infringements into controlled airspace from the height of the residential tower resulted in 8 Parramatta Square being turned into a 55-story commercial building, rather than the originally proposed 65-storey residential tower.[36] Parramatta Square became home to 3,000 National Australia Bank employees, relocated from the Sydney CBD.[37] Other notable commercial tenants who have established a presence at Parramatta Square include Westpac, Endeavour Energy, KPMG and Deloitte.[38]
Centenary Square, formerly known as Centenary Plaza, was created in 1975 when the then Parramatta City Council closed a section of the main street to traffic to create a pedestrian plaza. It features an 1888 Centennial Memorial Fountain and adjoins the 1883 Parramatta Town Hall and St John's Cathedral.[39]
A hospital known as The Colonial Hospital was established in Parramatta in 1818.[40] This then became Parramatta District Hospital. Jeffery House was built in the 1940s. With the construction of the nearby Westmead Hospital complex public hospital services in Parramatta were reduced but after refurbishment Jeffery House again provides clinical health services. Nearby, Brislington House has had a long history with health services. It is the oldest colonial building in Parramatta, dating to 1821.[41] It became a doctors residence before being incorporated into the Parramatta Hospital in 1949.
Parramatta is a major business and commercial centre, and home to Westfield Parramatta, the tenth largest shopping centre in Australia.[42] Parramatta is also the major transport hub for Western Sydney, servicing trains and buses, as well as having a ferry wharf and future light rail and metro services. Major upgrades have occurred around Parramatta railway station with the creation of a new transport interchange, and the ongoing development of the Parramatta Square local government precinct.[43]

Church Street takes its name from St John's Cathedral (Anglican), which was built in 1802 and is the oldest church in Parramatta. While the present building is not the first on the site, the towers were built during the time of Governor Macquarie, and were based on those of the church at Reculver, England, at the suggestion of his wife, Elizabeth.[44] The historic St John's Cemetery is located nearby on O'Connell Street.[45]


St Patrick's Cathedral (Roman Catholic) is one of the oldest Catholic churches in Australia. Construction commenced in 1836, but it wasn't officially complete until 1837. In 1854 a new church was commissioned, although the tower was not completed until 1880, with the spire following in 1883.[46] It was built on the site to meet the needs of a growing congregation. It was destroyed by fire in 1996, with only the stone walls remaining.
On 29 November 2003, the new St Patrick's Cathedral was dedicated.[47] The historic St Patrick's Cemetery is located in North Parramatta. The Uniting Church is represented by Leigh Memorial Church.[48] Parramatta Salvation Army is one of the oldest active Salvation Army Corps in Australia. Parramatta is also home to the Parramatta and Districts Synagogue, which services the Jewish community of western Sydney.[49]
The Greek Orthodox Parish and Community of St Ioannis (St John The Frontrunner) Greek Orthodox Church was established in Parramatta in May 1960 under the ecumenical jurisdiction of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Australia to serve the predominantly emigrating Greek population of Greater Western Sydney. Originally, the liturgies were held in the hall of St John's Ambulance Brigade in Harris Park until the completion of the church in December 1966 located in Hassall Street Parramatta. The parish sold this property in 2014 and is now located at the corner of George and Purchase Streets.[50] The Parish Community of St Ioannis continues to serve over 5,000 Greek parishioners.[51]
A Buddhist temple is located in Cowper Street, Parramatta.[52] Parramatta's Mosque is in an apartment building on Marsden Street, Parramatta.[53] The district is served by BAPS Swaminarayan Hindu temple located on Eleanor St, Rosehill,[54] and a Murugan Hindu temple in Mays Hill, off Great Western Highway.[55]


