

"landscape design Las Vegas","Discover the potential of landscape design Las Vegas. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Best Landscaping Las Vegas Nevada. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape design Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"xeriscape Las Vegas","Achieve remarkable results with xeriscape Las Vegas.
"landscaping companies Las Vegas","Discover the potential of landscaping companies Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Expert Landscaping Services in Las Vegas Nevada. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscaping companies Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"Las Vegas landscape contractors","Maximize every square foot with Las Vegas landscape contractors. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in Las Vegas landscape contractors ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"desert landscaping Las Vegas","Reinvent your exterior with desert landscaping Las Vegas. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Top Landscaping in Las Vegas Nevada. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment.
"backyard landscaping Las Vegas","Experience unparalleled value in backyard landscaping Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in backyard landscaping Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"front yard landscaping Las Vegas","Enhance curb appeal via front yard landscaping Las Vegas. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in front yard landscaping Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape installation Las Vegas","Experience the advantage of landscape installation Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Best Landscaping Nevada USA. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape installation Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape maintenance Las Vegas","Explore a new dimension of landscape maintenance Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape maintenance Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."


"Landscaping Las Vegas Nevada","Reinvent your exterior with Landscaping Las Vegas Nevada. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in Landscaping Las Vegas Nevada ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"Las Vegas garden design","Unleash the full beauty of Las Vegas garden design. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in Las Vegas garden design ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"outdoor living Las Vegas","Combine style and function in outdoor living Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in outdoor living Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
Nevada Las Vegas Landscaping Services."patio design Las Vegas","Optimize your property through patio design Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in patio design Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"pool landscaping Las Vegas","Embark on a journey toward pool landscaping Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in pool landscaping Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"artificial grass Las Vegas","Open the door to artificial grass Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency.


"pavers Las Vegas","Experience the advantage of pavers Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in pavers Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"retaining walls Las Vegas","Embrace the possibilities with retaining walls Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in retaining walls Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"irrigation systems Las Vegas","Explore a new dimension of irrigation systems Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in irrigation systems Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape lighting Las Vegas","Unleash the full beauty of landscape lighting Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape lighting Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"Las Vegas landscape architecture","Achieve remarkable results with Las Vegas landscape architecture. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in Las Vegas landscape architecture ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape renovation Las Vegas","Enhance curb appeal via landscape renovation Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape renovation Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."

|
Las Vegas
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Etymology: from Spanish las vegas 'the meadows' | |
| Nicknames: | |
| Coordinates: 36°10′2″N 115°8′55″W / 36.16722°N 115.14861°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Nevada |
| County | Clark |
| Founded | May 15, 1905 |
| Incorporated | March 16, 1911 |
| Government
|
|
| • Type | Council–manager |
| • Mayor | Shelley Berkley (D) |
| • Mayor Pro Tem | Brian Knudsen (D) |
| • City council |
Members
|
| • City manager | Jorge Cervantes |
| Area | |
|
• City
|
141.91 sq mi (367.53 km2) |
| • Land | 141.85 sq mi (367.40 km2) |
| • Water | 0.05 sq mi (0.14 km2) |
| • Urban
|
540 sq mi (1,400 km2) |
| • Metro
|
1,580 sq mi (4,100 km2) |
| Elevation
|
2,001 ft (610 m) |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
|
• City
|
641,903 |
| • Rank | 75th in North America 24th in the United States[6] 1st in Nevada |
| • Density | 4,525.16/sq mi (1,747.17/km2) |
| • Urban
|
2,196,623 (US: 21st) |
| • Urban density | 5,046.3/sq mi (1,948.4/km2) |
| • Metro | 2,265,461 (US: 29th) |
| Demonym | Las Vegan |
| GDP | |
| • Metro | $160.728 billion (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC−08:00 (PST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| ZIP Codes |
89044, 89054, 891xx
|
| Area code(s) | 702 and 725 |
| FIPS code | 32-40000 |
| GNIS feature ID | 847388 |
| Website | lasvegasnevada |
Las Vegas,[a] colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-largest in the Southwestern United States. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city had 641,903 residents in 2020,[9] with a metropolitan population of 2,227,053,[10] making it the 24th-most populous city in the United States. Las Vegas is an internationally renowned major resort city, known primarily for its gambling, shopping, fine dining, entertainment, and nightlife, with most venues centered on downtown Las Vegas and more to the Las Vegas Strip just outside city limits in the unincorporated towns of Paradise and Winchester. The Las Vegas Valley serves as the leading financial, commercial, and cultural center in Nevada.
Las Vegas was settled in 1905 and officially incorporated in 1911.[11] At the close of the 20th century, it was the most populated North American city founded within that century (a similar distinction was earned by Chicago in the 19th century). Population growth has accelerated since the 1960s and into the 21st century, and between 1990 and 2000 the population increased by 85.2%.
The city bills itself as the Entertainment Capital of the World, and is famous for its luxurious and large casino-hotels. With over 40.8 million visitors annually as of 2023,[12] Las Vegas is one of the most visited cities in the United States, annually ranking as one of the world's most visited tourist destinations.[13][14] It is the third most popular U.S. destination for business conventions[15] and a global leader in the hospitality industry.[16] The city's tolerance for numerous forms of adult entertainment has earned it the nickname "Sin City",[17] and has made it a popular setting for literature, films, television programs, commercials and music videos.
In 1829, Mexican trader and explorer Antonio Armijo led a group consisting of 60 men and 100 mules along the Old Spanish Trail from modern day New Mexico to California. Along the way, the group stopped in what would become Las Vegas and noted its natural water sources, now referred to as the Las Vegas Springs, which supported extensive vegetation such as grasses and mesquite trees. The springs were a significant natural feature in the valley, with streams that supported a meadow ecosystem. This region served as the winter residence for the Southern Paiute people, who utilized the area's resources before moving to higher elevations during the summer months. The Spanish "las vegas" or "the meadows" (more precisely, lower land near a river) in English, was applied to describe the fertile lowlands near the springs. Over time, the name began to refer to the populated settlement.[18][19][20]

Nomadic Paleo-Indians traveled to the Las Vegas area 10,000 years ago, leaving behind petroglyphs. Ancient Puebloan and Paiute tribes followed at least 2,000 years ago.[21]
A young Mexican scout named Rafael Rivera is credited as the first non-Native American to encounter the valley, in 1829.[22] Trader Antonio Armijo led a 60-man party along the Spanish Trail to Los Angeles, California, in 1829.[23][24] In 1844, John C. Frémont arrived, and his writings helped lure pioneers to the area. Downtown Las Vegas's Fremont Street is named after him.
Eleven years later, members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints chose Las Vegas as the site to build a fort halfway between Salt Lake City and Los Angeles, where they would travel to gather supplies. The fort was abandoned several years afterward. The remainder of this Old Mormon Fort can still be seen at the intersection of Las Vegas Boulevard and Washington Avenue.
Las Vegas was founded as a city in 1905, when 110 acres (45 ha) of land adjacent to the Union Pacific Railroad tracks were auctioned in what would become the downtown area. In 1911, Las Vegas was incorporated as a city.[25]

The year 1931 was pivotal for Las Vegas. At that time, Nevada legalized casino gambling[26] and reduced residency requirements for divorce to six weeks.[27] This year also witnessed the beginning of construction of the tunnels of nearby Hoover Dam. The influx of construction workers and their families helped Las Vegas avoid economic calamity during the Great Depression. The construction work was completed in 1935.
In late 1941, Las Vegas Army Airfield was established. Renamed Nellis Air Force Base in 1950, it is now home to the United States Air Force Thunderbirds aerobatic team.[28]
Following World War II, lavishly decorated hotels, gambling casinos, and big-name entertainment became synonymous with Las Vegas.

In 1951, nuclear weapons testing began at the Nevada Test Site, 65 miles (105 km) northwest of Las Vegas. During this time, the city was nicknamed the "Atomic City." Residents and visitors were able to witness the mushroom clouds (and were exposed to the fallout) until 1963 when the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty required that nuclear tests be moved underground.[29]
In 1955, the Moulin Rouge Hotel opened and became the first racially integrated casino-hotel in Las Vegas.

