Understanding the Stages of Gum Disease and Their Treatments
You might not realize it, but your gums could be in danger. Understanding the stages of gum disease and their treatments is crucial to maintaining a healthy smile. Coincidentally, this guide will provide you with all the essential information you need.
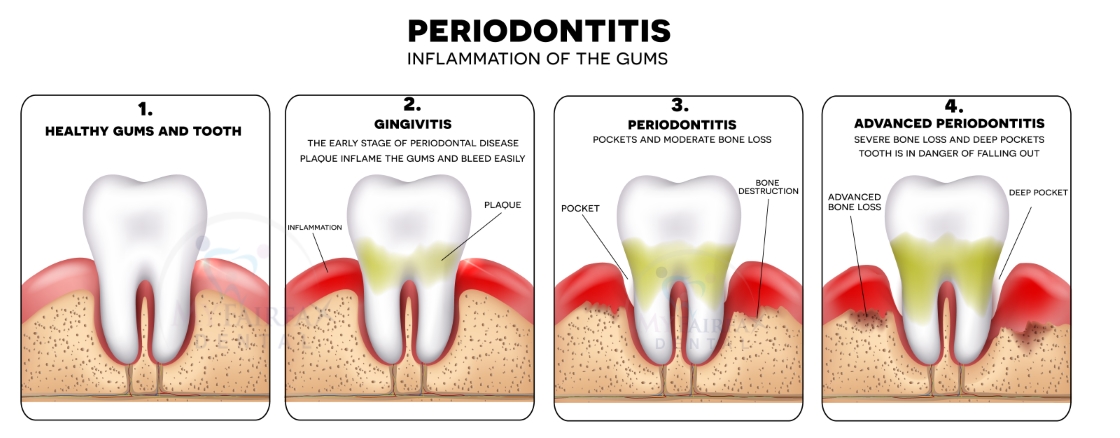
First, let’s start with the basics. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It begins with gingivitis, which causes inflammation and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can progress to early, moderate, and advanced periodontitis.
But don’t worry, there are effective treatment options available. From deep cleanings to surgical procedures, your dentist can help you combat gum disease and restore your oral health.
So, let’s dive in and learn more about how to keep your gums in tip-top shape.
Key Takeaways
– Gum disease progresses through stages: gingivitis, early periodontitis, moderate periodontitis, and advanced periodontitis.
– Good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings can prevent gum disease.
– Early intervention in stage 2 gum disease is crucial to halt progression and preserve natural teeth.
– Treatments for gum disease vary depending on the stage and may include dental cleanings, scaling, root planing, antibiotics, laser therapy, flap surgery, and ongoing treatment.
The Basics of Gum Disease
To understand the basics of gum disease, you need to know that it’s a common oral health condition that affects the tissues surrounding your teeth. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and gums if proper oral hygiene practices aren’t followed. When plaque isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which can only be removed by a professional dental cleaning.
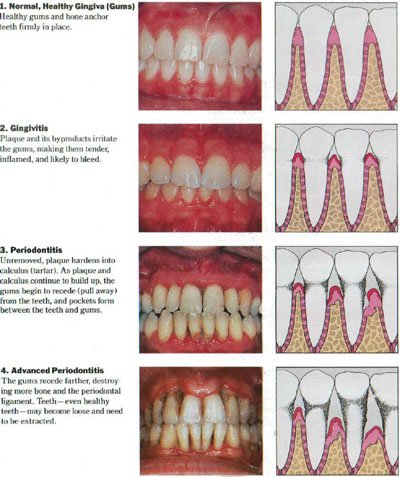
If left untreated, gum disease can progress through several stages. The first stage is known as gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Thankfully, gingivitis is reversible with prompt treatment and improved oral hygiene practices. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more serious form of gum disease.
Periodontitis occurs when the infection spreads below the gum line, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These pockets can become infected, leading to further damage to the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. As the disease progresses, the teeth may become loose and eventually fall out.
To prevent gum disease, it’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene habits, including brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. By taking these preventive measures, you can help keep your gums healthy and avoid the complications of gum disease.
Stage 1: Gingivitis
If you neglect proper oral hygiene, you may find yourself dealing with the first stage of gum disease: gingivitis. Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that affects the gums surrounding your teeth. It’s characterized by inflammation and swelling of the gums, which may appear red or puffy.
One of the main causes of gingivitis is the buildup of plaque on your teeth and along the gumline. When plaque isn’t properly removed through brushing and flossing, it can irritate the gums and lead to gingivitis.