Parramatta Park is a large park adjacent to Western Sydney Stadium that is a popular venue for walking, jogging and bike riding. It was formerly the Governor's Domain, being land set aside for the Governor to supply his farming needs, until it was gazetted as a public park in 1858.[56] As the Governor's Domain, the grounds were considerably larger than the current 85 hectare Parramatta Park, extending from Parramatta Road in the south as evident by a small gatehouse adjacent to Parramatta High School. For a time Parramatta Park housed a zoo[57] until 1951 when the animals were transferred to Taronga Zoo.
Parramatta is known as the 'River City' as the Parramatta River flows through the Parramatta CBD.[58] Its foreshore features a playground, seating, picnic tables and pathways that are increasingly popular with residents, visitors and CBD workers.[59]
Prince Alfred Square is a Victorian era park located within the CBD on the northern side of the Parramatta River. It is one of the oldest public parks in New South Wales with trees dating from c. 1869. Prior to being a public park, it was the site of Parramatta's second gaol from 1804 until 1841 and the first female factory in Australia between 1804 and 1821.
In contrast to the high level of car dependency throughout Sydney, a greater proportion of Parramatta's workers travelled to work on public transport (45.2%) than by car (36.2%) in 2016.[60]

Parramatta railway station is served by Sydney Trains' Cumberland Line, Leppington & Inner West Line and North Shore & Western Line services.[61] NSW TrainLink operates intercity services on the Blue Mountains Line as well as services to rural New South Wales. The station was originally opened in 1855, located in what is now Granville, and known as Parramatta Junction. The station was moved to its current location and opened on 4 July 1860, five years after the first railway line in Sydney was opened, running from Sydney to Parramatta Junction.[62] It was upgraded in the 2000s, with work beginning in late 2003 and the new interchange opening on 19 February 2006.[63]
The light rail Westmead & Carlingford Line runs from Westmead to Carlingford via the Parramatta city centre. A future branch will run to Sydney Olympic Park.[64]
The under construction Sydney Metro West will be a metro line run between the Sydney central business district and Westmead. Announced in 2016,[65] the line is set to open in 2032 with a station in Parramatta.[66]
Parramatta is also serviced by a major bus interchange located on the south eastern side of the railway station. The interchange is served by buses utilising the North-West T-way to Rouse Hill and the Liverpool–Parramatta T-way to Liverpool. Parramatta is also serviced by one high frequency Metrobus service:
A free bus Route 900 is operated by Transit Systems in conjunction with the state government. Route 900 circles Parramatta CBD.[67] A free bus also links Western Sydney Stadium to Parramatta railway station during major sporting events.

The Parramatta ferry wharf is at the Charles Street Weir, which divides the tidal saltwater from the freshwater of the upper river, on the eastern boundary of the Central Business District. The wharf is the westernmost destination of Sydney Ferries' Parramatta River ferry services.[68]
Parramatta Road has always been an important thoroughfare for Sydney from its earliest days. From Parramatta the major western road for the state is the Great Western Highway. The M4 Western Motorway, running parallel to the Great Western Highway has taken much of the traffic away from these roads, with entrance and exit ramps close to Parramatta.
James Ruse Drive serves as a partial ring-road circling around the eastern part of Parramatta to join with the Cumberland Highway to the north west of the city.
The main north-south route through Parramatta is Church Street. To the north it becomes Windsor Road, and to the south it becomes Woodville Road.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 17,982 | — |
| 2006 | 18,448 | +2.6% |
| 2011 | 19,745 | +7.0% |
| 2016 | 25,798 | +30.7% |
| 2021 | 30,211 | +17.1% |

According to the 2016 census conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics, the suburb of Parramatta had a population of 30,211. Of these:[69]

Parramatta is home to several primary and secondary schools. Arthur Phillip High School was established in 1960 in its own right, in buildings which had been used continuously as a school since 1875 is the oldest continuously operating public school in Parramatta. Parramatta High School was the first coeducational school in the Sydney metropolitan area established in 1913. Our Lady of Mercy College is one of the oldest Catholic schools in Australia. Macarthur Girls High School is successor to an earlier school 'Parramatta Commercial and Household Arts School'. Others schools include Parramatta Public School, Parramatta East Public School, Parramatta West Public School, and St Patrick's Primary Parramatta.