During the 1960s, corporations and business tycoons such as Howard Hughes were building and buying hotel-casino properties. Gambling was referred to as "gaming," which transitioned it into a legitimate business. Learning from Las Vegas, published during this era, asked architects to take inspiration from the city's highly decorated buildings, helping to start the postmodern architecture movement.
In 1995, the Fremont Street Experience opened in Las Vegas's downtown area. This canopied five-block area features 12.5 million LED lights and 550,000 watts of sound from dusk until midnight during shows held at the top of each hour.
Due to the realization of many revitalization efforts, 2012 was dubbed "The Year of Downtown." Projects worth hundreds of millions of dollars made their debut at this time, including the Smith Center for the Performing Arts, the Discovery Children's Museum, the Mob Museum, the Neon Museum, a new City Hall complex, and renovations for a new Zappos.com corporate headquarters in the old City Hall building.[30][31]


Las Vegas is the county seat of Clark County, in a basin on the floor of the Mojave Desert,[32] and is surrounded by mountain ranges. Much of the landscape is rocky and arid, with desert vegetation and wildlife. It can be subjected to torrential flash floods, although much has been done to mitigate the effects of flash floods through improved drainage systems.[33]
The city's elevation is approximately 2,030 ft (620 m) above sea level, though the surrounding peaks reach elevations of over 10,000 feet (3,000 m) and act as barriers to the strong flow of moisture from the surrounding area. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has an area of 135.86 sq mi (351.9 km2), of which 135.81 sq mi (351.7 km2) is land and 0.05 sq mi (0.13 km2) (0.03%) is water.
After Alaska and California, Nevada is the third most seismically active state in the U.S. It has been estimated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) that over the next 50 years, there is a 10–20% chance of an M6.0 or greater earthquake occurring within 50 km (31 mi) of Las Vegas.[34]
Within the city are many lawns, trees, and other greenery. Due to water resource issues, there has been a movement to encourage xeriscapes. Another part of conservation efforts is scheduled watering days for residential landscaping. A U.S. Environmental Protection Agency grant in 2008 funded a program that analyzed and forecast growth and environmental effects through 2019.[35]


Las Vegas has a subtropical hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification: BWh, Trewartha climate classification BWhk), typical of the Mojave Desert in which it lies. This climate is typified by long, extremely hot summers; warm transitional seasons; and short winters with mild days and cool nights. There is abundant sunshine throughout the year, with an average of 310 sunny days and bright sunshine during 86% of all daylight hours.[36][37] Rainfall is scarce, with an average of 4.2 in (110 mm) dispersed between roughly 26 total rainy days per year.[38] Las Vegas is among the sunniest, driest, and least humid locations in North America, with exceptionally low dew points and humidity that sometimes remains below 10%.[39]
The summer months of June through September are extremely hot, though moderated by the low humidity levels. July is the hottest month, with an average daytime high of 104.5 °F (40.3 °C). On average, 137 days per year reach or exceed 90 °F (32 °C), of which 78 days reach 100 °F (38 °C) and 10 days reach 110 °F (43 °C). During the peak intensity of summer, overnight lows frequently remain above 80 °F (27 °C), and occasionally above 85 °F (29 °C).[36]
While most summer days are consistently hot, dry, and cloudless, the North American Monsoon sporadically interrupts this pattern and brings more cloud cover, thunderstorms, lightning, increased humidity, and brief spells of heavy rain. Potential monsoons affect Las Vegas between July and August. Summer in Las Vegas is marked by significant diurnal temperature variation. While less extreme than other parts of the state, nighttime lows in Las Vegas are often 30 °F (16.7 °C) or more lower than daytime highs.[40] The average hottest night of the year is 90 °F (32 °C). The all-time record is at 95 °F (35 °C).[36]
Las Vegas winters are relatively short, with typically mild daytime temperatures and chilly nights. Sunshine is abundant in all seasons. December is both the year's coolest and cloudiest month, with an average daytime high of 56.9 °F (13.8 °C) and sunshine occurring during 78% of its daylight hours. Winter evenings are defined by clear skies and swift drops in temperature after sunset, with overnight minima averaging around 40 °F (4.4 °C) in December and January. Owing to its elevation that ranges from 2,000 to 3,000 feet (610 to 910 m), Las Vegas experiences markedly cooler winters than other areas of the Mojave Desert and the adjacent Sonoran Desert that are closer to sea level. The city records freezing temperatures an average of 10 nights per winter. It is exceptionally rare for temperatures to reach or fall below 25 °F (−4 °C).[36]

Most of the annual precipitation falls during the winter. February, the wettest month, averages only four days of measurable rain. The mountains immediately surrounding the Las Vegas Valley accumulate snow every winter, but significant accumulation within the city is rare, although moderate accumulations occur every few years. The most recent accumulations occurred on February 18, 2019, when parts of the city received about 1 to 2 inches (2.5 to 5.1 cm) of snow[41] and on February 20 when the city received almost 0.5 inches (1.3 cm).[42] Other recent significant snow accumulations occurred on December 25, 2015, and December 17, 2008.[43] Unofficially, Las Vegas's largest snowfall on record was the 12 inches (30 cm) that fell in 1909.[44] In recent times, ice days have not occurred, although 29 °F (−2 °C) was measured in 1963.[36] On average the coldest day is 44 °F (7 °C).[36]
The highest temperature officially observed for Las Vegas is 120 °F (48.9 °C), as measured at Harry Reid International Airport on July 7, 2024.[36][45] The lowest temperature was 8 °F (−13 °C), recorded on two days: January 25, 1937, and January 13, 1963.[36] The official record hot daily minimum is 95 °F (35 °C) on July 19, 2005, and July 1, 2013. The official record cold daily maximum is 28 °F (−2 °C) on January 8 and 21, 1937.[36] July 2024 was the hottest month ever recorded in Las Vegas, with its highest recorded mean daily average temperature over the month of 99.9 °F (38 °C), its highest recorded mean daily maximum temperature of 111.5 °F (44 °C), and its highest recorded mean nightly minimum temperature of 88.3 °F (31 °C).[46]
Due to concerns about climate change in the wake of a 2002 drought, daily water consumption has been reduced from 314 US gallons (1,190 L) per resident in 2003 to around 205 US gallons (780 L) in 2015.[47]
| Climate data for Harry Reid International Airport (Paradise, Nevada), 1991–2020 normals,[b] extremes 1937–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 77 (25) |
87 (31) |
92 (33) |
99 (37) |
109 (43) |
117 (47) |
120 (49) |
116 (47) |
114 (46) |
104 (40) |
87 (31) |
78 (26) |
120 (49) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 68.7 (20.4) |
74.2 (23.4) |
84.3 (29.1) |
93.6 (34.2) |
101.8 (38.8) |
110.1 (43.4) |
112.9 (44.9) |
110.3 (43.5) |
105.0 (40.6) |
94.6 (34.8) |
80.5 (26.9) |
67.9 (19.9) |
113.6 (45.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 58.5 (14.7) |
62.9 (17.2) |
71.1 (21.7) |
78.5 (25.8) |
88.5 (31.4) |
99.4 (37.4) |
104.5 (40.3) |
102.8 (39.3) |
94.9 (34.9) |
81.2 (27.3) |
67.1 (19.5) |
56.9 (13.8) |
80.5 (26.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 49.5 (9.7) |
53.5 (11.9) |
60.8 (16.0) |
67.7 (19.8) |
77.3 (25.2) |
87.6 (30.9) |
93.2 (34.0) |
91.7 (33.2) |
83.6 (28.7) |
70.4 (21.3) |
57.2 (14.0) |
48.2 (9.0) |
70.1 (21.2) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 40.5 (4.7) |
44.1 (6.7) |
50.5 (10.3) |
56.9 (13.8) |
66.1 (18.9) |
75.8 (24.3) |
82.0 (27.8) |
80.6 (27.0) |
72.4 (22.4) |
59.6 (15.3) |
47.3 (8.5) |
39.6 (4.2) |
59.6 (15.3) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 29.8 (−1.2) |
32.9 (0.5) |
38.7 (3.7) |
45.2 (7.3) |
52.8 (11.6) |
62.2 (16.8) |
72.9 (22.7) |
70.8 (21.6) |
60.8 (16.0) |
47.4 (8.6) |
35.2 (1.8) |
29.0 (−1.7) |
27.4 (−2.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 8 (−13) |
16 (−9) |
19 (−7) |
31 (−1) |
38 (3) |
48 (9) |
56 (13) |
54 (12) |
43 (6) |
26 (−3) |
15 (−9) |
11 (−12) |
8 (−13) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.56 (14) |
0.80 (20) |
0.42 (11) |
0.20 (5.1) |
0.07 (1.8) |
0.04 (1.0) |
0.38 (9.7) |
0.32 (8.1) |
0.32 (8.1) |
0.32 (8.1) |
0.30 (7.6) |
0.45 (11) |
4.18 (106) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
0.2 (0.51) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 3.1 | 4.1 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 25.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 45.1 | 39.6 | 33.1 | 25.0 | 21.3 | 16.5 | 21.1 | 25.6 | 25.0 | 28.8 | 37.2 | 45.0 | 30.3 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 22.1 (−5.5) |
23.7 (−4.6) |
23.9 (−4.5) |
24.1 (−4.4) |
28.2 (−2.1) |
30.9 (−0.6) |
40.6 (4.8) |
44.1 (6.7) |
37.0 (2.8) |
30.4 (−0.9) |
25.3 (−3.7) |
22.3 (−5.4) |
29.4 (−1.5) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 245.2 | 246.7 | 314.6 | 346.1 | 388.1 | 401.7 | 390.9 | 368.5 | 337.1 | 304.4 | 246.0 | 236.0 | 3,825.3 |
| Percentage possible sunshine | 79 | 81 | 85 | 88 | 89 | 92 | 88 | 88 | 91 | 87 | 80 | 78 | 86 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point and sun 1961–1990)[36][38][37] | |||||||||||||
|
|
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org.
|
See or edit raw graph data.

| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | 25 | — | |
| 1910 | 800 | 3,100.0% | |
| 1920 | 2,304 | 188.0% | |
| 1930 | 5,165 | 124.2% | |
| 1940 | 8,422 | 63.1% | |
| 1950 | 24,624 | 192.4% | |
| 1960 | 64,405 | 161.6% | |
| 1970 | 125,787 | 95.3% | |
| 1980 | 164,674 | 30.9% | |
| 1990 | 258,295 | 56.9% | |
| 2000 | 478,434 | 85.2% | |
| 2010 | 583,756 | 22.0% | |
| 2020 | 641,903 | 10.0% | |
| 2022 (est.) | 656,274 | 2.2% | |
| source:[48][49] 2010–2010[9] |
|||
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) | Pop 2000[50] | Pop 2010[51] | Pop 2020[52] | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 277,704 | 279,703 | 259,561 | 58.04% | 47.91% | 40.44% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 48,380 | 62,008 | 79,129 | 10.11% | 10.62% | 12.33% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 2,405 | 2,391 | 2,291 | 0.50% | 0.41% | 0.36% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 22,411 | 34,606 | 44,995 | 4.68% | 5.93% | 7.01% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 1,935 | 3,103 | 4,204 | 0.40% | 0.53% | 0.65% |
| Other race alone (NH) | 650 | 1,101 | 3,855 | 0.14% | 0.19% | 0.60% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) | 11,987 | 16,985 | 34,040 | 2.51% | 2.91% | 5.30% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 112,962 | 183,859 | 213,828 | 23.61% | 31.50% | 33.31% |
| Total | 474,434 | 583,756 | 641,903 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
According to the 2020 United States census, the city of Las Vegas had 644,883 people living in 244,429 households. The racial composition of the City of Las Vegas was 49.2% white, 11.9% black, 1.1% American Indian or Alaska Native, 6.9% Asian, Hispanic or Latino residents of any race were 34.1% and 16.2% from two or more races. 40.8% were non-Hispanic white.[53]
Approximately 5.8% of residents are under the age of five, 22.8% under the age of eighteen and 15.6% over 65 years old. Females are 50.0% of the total population.[53]

⬤ Black
⬤ Asian
⬤ Hispanic
⬤ Other
From 2019 to 2023, Las Vegas had approximately 244,429 households, with an average of 2.63 persons per household. About 55.7% of housing units were owner-occupied, and the median value of owner-occupied housing was $395,300. Median gross rent during this period was $1,456 per month (in 2023 dollars).[53]
The median household income in Las Vegas from 2019 to 2023 was $70,723, while the per capita income was $38,421 (in 2023 dollars). Approximately 14.2% of the population lived below the poverty line during the same period.[53]
Residents over 25 years old with a high school diploma were 85.8% of the population with 27.3% having attained a bachelor's degree or higher.[53]
About 33.0% of residents aged 5 and older speak a language other than English at home. 20.9% of residents are foreign-born.[53]
The mean travel time to work for residents aged 16 and older was approximately 25.8 minutes between 2019 and 2023. The vast majority of households in Las Vegas are digitally connected, with 95.6% having a computer and 89.1% subscribing to broadband internet services .
According to demographer William H. Frey using data from the 2010 United States census, Las Vegas has the second-lowest level of black-white segregation of any of the 100 largest U.S. metropolitan areas after Tucson, Arizona.[54]
According to the Las Vegas Asian Chamber of Commerce, Filipinos make up the largest ethnic population within Vegas. at 20% of the city's population.[55] Native Hawaiians are also a major demographic in the city, with some Hawaiians and Las Vegas residents calling the city the "ninth island of Hawaii" due to the major influx of Hawaiians to Vegas.[56]
According to a 2004 study, Las Vegas has one of the highest divorce rates.[57][58] The city's high divorce rate is not wholly due to Las Vegans themselves getting divorced. Compared to other states, Nevada's nonrestrictive requirements for divorce result in many couples temporarily moving to Las Vegas in order to get divorced.[59] Similarly, Nevada marriage requirements are equally lax resulting in one of the highest marriage rates of U.S. cities, with many licenses issued to people from outside the area (see Las Vegas weddings).[59]
According to the 2010 Census, the city of Las Vegas had a population of 583,756. The city's racial composition had shifted slightly, with 47.91% of the population identifying as White alone (non-Hispanic), 10.63% as Black or African American alone (non-Hispanic), 0.41% as Native American or Alaska Native alone (non-Hispanic), 5.93% as Asian alone (non-Hispanic), 0.53% as Pacific Islander alone (non-Hispanic), 0.19% as Other Race alone (non-Hispanic), and 2.91% as Mixed race or Multiracial (non-Hispanic). Hispanic or Latino individuals of any race represented 31.50% of the population.[51]
According to the 2000 census, Las Vegas had a population of 474,434 people. The racial makeup of the city was 58.52% White alone (non-Hispanic), 10.19% Black or African American alone (non-Hispanic), 0.51% Native American or Alaska Native alone (non-Hispanic), 4.72% Asian alone (non-Hispanic), 0.41% Pacific Islander alone (non-Hispanic), 0.14% Other Race alone (non-Hispanic), and 2.52% Mixed race or Multiracial (non-Hispanic). Hispanic or Latino individuals of any race made up 23.81% of the population.[50]
| Historical racial profile | 2020[60] | 2010[61] | 2000[62] | 1990[63] | 1970[63] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 46.0% | 62.1% | 69.9% | 78.4% | 87.6% |
| —Non-Hispanic Whites | 40.4% | 47.9% | 58.0% | 72.1% | 83.1%[c] |
| Black or African American | 12.9% | 11.1% | 10.4% | 11.4% | 11.2% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 33.3% | 31.5% | 23.6% | 12.5% | 4.6%[c] |
| Asian | 7.2% | 6.1% | 4.8% | 3.6% | 0.7% |
The primary drivers of the Las Vegas economy are tourism, gaming, and conventions, which in turn feed the retail and restaurant industries.



The major attractions in Las Vegas are the casinos and the hotels, although in recent years other new attractions have begun to emerge.
Most casinos in the downtown area are on Fremont Street, with The STRAT Hotel, Casino & Skypod as one of the few exceptions. Fremont East, adjacent to the Fremont Street Experience, was granted variances to allow bars to be closer together, similar to the Gaslamp Quarter of San Diego, the goal being to attract a different demographic than the Strip attracts.
The Golden Gate Hotel and Casino, downtown along the Fremont Street Experience, is the oldest continuously operating hotel and casino in Las Vegas; it opened in 1906 as the Hotel Nevada.
In 1931, the Northern Club (now the La Bayou) opened.[64][65] The most notable of the early casinos may have been Binion's Horseshoe (now Binion's Gambling Hall and Hotel) while it was run by Benny Binion.
Boyd Gaming has a major presence downtown operating the California Hotel & Casino, the Fremont Hotel & Casino, and the Main Street Casino. The Four Queens also operates downtown along the Fremont Street Experience.
Downtown casinos that have undergone major renovations and revitalization in recent years include the Golden Nugget Las Vegas, The D Las Vegas (formerly Fitzgerald's), the Downtown Grand Las Vegas (formerly Lady Luck), the El Cortez Hotel & Casino, and the Plaza Hotel & Casino.[66]
In 2020, Circa Resort & Casino opened, becoming the first all-new hotel-casino to be built on Fremont Street since 1980.[67]
The center of the gambling and entertainment industry is the Las Vegas Strip, outside the city limits in the surrounding unincorporated communities of Paradise and Winchester in Clark County. Some of the largest casinos and buildings are there.[68]
In 1929, the city installed a welcome arch over Fremont Street, at the corner of Main Street.[69][70][71] It remained in place until 1931.[72][73]
In 1959, the 25-foot-tall (7.6 m) Welcome to Fabulous Las Vegas sign was installed at the south end of the Las Vegas Strip. A replica welcome sign, standing nearly 16 feet (4.9 m) tall, was installed within city limits in 2002, at Las Vegas Boulevard and Fourth Street.[74][75][76] The replica was destroyed in 2016, when a pickup truck crashed into it.[77]
In 2018, the city approved plans for a new gateway landmark in the form of neon arches. It was built within city limits, in front of the Strat resort and north of Sahara Avenue.[78] The project, built by YESCO, cost $6.5 million and stands 80 feet (24 m) high.[79] Officially known as the Gateway Arches, the project was completed in 2020. The steel arches are blue during the day, and light up in a variety of colors at night.[80]
Also located just north of the Strat are a pair of giant neon showgirls, initially added in 2018 as part of a $400,000 welcome display. The original showgirls were 25 feet (7.6 m) tall, but were replaced by new ones in 2022, rising 50 feet (15 m).[81][82] The originals were refurbished following weather damage and installed at the Las Vegas Arts District.[82][83]
When The Mirage opened in 1989, it started a trend of major resort development on the Las Vegas Strip outside of the city. This resulted in a drop in tourism in the downtown area, but many recent projects have increased the number of visitors to downtown.
An effort has been made by city officials to diversify the economy by attracting health-related, high-tech and other commercial interests. No state tax for individuals or corporations, as well as a lack of other forms of business-related taxes, have aided the success of these efforts.[84]
The Fremont Street Experience was built in an effort to draw tourists back to the area and has been popular since its startup in 1995.
The city conducted a land-swap deal in 2000 with Lehman Brothers, acquiring 61 acres (25 ha) of property near downtown Las Vegas in exchange for 91 acres (37 ha) of the Las Vegas Technology Center.[85] In 2004, Las Vegas Mayor Oscar Goodman announced that the area would become home to Symphony Park (originally called "Union Park"[86]), a mixed-use development. The development is home to the Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health, The Smith Center for the Performing Arts, the Discovery Children's Museum, the Las Vegas Chamber of Commerce, and four residential projects totaling 600 residential units as of 2024.[87]

In 2005, the World Market Center opened, consisting of three large buildings taking up 5,400,000 square feet (500,000 m2). Trade shows for the furniture and furnishing industries are held there semiannually.[88]
Also nearby is the Las Vegas North Premium Outlets. With a second expansion, completed in May 2015, the mall currently offers 175 stores.[89]
City offices moved to a new Las Vegas City Hall in February 2013 on downtown's Main Street. The former city hall building is now occupied by the corporate headquarters for the online retailer Zappos.com, which opened downtown in 2013. Zappos CEO Tony Hsieh took an interest in the urban area and contributed $350 million toward a revitalization effort called the Downtown Project.[90][91] Projects funded include Las Vegas's first independent bookstore, The Writer's Block.[92]
A number of new industries have moved to Las Vegas in recent decades. Zappos.com (now an Amazon subsidiary) was founded in San Francisco but by 2013 had moved its headquarters to downtown Las Vegas. Allegiant Air, a low-cost air carrier, launched in 1997 with its first hub at Harry Reid International Airport and headquarters in nearby Summerlin.
Planet 13 Holdings, a cannabis company, opened the world's largest cannabis dispensary in Las Vegas at 112,000 sq ft (10,400 m2).[93][94]
A growing population means the Las Vegas Valley used 1.2 billion US gal (4.5 billion L) more water in 2014 than in 2011. Although water conservation efforts implemented in the wake of a 2002 drought have had some success, local water consumption remains 30 percent greater than in Los Angeles, and over three times that of San Francisco metropolitan area residents. The Southern Nevada Water Authority is building a $1.4 billion tunnel and pumping station to bring water from Lake Mead, has purchased water rights throughout Nevada, and has planned a controversial $3.2 billion pipeline across half the state. By law, the Las Vegas Water Service District "may deny any request for a water commitment or request for a water connection if the District has an inadequate supply of water." But limiting growth on the basis of an inadequate water supply has been unpopular with the casino and building industries.[47]


The city is home to several museums, including the Neon Museum (the location for many of the historical signs from Las Vegas's mid-20th century heyday), The Mob Museum, the Las Vegas Natural History Museum, the Discovery Children's Museum, the Nevada State Museum and the Old Las Vegas Mormon Fort State Historic Park.
The city is home to an extensive Downtown Arts District, which hosts numerous galleries and events including the annual Las Vegas Film Festival. "First Friday" is a monthly celebration that includes arts, music, special presentations and food in a section of the city's downtown region called 18b, The Las Vegas Arts District.[95] The festival extends into the Fremont East Entertainment District.[96] The Thursday evening before First Friday is known in the arts district as "Preview Thursday," which highlights new gallery exhibitions throughout the district.[97]
The Las Vegas Academy of International Studies, Performing and Visual Arts is a Grammy award-winning magnet school located in downtown Las Vegas. The Smith Center for the Performing Arts is downtown in Symphony Park and hosts various Broadway shows and other artistic performances.
Las Vegas has earned the moniker "Gambling Capital of the World," as it has the world's most land-based casinos.[98] The city is also host to more AAA Five Diamond hotels than any other city in the world.[99]

The Las Vegas Valley is the home of three major professional teams: the National Hockey League (NHL)'s Vegas Golden Knights, an expansion team that began play in the 2017–18 NHL season at T-Mobile Arena in nearby Paradise,[100] the National Football League (NFL)'s Las Vegas Raiders, who relocated from Oakland, California, in 2020 and play at Allegiant Stadium in Paradise,[101] and the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA)'s Las Vegas Aces, who play at the Mandalay Bay Events Center. The Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball (MLB) will move to Las Vegas by 2028.[102][103]
Two minor league sports teams play in the Las Vegas area. The Las Vegas Aviators of the Pacific Coast League, the Triple-A farm club of the Athletics, play at Las Vegas Ballpark in nearby Summerlin.[104] The Las Vegas Lights FC of the United Soccer League play in Cashman Field in Downtown Las Vegas.[105][106]
The mixed martial arts promotion, Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC), is headquartered in Las Vegas and also frequently holds fights in the city at T-Mobile Arena and at the UFC Apex training facility near the headquarters.[107]
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Raiders | Football | NFL | Allegiant Stadium (65,000) | 2020 | 3[d] |
| Vegas Golden Knights | Ice hockey | NHL | T-Mobile Arena (17,500) | 2017 | 1 |
| Las Vegas Aces | Women's basketball | WNBA | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2018 | 2 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Aviators | Baseball | MiLB (AAA-PCL) | Las Vegas Ballpark (10,000) | 1983 | 2 |
| Henderson Silver Knights | Ice hockey | AHL | Lee's Family Forum (5,567) | 2020 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Lights FC | Soccer | USLC | Cashman Field (9,334) | 2018 | 0 |
| Vegas Knight Hawks | Indoor football | IFL | Lee's Family Forum (6,019) | 2021 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Desert Dogs | Box lacrosse | NLL | Lee's Family Forum (5,567) | 0 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Dream | Basketball | ABA | 2023 | ||
| Las Vegas Royals | 2020 | ||||
| Vegas Jesters | Ice hockey | MWHL | City National Arena (600) | 2012 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Thunderbirds | USPHL | 2019 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Legends | Soccer | NPSL | Peter Johann Memorial Field (2,500) | 2021 | 0 |
| Vegas NVaders | Women's football | WFA - D2 | Desert Pines High School (N/A) | 2023 | 0 |
| School | Team | League | Division | Primary Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) | UNLV Rebels | NCAA | NCAA Division I | Mountain West |
| College of Southern Nevada (CSN) | CSN Coyotes | NJCAA | NJCAA Division I | Scenic West |

The city's parks and recreation department operates 78 regional, community, neighborhood, and pocket parks; four municipal swimming poools, 11 recreational centers, four active adult centers, eight cultural centers, six galleries, eleven dog parks, and four golf courses: Angel Park Golf Club, Desert Pines Golf Club, Durango Hills Golf Club, and the Las Vegas Municipal Golf Course.[108]
It is also responsible for 123 playgrounds, 23 softball fields, 10 football fields, 44 soccer fields, 10 dog parks, six community centers, four senior centers, 109 skate parks, and six swimming pools.[109]

The city of Las Vegas has a council–manager government.[110] The mayor sits as a council member-at-large and presides over all city council meetings.[110] If the mayor cannot preside over a city council meeting, then the Mayor pro tempore is the presiding officer of the meeting until the Mayor returns to his/her seat.[111] The city manager is responsible for the administration and the day-to-day operations of all municipal services and city departments.[112] The city manager maintains intergovernmental relationships with federal, state, county and other local governments.[112]
Out of the 2,265,461 people in Clark County as of the 2020 Census, approximately 1,030,000 people live in unincorporated Clark County, and around 650,000 live in incorporated cities such as North Las Vegas, Henderson and Boulder City.[113] Las Vegas and Clark County share a police department, the Las Vegas Metropolitan Police Department, which was formed after a 1973 merger of the Las Vegas Police Department and the Clark County Sheriff's Department.[114] North Las Vegas, Henderson, Boulder City, Mesquite, UNLV and CCSD have their own police departments.[115]
The federally-recognized Las Vegas Tribe of Paiute Indians (Southern Paiute: Nuvagantucimi) occupies a 31-acre (130,000 m2) reservation just north downtown between Interstate-15 and Main Street.[116][117][118]
Downtown is the location of Lloyd D. George Federal District Courthouse[119] and the Regional Justice Center,[120] draws numerous companies providing bail, marriage, divorce, tax, incorporation and other legal services.
| Name | Position | Party | References | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shelley Berkley | Mayor | Democratic | [121] | |
| Brian Knudsen | 1st Ward Council member | Democratic | [122][123] | Mayor Pro Tem |
| Victoria Seaman | 2nd Ward Council member | Republican | [124][123] | |
| Olivia Diaz | 3rd Ward Council member | Democratic | [125][123] | |
| Francis Allen-Palenske | 4th Ward Council member | Republican | ||
| Shondra Summers-Armstrong | 5th Ward Council member | Democratic | [126] | |
| Nancy Brune | 6th Ward Council member | Democratic |
Primary and secondary public education is provided by the Clark County School District.[127]
Public higher education is provided by the Nevada System of Higher Education (NSHE). Public institutions serving Las Vegas include the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), the College of Southern Nevada (CSN), Nevada State University (NSU), and the Desert Research Institute (DRI).[128]
UNLV is a public, land-grant, R1 research university and is home to the Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine[129] and the William S. Boyd School of Law, the only law school in Nevada.[130] The university's campus is urban and located about two miles east of the Las Vegas strip. The Desert Research Institute's southern campus sits next to UNLV, while its northern campus is in Reno.[131]
CSN, with campuses throughout Clark County,[132] is a community college with one of the largest enrollments in the United States.[133] In unincorporated Clark County, CSN's Charleston campus is home to the headquarters of Nevada Public Radio (KNPR), an NPR member station.[134][135]
Touro University Nevada located in Henderson is a non-profit, private institution primarily focusing on medical education.[136] Other institutions include a number of for-profit private schools (e.g., Le Cordon Bleu College of Culinary Arts, DeVry University, among others).[137]

Las Vegas is served by 10 full power television stations and 46 radio stations. The area is also served by two NOAA Weather Radio transmitters (162.55 MHz located in Boulder City and 162.40 MHz located on Potosi Mountain).



RTC Transit is a public transportation system providing bus service throughout Las Vegas, Henderson, North Las Vegas and other areas of the valley. Inter-city bus service to and from Las Vegas is provided by Greyhound, BoltBus, Orange Belt Stages, Tufesa, and several smaller carriers.[144]
Amtrak trains have not served Las Vegas since the service via the Desert Wind at Las Vegas station ceased in 1997, but Amtrak California operates Amtrak Thruway dedicated service between the city and its passenger rail stations in Bakersfield, California, as well as Los Angeles Union Station via Barstow.[145]
High-speed rail project Brightline West began construction in 2024 to connect Brightline's Las Vegas station and the Rancho Cucamonga station in Greater Los Angeles.[146]
The Las Vegas Monorail on the Strip was privately built, and upon bankruptcy taken over by the Las Vegas Convention and Visitors Authority.[147]
Silver Rider Transit operates three routes within Las Vegas, offering connections to Laughlin,[148] Mesquite,[149] and Sandy Valley.[150]
The Union Pacific Railroad is the only Class I railroad providing rail freight service to the city. Until 1997, the Amtrak Desert Wind train service ran through Las Vegas using the Union Pacific Railroad tracks.
In March 2010, the RTC launched bus rapid transit link in Las Vegas called the Strip & Downtown Express with limited stops and frequent service that connects downtown Las Vegas, the Strip and the Las Vegas Convention Center. Shortly after the launch, the RTC dropped the ACE name.[151]
In 2016, 77.1 percent of working Las Vegas residents (those living in the city, but not necessarily working in the city) commuted by driving alone. About 11 percent commuted via carpool, 3.9 percent used public transportation, and 1.4 percent walked. About 2.3 percent of Las Vegas commuters used all other forms of transportation, including taxi, bicycle, and motorcycle. About 4.3% of working Las Vegas residents worked at home.[152] In 2015, 10.2 percent of city of Las Vegas households were without a car, which increased slightly to 10.5 percent in 2016. The national average was 8.7 percent in 2016. Las Vegas averaged 1.63 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8 per household.
With some exceptions, including Las Vegas Boulevard, Boulder Highway (SR 582) and Rancho Drive (SR 599), the majority of surface streets in Las Vegas are laid out in a grid along Public Land Survey System section lines. Many are maintained by the Nevada Department of Transportation as state highways. The street numbering system is divided by the following streets:
Interstates 15, 11, and US 95 lead out of the city in four directions. Two major freeways – Interstate 15 and Interstate 11/U.S. Route 95 – cross in downtown Las Vegas. I-15 connects Las Vegas to Los Angeles, and heads northeast to and beyond Salt Lake City. I-11 goes northwest to the Las Vegas Paiute Indian Reservation and southeast to Henderson and to the Mike O'Callaghan–Pat Tillman Memorial Bridge, where from this point I-11 will eventually continue along US 93 towards Phoenix, Arizona. US 95 (and eventually I-11) connects the city to northwestern Nevada, including Carson City and Reno. US 93 splits from I-15 northeast of Las Vegas and goes north through the eastern part of the state, serving Ely and Wells. US 95 heads south from US 93 near Henderson through far eastern California. A partial beltway has been built, consisting of Interstate 215 on the south and Clark County 215 on the west and north. Other radial routes include Blue Diamond Road (SR 160) to Pahrump and Lake Mead Boulevard (SR 147) to Lake Mead.
East–west roads, north to south[153]
Harry Reid International Airport handles international and domestic flights into the Las Vegas Valley. The airport also serves private aircraft and freight/cargo flights. Most general aviation traffic uses the smaller North Las Vegas Airport and Henderson Executive Airport.
Exposures 50 years ago still have health implications today that will continue into the future...Deposition...generally decreases with distance from the test site in the direction of the prevailing wind across North America, although isolated locations received significant deposition as a result of rainfall. Trajectories of the fallout debris clouds across the U.S. are shown for four altitudes. Each dot indicates six hours.
"Probability of an earthquake of magnitude 6.0 or greater occurring within 50 km in 50 years (from USGS probabilistic seismic hazard analysis) 10–20% chance for Las Vegas area, magnitude 6".
|
|
It has been suggested that Southern Nevada be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since February 2025.
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|---|---|
| Nickname(s):
The Silver State (official);
The Sagebrush State; The Battle Born State |
|
| Motto:
All for Our Country
|
|
| Anthem: "Home Means Nevada" | |
Location of Nevada within the United States
|
|
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Nevada Territory, Utah Territory, Arizona Territory |
| Admitted to the Union | October 31, 1864 (36th) |
| Capital | Carson City |
| Largest city | Las Vegas |
| Largest county or equivalent | Clark |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Las Vegas Valley |
| Government
|
|
| • Governor | Joe Lombardo (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Stavros Anthony (R) |
| Legislature | Nevada Legislature |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | Assembly |
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Nevada |
| U.S. senators | Catherine Cortez Masto (D) Jacky Rosen (D) |
| U.S. House delegation | 3 Democrats 1 Republican (list) |
| Area
|
|
|
• Total
|
110,577 sq mi (286,382 km2) |
| • Land | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332 km2) |
| • Water | 791 sq mi (2,048 km2) 0.72% |
| • Rank | 7th |
| Dimensions
|
|
| • Length | 492 mi (787 km) |
| • Width | 322 mi (519 km) |
| Elevation
|
5,500 ft (1,680 m) |
| Highest elevation | 13,147 ft (4,007.1 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 481 ft (147 m) |
| Population
(2024)
|
|
|
• Total
|
|
| • Rank | 32nd |
| • Density | 26.8/sq mi (10.3/km2) |
| • Rank | 42nd |
| • Median household income
|
$76,400 (2023)[4] |
| • Income rank
|
24th |
| Demonym | Nevadan |
| Language
|
|
| • Official language | None |
| Time zones | |
| most of state | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| West Wendover | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) |
| USPS abbreviation |
NV
|
| ISO 3166 code | US-NV |
| Traditional abbreviation | Nev. |
| Latitude | 35° N to 42° N |
| Longitude | 114°ÃƒÆ’ƒÂ¢Ã¢â€šÂ¬Ã… 2′ W to 120° W |
| Website | nv |
| List of state symbols | |
|---|---|
| Song | Home Means Nevada |
| Living insignia | |
| Bird | Mountain bluebird (Sialia currucoides) |
| Fish | Lahontan cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii henshawi) |
| Flower | Sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) |
| Grass | Indian Rice Grass |
| Insect | Vivid Dancer Damselfly (Argia vivida) |
| Mammal | Desert bighorn sheep |
| Reptile | Desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) |
| Tree | Bristlecone pine, Single-leaf Piñon (Pinus monophylla) |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Color(s) | Silver, Blue |
| Fossil | Ichthyosaur (Shonisaurus popularis) |
| Gemstone | Virgin Valley Black Fire Opal |
| Mineral | Silver |
| Rock | Sandstone |
| Soil | Orovada series |
| Other | Element: Neon |
| State route marker | |
 |
|
| State quarter | |

Released in 2006
|
|
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Nevada (/nəˈvædÉ™, -vÉ‘ËÂÂÂÂ-/ ⓘ nÉ™-VAD-É™, -â VAH-;[5][6] Spanish: [neˈβaða]) is a landlocked state in the Western United States.[c] It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the ninth-least densely populated U.S. state. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's population live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area,[7] including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities.[8] Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.
Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); due to the presidency of Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of the monetary support of nearly $400 million in silver ore generated at the time by the Comstock Lode.[9] It is also known as the "Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as the "Sage-hen State".[10] The state's name means "snowy" in Spanish, referring to Nevada's small overlap with the Sierra Nevada mountain range; however, the rest of Nevada is largely desert and semi-arid, much of it within the Great Basin. Areas south of the Great Basin are within the Mojave Desert, while Lake Tahoe and the Sierra Nevada lie on the western edge. In 2020, 80.1% of the state's land was managed by various jurisdictions of the U.S. federal government, both civilian and military.[11]
Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabit what is now Nevada. The first Europeans to explore the region were Spanish. They called the region Nevada (snowy) because of the snow which covered the mountains in winter, similar to the Sierra Nevada in Spain. The area formed from mostly Alta California and part of Nuevo México's territory within the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which gained independence as Mexico in 1821. The United States annexed the area in 1848 after its victory in the Mexican–American War, and it was incorporated as part of the New Mexico and Utah Territory in 1850. The discovery of silver at the Comstock Lode in 1859 led to a population boom that became an impetus to the creation of Nevada Territory out of western Utah Territory in 1861. Nevada became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, as the second of two states added to the Union during the Civil War (the first being West Virginia).[12]
Nevada is known for its libertarian laws. In 1940, with a population of just over 110,000 people, Nevada was by far the least-populated state, with less than half the population of the next least-populous state, Wyoming.[13] However, legalized gambling and lenient marriage and divorce laws transformed Nevada into a major tourist destination in the 20th century.[14][15] Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legal, though it is illegal in its most populated regions – Clark County (Las Vegas), Washoe County (Reno) and Carson City (which, as an independent city, is not within the boundaries of any county). The tourism industry remains Nevada's largest employer,[16] with mining continuing as a substantial sector of the economy: Nevada is the fourth-largest producer of gold in the world.[17] It is the driest state. Droughts in Nevada, which are influenced by climate change, have been increasing in frequency and severity,[18] putting a further strain on Nevada's water security.
The name "Nevada" comes from the Spanish adjective nevada ([neˈβaða]), meaning "snow-covered" or "snowy".[19] The state takes its name from the Nevada Territory, which in turn was named for the Sierra Nevada.[20]
Nevadans pronounce the second syllable with the "a" of "apple" (/nəˈvædÉ™/) while some people from outside of the state pronounce it with the "a" of "palm" (/nəˈvÉ‘ËÂÂÂÂdÉ™/).[21] Although the quality, but not the length, of the latter pronunciation is closer to the Spanish pronunciation (Spanish /a/ is open central [ä],[22] whereas American English /É‘ËÂÂÂÂ/ varies from back [É‘ËÂÂÂÂ] to central [äËÂÂÂÂ]),[23] it is not the pronunciation used by Nevadans. State Assemblyman Harry Mortenson proposed a bill to recognize the alternative pronunciation of Nevada,[24] though the bill was not supported by most legislators and never received a vote. The Nevadan pronunciation is the one used by the state legislature. At one time, the state's official tourism organization, TravelNevada, stylized the name of the state as "Nevăda", with a breve over the a indicating the locally preferred pronunciation,[25] which was also available as a license plate design until 2007.[26]
Before the arrival of Europeans, the earliest inhabitants were Indigenous tribes including the Goshute, Southern Paiute, Mohave, and Wašišiw (Washoe people).[27][28]

Francisco Garcés was the first European in the area.[29] Nevada was annexed as a part of the Spanish Empire in the northwestern territory of New Spain. Administratively, the area of Nevada was part of the Commandancy General of the Provincias Internas in the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Nevada became a part of Alta California (Upper California) province in 1804 when the Californias were split. With the Mexican War of Independence won in 1821, the province of Alta California became a territory (state) of Mexico, with a small population.
Jedediah Smith entered the Las Vegas Valley in 1827, Peter Skene Ogden traveled the Humboldt River in 1828, and in 1829 a merchant from Nuevo México named Antonio Armijo streamlined travel along the Old Spanish Trail. Chronicling Armijo's route his scout Raphael Rivera was the first to name Las Vegas, in an 1830 report to governor José Antonio Chaves. Following the suggestions by Rivera of a spring, on the published expedition's map, located in the Las Vegas area John C. Frémont set up camp in Las Vegas Springs in 1844. In 1847, Mormons established the State of Deseret, claiming all of Nevada within the Great Basin and the Colorado watershed. They built the first permanent settlement in what is now Nevada, called Mormon Station (now Genoa), in 1851. Additionally, in June 1855, William Bringhurst and 29 other Mormon missionaries built the first permanent structure, a 150-foot square adobe fort, northeast of downtown Las Vegas, converging on the Spanish and Mormon Roads. The fort remained under Salt Lake City's control until the winter of 1858–1859, and the route remained largely under the control of Salt Lake City and Santa Fe tradespersons.
As such, these pioneers laid the foundation for the emergence of the initial settlements between the Sierra Nevadas and Mojave Desert and within the Las Vegas Valley. The enduring influence of New Mexico and Utah culture has since profoundly impacted Nevada's identity, manifesting through New Mexican cuisine and Mormon foodways or New Mexican and Mormon folk musics, into the fabric of Nevada's own cultural landscape.
As a result of the Mexican–American War and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexico permanently lost Alta California in 1848. The new areas acquired by the United States continued to be administered as territories. As part of the Mexican Cession (1848) and the subsequent California Gold Rush that used Emigrant Trails through the area, the state's area evolved first as part of the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory, then the Nevada Territory (March 2, 1861; named for the Sierra Nevada).[30]

The first discovery of a major U.S. deposit of silver ore occurred in Comstock Lode under Virginia City, Nevada, in 1859.
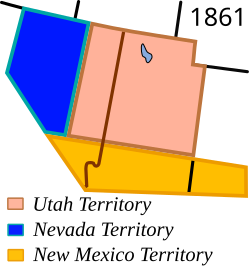
On March 2, 1861, the Nevada Territory separated from the Utah Territory and adopted its current name, shortened from The Sierra Nevada (Spanish for "snow-covered mountain range"). The 1861 southern boundary is commemorated by Nevada Historical Markers 57 and 58 in Lincoln and Nye counties.
Eight days before the presidential election of 1864, Nevada became the 36th state in the Union, despite lacking the minimum 60,000 residents that Congress typically required a potential state to have in order to become a state.[31] At the time, Nevada's population was little more than 40,000.[32] Governor Nye was frustrated that previous attempts to send the constitution via overland mail and by sea had failed by October 24, so on October 26 the full text was sent by telegraph at a cost of $4,303.27[33][d] – the most costly telegraph on file at the time for a single dispatch, equivalent to $86,514.04 in 2024. Finally, the response from Washington came on October 31, 1864: "the pain is over, the child is born, Nevada this day was admitted into the Union". Statehood was rushed to the date of October 31 to help ensure Abraham Lincoln's reelection on November 8 and post-Civil War Republican dominance in Congress,[34] as Nevada's mining-based economy tied it to the more industrialized Union. As it turned out, however, Lincoln and the Republicans won the election handily and did not need Nevada's help.
Nevada is one of only two states to significantly expand its borders after admission to the Union, with the other being Missouri, which acquired additional territory in 1837 due to the Platte Purchase. In 1866 another part of the western Utah Territory was added to Nevada in the eastern part of the state, setting the current eastern boundary. Nevada achieved its current southern boundaries on January 18, 1867, when it absorbed the portion of Pah-Ute County in the Arizona Territory west of the Colorado River, essentially all of present-day Nevada south of the 37th parallel. The transfer was prompted by the discovery of gold in the area, and officials thought Nevada would be better able to oversee the expected population boom. This area includes all of what is now Clark County and the southern-most portions of Esmeralda, Lincoln, and Nye counties.[35]

Mining shaped Nevada's economy for many years (see Silver mining in Nevada). When Mark Twain lived in Nevada during the period described in Roughing It, mining had led to an industry of speculation and immense wealth. Both mining and population temporarily declined in the late 19th century. However, the rich silver strike at Tonopah in 1900, followed by strikes in Goldfield and Rhyolite, created a second mining boom in Nevada and Nevada's population.
Unregulated gambling was commonplace in the early Nevada mining towns but was outlawed in 1909 as part of a nationwide anti-gambling crusade. Because of subsequent declines in mining output and the decline of the agricultural sector during the Great Depression, Nevada again legalized gambling on March 19, 1931, with approval from the legislature. Governor Fred B. Balzar's signature enacted the most liberal divorce laws in the country and open gambling. The reforms came just eight days after the federal government presented the $49 million construction contract for Boulder Dam (now Hoover Dam).[37]
The Nevada Test Site, 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas, was founded on January 11, 1951, for the testing of nuclear weapons. The site consists of about 1,350 square miles (3,500 km2) of the desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site began with a 1 kiloton of TNT (4.2 TJ) nuclear bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. The last atmospheric test was conducted on July 17, 1962, and the underground testing of weapons continued until September 23, 1992. The location is known for having the highest concentration of nuclear-detonated weapons in the U.S.
Over 80% of the state's area is owned by the federal government. This is mainly because homesteads were not permitted in large enough sizes to be viable in the arid conditions that prevail throughout desert Nevada. Instead, early settlers would homestead land surrounding a water source, and then graze livestock on the adjacent public land, which is useless for agriculture without access to water (this pattern of ranching still prevails).
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed in Nevada on March 5, 2020. Because of concerns about coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Nevada governor Steve Sisolak declared a state of emergency on March 12, 2020. Four days later, Nevada reported its first death. On March 17, 2020, Sisolak ordered the closure of non-essential businesses in the state to help prevent the spread of the coronavirus.
Various protests were held against Sisolak's shutdown order beginning in April 2020. Nevada launched the first phase of its reopening on May 9, 2020. Restaurants, retailers, outdoor malls, and hair salons were among the businesses allowed to reopen, but with precautions in place, such as limiting occupancy to 50 percent. A second phase went into effect on May 29, 2020. It allowed for the reopening of state parks and businesses such as bars, gyms, and movie theaters. Casinos began reopening on June 4, 2020.
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2021)
|



Nevada is almost entirely within the Basin and Range Province and is broken up by many north–south mountain ranges. Most of these ranges have endorheic valleys between them.
Much of the northern part of the state is within the Great Basin, a mild desert that experiences hot temperatures in the summer and cold temperatures in the winter. Occasionally, moisture from the Arizona Monsoon will cause summer thunderstorms; Pacific storms may blanket the area with snow. The state's highest recorded temperature was 125 °F (52 °C) in Laughlin (elevation of 605 feet or 184 meters) on June 29, 1994.[38] The coldest recorded temperature was −52 °F (−47 °C) set in San Jacinto in 1972, in the northeastern portion of the state.[38]
The Humboldt River crosses the state from east to west across the northern part of the state, draining into the Humboldt Sink near Lovelock. Several rivers drain from the Sierra Nevada eastward, including the Walker, Truckee, and Carson rivers. All of these rivers are endorheic basins, ending in Walker Lake, Pyramid Lake, and the Carson Sink, respectively. However, not all of Nevada is within the Great Basin. Tributaries of the Snake River drain the far north, while the Colorado River, which also forms much of the boundary with Arizona, drains much of southern Nevada.
The mountain ranges, some of which have peaks above 13,000 feet (4,000 m), harbor lush forests high above desert plains, creating sky islands for endemic species. The valleys are often no lower in elevation than 3,000 feet (910 m), while some in central Nevada are above 6,000 feet (1,800 m).

The southern third of the state, where the Las Vegas area is situated, is within the Mojave Desert. The area receives less rain in the winter but is closer to the Arizona Monsoon in the summer. The terrain is also lower, mostly below 4,000 feet (1,200 m), creating conditions for hot summer days and cool to chilly winter nights.
Nevada and California have by far the longest diagonal line (in respect to the cardinal directions) as a state boundary at just over 400 miles (640 km). This line begins in Lake Tahoe nearly 4 miles (6.4 km) offshore (in the direction of the boundary), and continues to the Colorado River where the Nevada, California, and Arizona boundaries merge 12 miles (19 km) southwest of the Laughlin Bridge.
The largest mountain range in the southern portion of the state is the Spring Mountain Range, just west of Las Vegas. The state's lowest point is along the Colorado River, south of Laughlin.
Nevada has 172 mountain summits with 2,000 feet (610 m) of prominence. Nevada ranks second, after Alaska, for the greatest number of mountains in the United States, followed by California, Montana, and Washington.[39]

Nevada is the driest state in the United States.[40] It is made up of mostly desert and semi-arid climate regions, and, with the exception of the Las Vegas Valley, the average summer diurnal temperature range approaches 40 °F (22 °C) in much of the state. While winters in northern Nevada are long and fairly cold, the winter season in the southern part of the state tends to be of short duration and mild. Most parts of Nevada receive scarce precipitation during the year. The most rain that falls in the state falls on the east and northeast slopes of the Sierra Nevada.
The average annual rainfall per year is about 7 inches (180 mm); the wettest parts get around 40 inches (1,000 mm). Nevada's highest recorded temperature is 125 °F (52 °C) at Laughlin on June 29, 1994, and the lowest recorded temperature is −50 °F (−46 °C) at San Jacinto on January 8, 1937. Nevada's 125 °F (52 °C) reading is the third highest statewide record high temperature of a U.S. state, just behind Arizona's 128 °F (53 °C) reading and California's 134 °F (57 °C) reading.
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | December (°F) | December (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | |
| Las Vegas | 106 | 81 | 41 | 27 | 56 | 38 | 13 | 3 |
| Reno | 92 | 57 | 33 | 14 | 45 | 25 | 7 | –4 |
| Carson City | 89 | 52 | 32 | 11 | 45 | 22 | 7 | –5 |
| Elko | 90 | 50 | 32 | 10 | 37 | 14 | 2 | –9 |
| Fallon | 92 | 54 | 33 | 12 | 45 | 19 | 7 | –7 |
| Winnemucca | 93 | 52 | 34 | 11 | 41 | 17 | 5 | –8 |
| Laughlin | 112 | 80 | 44 | 27 | 65 | 43 | 18 | 6 |
The vegetation of Nevada is diverse and differs by state area. Nevada contains six biotic zones: alpine, sub-alpine, ponderosa pine, pinion-juniper, sagebrush and creosotebush.[42]


Nevada is divided into political jurisdictions designated as counties. Carson City is officially a consolidated municipality, meaning it legally functions as both a city and a county. As of 1919, there were 17 counties in the state, ranging from 146 to 18,159 square miles (380 to 47,030 km2).
Lake County, one of the original nine counties formed in 1861, was renamed Roop County in 1862. Part of the county became Lassen County, California, in 1864, resolving border uncertainty. In 1883, Washoe County annexed the portion that remained in Nevada.[43]
In 1969, Ormsby County was dissolved and the Consolidated Municipality of Carson City was created by the Legislature in its place coterminous with the old boundaries of Ormsby County.
Bullfrog County was formed in 1987 from part of Nye County. After the creation was declared unconstitutional, the county was abolished in 1989.[43]
Humboldt County was designated as a county in 1856 by Utah Territorial Legislature and again in 1861 by the new Nevada Legislature.
Clark County is the most populous county in Nevada, accounting for nearly three-quarters of its residents. Las Vegas, Nevada's most populous city, has been the county seat since the county was created in 1909 from a portion of Lincoln County, Nevada. Before that, it was a part of Arizona Territory. Clark County attracts numerous tourists: An estimated 44 million people visited Clark County in 2014.[44]
Washoe County is the second-most populous county of Nevada. Its county seat is Reno. Washoe County includes the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
Lyon County is the third most populous county. It was one of the nine original counties created in 1861. It was named after Nathaniel Lyon, the first Union General to be killed in the Civil War. Its current county seat is Yerington. Its first county seat was established at Dayton on November 29, 1861.[45]
| County name | County seat | Year founded | 2022 population[46] | Percent of total | Area | Percent of total | Population density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sq mi | km2 | per sq mi | per km2 | ||||||
| Carson City | Carson City | 1861 | 58,130 | 1.83 % | 157 | 410 | 0.14 % | 370.25 | 142.95 |
| Churchill | Fallon | 1861 | 25,843 | 0.81 % | 5,024 | 13,010 | 4.54 % | 5.14 | 1.98 |
| Clark | Las Vegas | 1908 | 2,322,985 | 73.10 % | 8,061 | 20,880 | 7.29 % | 288.18 | 111.27 |
| Douglas | Minden | 1861 | 49,628 | 1.56 % | 738 | 1,910 | 0.67 % | 67.25 | 25.97 |
| Elko | Elko | 1869 | 54,046 | 1.70 % | 17,203 | 44,560 | 15.56 % | 3.14 | 1.21 |
| Esmeralda | Goldfield | 1861 | 744 | 0.02 % | 3,589 | 9,300 | 3.25 % | 0.21 | 0.081 |
| Eureka | Eureka | 1869 | 1,863 | 0.06 % | 4,180 | 10,800 | 3.78 % | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Humboldt | Winnemucca | 1856/1861 | 17,272 | 0.54 % | 9,658 | 25,010 | 8.73 % | 1.79 | 0.69 |
| Lander | Battle Mountain | 1861 | 5,766 | 0.18 % | 5,519 | 14,290 | 4.99 % | 1.04 | 0.40 |
| Lincoln | Pioche | 1867 | 4,482 | 0.14 % | 10,637 | 27,550 | 9.62 % | 0.42 | 0.16 |
| Lyon | Yerington | 1861 | 61,585 | 1.94 % | 2,024 | 5,240 | 1.83 % | 30.43 | 11.75 |
| Mineral | Hawthorne | 1911 | 4,525 | 0.14 % | 3,813 | 9,880 | 3.45 % | 1.19 | 0.46 |
| Nye | Tonopah | 1864 | 54,738 | 1.72 % | 18,199 | 47,140 | 16.46 % | 3.01 | 1.16 |
| Pershing | Lovelock | 1919 | 6,462 | 0.20 % | 6,067 | 15,710 | 5.49 % | 1.07 | 0.41 |
| Storey | Virginia City | 1861 | 4,170 | 0.13 % | 264 | 680 | 0.24 % | 15.80 | 6.10 |
| Washoe | Reno | 1861 | 496,745 | 15.63 % | 6,542 | 16,940 | 5.92 % | 75.93 | 29.32 |
| White Pine | Ely | 1869 | 8,788 | 0.28 % | 8,897 | 23,040 | 8.05 % | 0.99 | 0.38 |
| Totals | Counties: 17 | 3,177,772 | 110,572 | 286,380 | 28.74 | 11.10 | |||
|
Largest cities or towns in Nevada
Source:[47]
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | County | Pop. | ||||||
 Las Vegas  Henderson |
1 | Las Vegas | Clark | 641,903 |  Reno North Las Vegas |
||||
| 2 | Henderson | Clark | 317,610 | ||||||
| 3 | Reno | Washoe | 264,165 | ||||||
| 4 | North Las Vegas | Clark | 262,527 | ||||||
| 5 | Enterprise | Clark | 221,831 | ||||||
| 6 | Spring Valley | Clark | 215,597 | ||||||
| 7 | Sunrise Manor | Clark | 205,618 | ||||||
| 8 | Paradise | Clark | 191,238 | ||||||
| 9 | Sparks | Washoe | 108,445 | ||||||
| 10 | Carson City | Carson City | 58,639 | ||||||