Fortunately, the good news is that gingivitis can be reversed with proper treatment and improved oral hygiene practices. Regular dental cleanings and thorough brushing and flossing can help remove plaque and prevent gingivitis from progressing to more severe stages of gum disease. Your dentist may also recommend antimicrobial mouthwashes or gels to help reduce the inflammation and control the bacteria in your mouth.
It’s important to address gingivitis early on to prevent further damage to your gums and teeth. So, make sure to prioritize your oral health and take the necessary steps to keep gingivitis at bay.
Stage 2: Early Periodontitis
Now that you’ve learned about gingivitis, it’s important to understand the next stage of gum disease: early periodontitis.
During this stage, you may start experiencing symptoms such as gums pulling away from the teeth, bad breath, and tooth sensitivity.
If left untreated, early periodontitis can progress and lead to tooth loss.
However, there are treatment options available, such as deep cleaning and scaling, to help prevent further damage and restore your oral health.
Symptoms and Progression
During stage 2 of gum disease, you may experience symptoms such as gum inflammation and early signs of bone loss. It’s important to recognize these symptoms and seek treatment to prevent the disease from progressing further.
Here are four key indicators of stage 2 gum disease:
1. Red, swollen gums: Your gums may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch. This inflammation is a clear sign of gum disease.
2. Bleeding gums: You may notice bleeding while brushing or flossing. This is a common symptom of gum disease and shouldn’t be ignored.
3. Bad breath: Persistent bad breath, despite good oral hygiene, can indicate the presence of gum disease. The bacteria in your mouth release odorous compounds that cause the foul smell.
4. Receding gums: Your gums may start to pull away from your teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s root. This can lead to tooth sensitivity and make your teeth appear longer.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to visit your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment Options Available
To address stage 2 gum disease, your dentist can offer a variety of treatment options. The goal of treatment at this stage is to control the infection and prevent further damage to the gum tissue and supporting structures.
One common treatment option is scaling and root planing, which involves deep cleaning of the teeth and roots to remove plaque and tartar buildup. This procedure helps to eliminate bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Your dentist may also recommend antibiotics to help fight the infection. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove infected tissue or reshape the gums.
It’s important to follow your dentist’s recommendations and maintain good oral hygiene habits to prevent the progression of gum disease.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is crucial in addressing stage 2 gum disease, as it allows for effective treatment and prevents further deterioration of your oral health. By taking action at this stage, you can significantly improve your chances of reversing the damage caused by gum disease.
Here are four reasons why early intervention is important:
1. Halting the progression: Acting early helps stop the disease from advancing to more severe stages, which can lead to irreversible damage.
2. Preserving your teeth: Treating gum disease in its early stages can save your natural teeth, preventing the need for extractions or dental implants.
3. Reducing discomfort: Early intervention can alleviate symptoms such as bleeding gums, bad breath, and tooth sensitivity, improving your overall oral comfort.
4. Saving money: Addressing gum disease early is more cost-effective than waiting until it reaches advanced stages, as extensive treatments may be required.
Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis
Now that you’re in the moderate stage of gum disease, it’s important to understand the treatment options available to you. Treating your gum disease at this stage is crucial to prevent further progression and damage to your oral health.
It’s important to address the progression of gum disease and the impact it can have on your overall oral health.
Treatment Options Available
If you’re experiencing moderate periodontitis, there are several treatment options available to address your gum disease. Here are four options that can help improve your oral health:
1. Scaling and root planing: This non-surgical procedure involves removing the plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and smoothing the tooth roots to promote gum reattachment.
2. Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation. These can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas.
3. Laser therapy: This minimally invasive treatment uses a laser to remove infected gum tissue and promote healing.
4. Flap surgery: In cases where the gum disease has advanced, your dentist may recommend flap surgery. This procedure involves lifting the gums to access and clean the deep pockets of infection, then repositioning the gums to fit snugly around the teeth.
Progression of Gum Disease
To address moderate periodontitis, there are several treatment options available that can help improve your oral health.
At this stage, the infection has progressed, and the gums may start to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets. These pockets can trap food particles and bacteria, leading to further damage to the gums and bone supporting the teeth.
Scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning, is a common treatment for moderate periodontitis. It involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smoothing the tooth roots to promote gum reattachment.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control the infection.
It’s crucial to seek professional treatment at this stage to prevent further damage and preserve your oral health.
Impact on Oral Health
Moderate periodontitis at Stage 3 has a significant impact on your oral health. Here are four ways it affects you:
1. Gum recession: Your gums start to pull away from your teeth, exposing the roots. This can lead to tooth sensitivity and make your teeth appear longer.
2. Bone loss: The bone supporting your teeth begins to deteriorate, causing your teeth to become loose. Without treatment, you may eventually lose these teeth.
3. Deep pockets: As the gum tissue pulls away, deep pockets form between your gums and teeth. These pockets create a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to further infection and inflammation.
4. Bad breath: The bacteria in your mouth release foul-smelling gases, causing chronic bad breath that can be embarrassing.
Understanding the impact of moderate periodontitis on your oral health is crucial in seeking timely treatment to prevent further damage.
Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis
At this stage, you’ll experience severe damage to the gums and underlying bone, requiring immediate intervention and treatment. Advanced periodontitis is the most severe form of gum disease, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious complications. At this point, the infection has spread deep into the gums and has caused significant damage to the tissues and bone supporting the teeth.
One of the most noticeable symptoms of advanced periodontitis is loose or shifting teeth. This occurs because the underlying bone has been destroyed, causing the teeth to lose their support. In addition, you may experience severe gum recession, exposing the roots of the teeth. This can lead to increased tooth sensitivity and pain.
To treat advanced periodontitis, your dentist or periodontist will need to perform deep cleaning procedures, such as scaling and root planing. This involves removing the plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the root surfaces to promote gum reattachment. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and restore lost bone.
It is important to seek immediate treatment for advanced periodontitis to prevent further damage and potential tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene habits can help prevent gum disease from progressing to this advanced stage.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
What are the available treatment options for gum disease?
When it comes to treating gum disease, there are a few options available to you. These treatments aim to control the infection, reduce inflammation, and restore the health of your gums.
Here are four common treatment options:
1. Scaling and root planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. The dentist will also smooth out the rough spots on the roots of your teeth to prevent bacteria from accumulating.
2. Antibiotics: In some cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection. These can be taken orally or applied directly to the gums in the form of gels or mouth rinses.
3. Gum surgery: If the gum disease is more advanced, you may require surgical intervention. Procedures like flap surgery or bone grafting can help reduce the depth of the pockets between your teeth and gums and promote gum tissue regeneration.
4. Ongoing maintenance: Once your gum disease is treated, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. This will help prevent future recurrences and keep your gums healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Gum Disease Be Completely Cured or Only Managed?
Gum disease can be completely cured if caught early and treated properly. However, if it progresses to more advanced stages, it can only be managed and not fully cured.
Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices are crucial in preventing gum disease. If you notice any signs or symptoms, such as bleeding gums or bad breath, it’s important to see a dentist for diagnosis and treatment options.
Are There Any Home Remedies or Natural Treatments for Gum Disease?
Yes, there are some home remedies and natural treatments you can try for gum disease.
For example, regularly brushing and flossing your teeth can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease from worsening.
Rinsing your mouth with a saltwater solution or using a natural mouthwash with antibacterial properties may also help reduce inflammation and fight bacteria.
However, it’s important to note that these remedies should be used in conjunction with professional dental care for best results.
How Long Does It Take for Gum Disease to Progress From One Stage to the Next?
It depends on various factors, such as your oral hygiene routine and the severity of your gum disease. The progression from one stage to the next can take anywhere from a few months to several years.
Regular dental check-ups and proper oral care can help slow down the progression of gum disease. It’s important to consult a dentist to determine the exact timeline for your specific case and to receive appropriate treatment.
Can Gum Disease Affect Other Parts of the Body Apart From the Mouth?
Yes, gum disease can affect other parts of your body apart from your mouth. The bacteria that cause gum disease can enter your bloodstream and travel to other areas, such as your heart and lungs, potentially causing infections or exacerbating existing health conditions.
It’s important to take care of your oral health to prevent gum disease and its potential complications. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can help keep your gums healthy and protect your overall well-being.
What Are the Potential Complications or Risks Associated With Gum Disease Treatment?
The potential complications or risks associated with gum disease treatment can vary depending on the severity of the disease and the treatment method used. Common complications may include pain, swelling, bleeding, and infection in the treated area.
In some cases, there may be temporary sensitivity or discomfort after the treatment. It’s important to follow the dentist’s instructions for post-treatment care to minimize these risks and ensure proper healing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the stages of gum disease is crucial for maintaining good oral health.
From the early stage of gingivitis to the advanced stage of periodontitis, there are treatment options available to address the progression of the disease.
Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and professional interventions can help prevent and manage gum disease effectively.
By taking proactive steps, we can ensure healthy gums and a beautiful smile.

Welcome to my website! My name is Jett Kirkland, and I am a passionate and dedicated Dental Educator with a strong focus on periodontal treatments, oral infections and care, dental laser therapy, and holistic gum health. With years of experience in the dental field, I am committed to providing valuable information and resources to help individuals achieve optimal oral health.