Several tertiary education facilities are also located within Parramatta. A University of New England study centre and two Western Sydney University campuses are situated in Parramatta. The Western Sydney University Parramatta Campus consists of two sites: Parramatta South (the primary site) which occupies the site of the historic Female Orphan School[72] and Parramatta North (the secondary site) which includes the adjacent Western Sydney University Village Parramatta (formerly UWS Village Parramatta) an on campus student village accommodation. Whereby, the flagship Parramatta City Campus Precinct consists of two buildings: the Engineering Innovation Hub located at 6 Hassall Street and the Peter Shergold Building located at 1 Parramatta Square (169 Macquarie Street).[73] Alphacrucis University College is a Christian liberal arts college with a campus in Parramatta located at 30 Cowper Street.[74] The University of Sydney has also announced that it intends to establish a new campus in Parramatta.[75]
The Parramatta Advertiser is the local newspaper serving Parramatta and surrounding suburbs.
On 16 March 2020, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation opened a new Western Sydney newsroom in Horwood Place at Parramatta incorporating space for 12 staff and news production equipment with the capacity to broadcast live radio programs.[76] According to the ABC, the opening formed part of its strategic goal to improve its presence in outer metropolitan areas.[76] Additionally, the ABC announced on 16 June 2021 its intention to relocate approximately 300 employees to Parramatta, which is part of a five-year plan which aims to have 75% of its content makers based away from the network's Ultimo headquarters by 2025.[77][78]


As the centre of the City of Parramatta, as well as the centre and second largest business district of Sydney, Parramatta hosts many festivals and events.[79] Riverside Theatres is a performing arts centre located on the northern bank of Parramatta River. The city hosts the following events:
Parramatta Park contains Old Government House and thus Parramatta was once the capital of the colony of New South Wales until Governors returned to residing in Sydney in 1846.[83] Another feature is the natural amphitheatre located on one of the bends of the river, named by Governor Philip as "the Crescent", which is used to stage concerts. It is home to the Dairy Cottage, built from 1798 to 1805, originally a single-room cottage and is one of the earliest surviving cottages in Australia.
The remains of Governor Brisbane's private astronomical observatory, constructed in 1822, are visible. Astronomers who worked at the observatory, discovering thousands of new stars and deep sky objects, include James Dunlop and Carl Rümker. In 1822, the architect S. L. Harris designed the Bath House for Governor Brisbane and built it in 1823. Water was pumped to the building through lead pipes from the river. In 1886, it was converted into a pavilion.[84]
Parramatta is the home of several professional sports teams. These teams include the Parramatta Eels of the National Rugby League and Western Sydney Wanderers of the A-League. Both teams formerly played matches at Parramatta Stadium that has since been demolished, and replaced with the 30,000-seat Western Sydney Stadium.[86] Parramatta Stadium was also home to the now dissolved Sydney Wave of the former Australian Baseball League and Parramatta Power of the former National Soccer League. The newly built Bankwest Stadium opened its gates for the community on 14 April 2019 with free entry for all fans. Located on O’Connell Street, the stadium is in proximity of the Parramatta CBD. The opening sporting event was the 2019 Round 6 NRL clash between Western Sydney rivals the Parramatta Eels and Wests Tigers on Easter Monday 22 April. The Eels won the match by a score of 51–6. It is being predicted that the new stadium will boost Western Sydney economy by contributing millions of dollars to it.[87]
Duran Duran's “Union of the Snake” music video with Russell Mulcahy was filmed in 1983 at Parramatta using 35mm film.[88]
The 2013 superhero film The Wolverine used the intersection of George Street and Smith Street as a filming location to depict Tokyo, Japan.[89]
Parramatta has a number of heritage-listed sites, including: