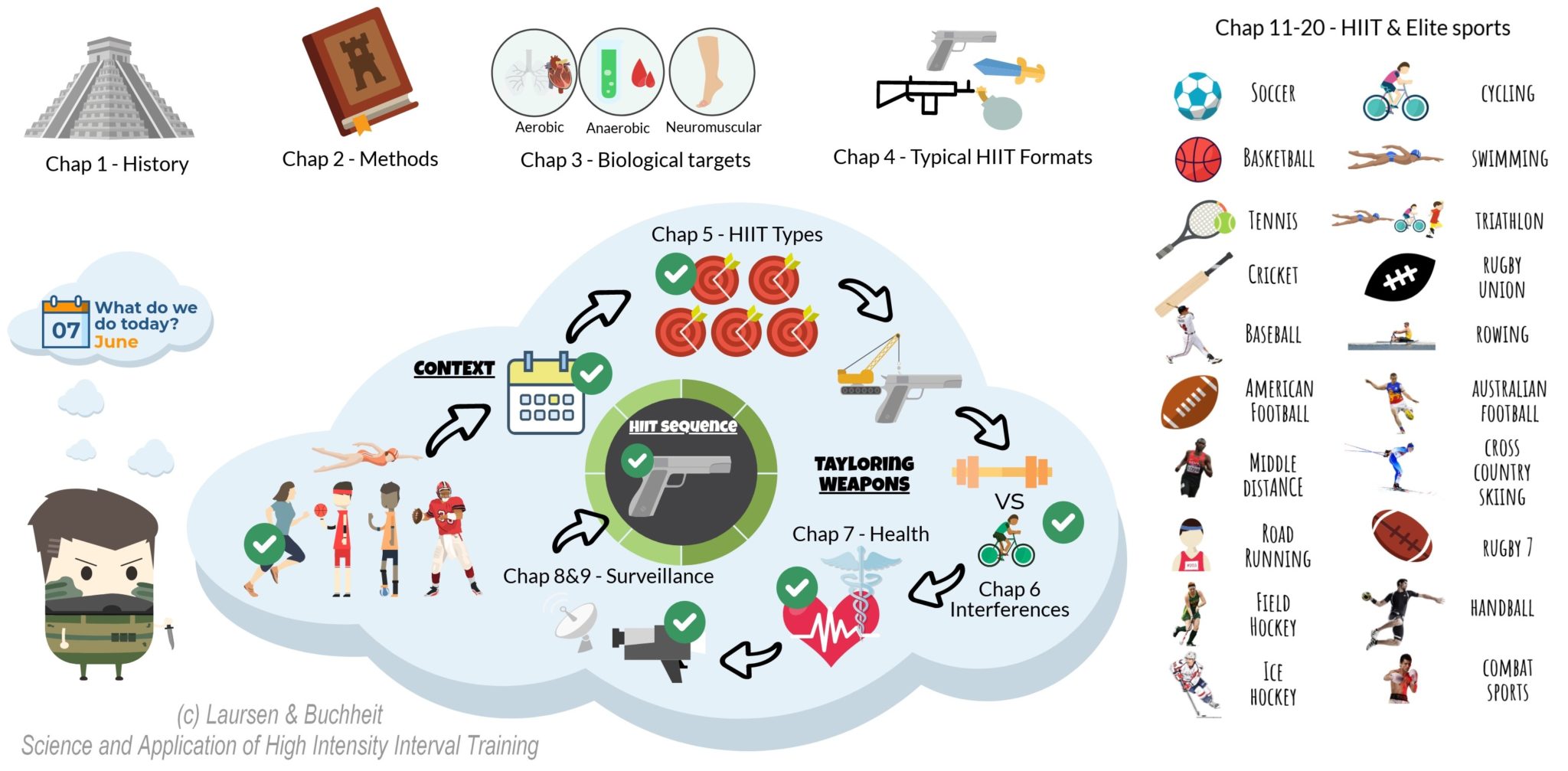
Introduction
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in improving fitness levels and burning calories in a short amount of time. This training method involves alternating between intense bursts of exercise and short recovery periods. But what is the science behind HIIT? In this blog post, we will delve into the research and explore the physiological benefits that make HIIT a powerful workout technique.
What is High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)?
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a form of exercise that involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. This type of training has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in improving fitness levels and burning calories.
How does HIIT work?
During HIIT, the intense bursts of exercise push your body to its maximum capacity, causing it to work harder and burn more calories than traditional steady-state cardio exercises. The short rest periods or low-intensity exercises allow your body to recover partially before the next intense interval, ensuring that you can maintain the high intensity throughout the workout.
The Benefits of HIIT
1. Increased calorie burn: HIIT workouts have been shown to burn more calories in a shorter amount of time compared to traditional cardio exercises. This is due to the higher intensity and the afterburn effect, where your body continues to burn calories even after the workout is over.
2. Improved cardiovascular fitness: HIIT improves your heart health by challenging your cardiovascular system and increasing your aerobic capacity. Regular HIIT workouts can lead to a lower resting heart rate and improved overall cardiovascular function.
3. Time-efficient: HIIT workouts are typically shorter in duration compared to traditional cardio workouts. This makes it a great option for individuals with busy schedules who still want to reap the benefits of exercise.
4. Increased fat loss: HIIT has been shown to be effective in reducing body fat, especially abdominal fat. The intense bursts of exercise stimulate the production of growth hormone, which aids in fat burning.
5. Preserves muscle mass: Unlike steady-state cardio exercises, HIIT workouts help preserve muscle mass while promoting fat loss. This is important for individuals looking to improve body composition and maintain a lean physique.
The Science Behind HIIT
1. EPOC: Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC) is the phenomenon where your body continues to consume oxygen at an elevated rate after intense exercise. This increased oxygen consumption helps restore your body to its pre-exercise state and contributes to the afterburn effect, where you continue to burn.
Summary
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is a workout technique that involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. The science behind HIIT lies in its ability to push the body to its limits and maximize the benefits of cardiovascular and muscular adaptations.
Research has shown that HIIT can significantly improve aerobic and anaerobic fitness levels, increase metabolism, and enhance fat burning. The intense nature of HIIT workouts stimulates the production of human growth hormone (HGH), which aids in muscle growth and repair.
Furthermore, HIIT has been found to improve insulin sensitivity, making it an effective tool for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. It also promotes the release of endorphins, providing a natural mood boost and reducing stress levels.
Overall, the science behind HIIT demonstrates its effectiveness in improving overall fitness, burning calories, and achieving various health benefits. In pop over here corporating HIIT into your exercise routine can help you maximize your workout time and achieve your fitness goals more efficiently.
- Q: What is High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)?
- A: HIIT is a form of exercise that involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise.
- Q: How does HIIT work?
- A: HIIT works by pushing your body to its maximum capacity during the intense intervals, which helps to increase your heart rate and burn more calories in a shorter amount of time.
- Q: What are the benefits of HIIT?
- A: HIIT has been shown to improve cardiovascular fitness, increase metabolism, burn fat, and build lean muscle mass.
- Q: How long should a HIIT workout be?
- A: A typical HIIT workout can range from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on your fitness level and the intensity of the intervals.
- Q: Can anyone do HIIT?
- A: HIIT can be modified to suit different fitness levels, but it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program.
- Q: How often should I do HIIT?
- A: It is recommended to incorporate HIIT workouts into your routine 2-3 times per week, allowing for rest and recovery days in between.
- Q: Is HIIT suitable for weight loss?
- A: Yes, HIIT can be an effective tool for weight loss as it helps to increase calorie burn and improve metabolic rate.
- Q: Can HIIT be done without equipment?
- A: Yes, HIIT can be done using just your body weight and minimal equipment, making it a convenient option for home workouts.
- Q: Are there any risks associated with HIIT?
- A: Like any form of exercise, there is a risk of injury with HIIT if proper form and technique are not followed. It is important to listen to your body and start at a level that is appropriate for you.
- Q: Can HIIT be combined with other forms of exercise?
- A

Welcome to my website! My name is Aiden Jacoby, and I am a passionate and dedicated professional Personal Trainer. With years of experience in the fitness industry, I have helped numerous individuals achieve their health and fitness goals, and I am excited to share my knowledge and expertise with you.