There are 68 designated wilderness areas in Nevada, protecting some 6,579,014 acres (2,662,433 ha) under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service, U.S. Forest Service, and Bureau of Land Management.[48]
The Nevada state parks comprise protected areas managed by the state of Nevada, including state parks, state historic sites, and state recreation areas. There are 24 state park units, including Van Sickle Bi-State Park which opened in July 2011 and is operated in partnership with the adjacent state of California.[49]

| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 6,857 | — | |
| 1870 | 42,941 | 526.2% | |
| 1880 | 62,266 | 45.0% | |
| 1890 | 47,355 | −23.9% | |
| 1900 | 42,335 | −10.6% | |
| 1910 | 81,875 | 93.4% | |
| 1920 | 77,407 | −5.5% | |
| 1930 | 91,058 | 17.6% | |
| 1940 | 110,247 | 21.1% | |
| 1950 | 160,083 | 45.2% | |
| 1960 | 285,278 | 78.2% | |
| 1970 | 488,738 | 71.3% | |
| 1980 | 800,493 | 63.8% | |
| 1990 | 1,201,833 | 50.1% | |
| 2000 | 1,998,257 | 66.3% | |
| 2010 | 2,700,551 | 35.1% | |
| 2020 | 3,104,614 | 15.0% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 3,267,467 | 5.2% | |
| Source: 1910–2020[50] | |||

The United States Census Bureau determined Nevada had a population of 3,104,614 at the 2020 U.S. census. In 2022, the estimated population of Nevada was 3,177,772, an increase of 73,158 residents (2.36%) since the 2020 census.[51] Nevada had the highest percentage growth in population from 2017 to 2018. At the 2020 census, 6.0% of the state's population were reported as under 5, 22.5% were under 18, and 16.1% were 65 or older. Females made up about 49.8% of the population. 19.1% of the population was reported as foreign-born.
Since the 2020 census, the population of Nevada had a natural increase of 2,374 (the net difference between 42,076 births and 39,702 deaths); and an increase due to net migration of 36,605 (of which 34,280 was due to domestic and 2,325 was due to international migration).[52]
The center of population of Nevada is in southern Nye County.[53] In this county, the unincorporated town of Pahrump, 60 miles (97 km) west of Las Vegas on the California state line, has grown very rapidly from 1980 to 2020. At the 2020 census, the town had 44,738 residents.[54] Las Vegas grew from a gulch of 100 people in 1900 to 10,000 by 1950 to 100,000 by 1970, and was America's fastest-growing city and metropolitan area from 1960 to 2000.
From about the 1940s until 2003, Nevada was the fastest-growing state in the U.S. percentage-wise. Between 1990 and 2000, Nevada's population increased by 66%, while the nation's population increased by 13%. More than two-thirds of the population live in Clark County, which is coextensive with the Las Vegas metropolitan area. Thus, in terms of population, Nevada is one of the most centralized states in the nation.
Henderson and North Las Vegas are among the top 20 fastest-growing U.S. cities with populations over 100,000. The rural community of Mesquite 65 miles (105 km) northeast of Las Vegas was an example of micropolitan growth in the 1990s and 2000s. Other desert towns like Indian Springs and Searchlight on the outskirts of Las Vegas have seen some growth as well.
Since 1950, the rate of population born in Nevada has never peaked above 27 percent, the lowest rate of all states. In 2012, only 25% of Nevadans were born in Nevada.[55]
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 7,618 homeless people in Nevada.[56][57]
| Race / Ethnicity | Pop 2000[58] | Pop 2010[59] | Pop 2020[60] | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 1,303,001 | 1,462,081 | 1,425,952 | 65.21% | 54.14% | 45.93% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 131,509 | 208,058 | 291,960 | 6.58% | 7.70% | 9.40% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 21,397 | 23,536 | 23,392 | 1.07% | 0.87% | 0.75% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 88,593 | 191,047 | 265,991 | 4.43% | 7.07% | 8.57% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 7,769 | 15,456 | 22,970 | 0.39% | 0.57% | 0.74% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 2,787 | 4,740 | 17,171 | 0.14% | 0.18% | 0.55% |
| Mixed Race/Multi-Racial (NH) | 49,231 | 79,132 | 166,921 | 2.46% | 2.93% | 5.38% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 393,970 | 716,501 | 890,257 | 19.72% | 26.53% | 28.68% |
| Total | 1,998,257 | 2,700,551 | 3,104,614 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Race and Ethnicity[61] | Alone | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 45.9% |
|
50.6% |
|
| Hispanic or Latino[e] | — | 28.7% |
|
|
| Multiracial | — | 14.0% |
|
|
| African American (non-Hispanic) | 9.4% |
|
11.1% |
|
| Asian | 8.6% |
|
10.7% |
|
| Native American | 0.8% |
|
2.1% |
|
| Pacific Islander | 0.7% |
|
1.5% |
|
| Other | 0.6% |
|
1.4% |
|
According to the 2022 American Community Survey, 30.3% of Nevada's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican (22%), Cuban (1.5%), Salvadoran (1.5%), Puerto Rican (1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (4.3%).[62] The largest European ancestry groups were: German (8.9%), English (8.1%), Irish (7.2%), and Italian (4.8%).[63] The largest Asian ancestry groups in the state were Filipino (6.4%) and Chinese (1.9%).[64]

| Non-Hispanic White
30–40%
|
In 1980, non-Hispanic whites made up 83.2% of the state's population.[65]
| Racial composition | 1970[65] | 1980 | 1990[65] | 2000[66] | 2010[67] | 2020[68] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 91.7% | 87.5% | 84.3% | 75.2% | 66.2% | 51.2% |
| Black | 5.7% | 6.4% | 6.6% | 6.8% | 8.1% | 9.8% |
| Asian | 0.7% | 1.8% | 3.2% | 4.5% | 7.2% | 8.8% |
| Native | 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.6% | 1.3% | 1.2% | 1.4% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander |
– | – | – | 0.4% | 0.6% | 0.8% |
| Other race | 0.3% | 2.7% | 4.4% | 8.0% | 12.0% | 14.0% |
| Two or more races | – | – | – | 3.8% | 4.7% | 14.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 5.6% | 6.7% | 10.4% | 19.7% | 26.5% | 28.7% |
| Non-Hispanic white | 86.7% | 83.2% | 78.7% | 65.2% | 54.1% | 45.9% |
As of 2011, 63.6% of Nevada's population younger than age 1 were minorities.[69] Las Vegas is a majority-minority city. According to the United States Census Bureau estimates, as of July 1, 2018, non-Hispanic Whites made up 48.7% of Nevada's population.[70]
In Douglas, Mineral, and Pershing counties, a plurality of residents are of Mexican ancestry. In Nye County and Humboldt County, residents are mostly of German ancestry; Washoe County has many Irish Americans. Americans of English descent form pluralities in Lincoln County, Churchill County, Lyon County, White Pine County, and Eureka County.
Asian Americans have lived in the state since at least the 1850s, when the California gold rush brought thousands of Chinese miners to Washoe County. They were followed by a few hundred Japanese farmworkers in the late 19th century. By the late 20th century, many immigrants from China, Japan, Korea, the Philippines, Bangladesh, India, and Vietnam came to the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The city now has a significant Asian American community, with a mostly Chinese and Taiwanese area known as "Chinatown" west of I-15 on Spring Mountain Road. Filipino Americans form the largest Asian American group in the state, with a population of more than 202,000. They comprise 59.8% of the Asian American population in Nevada and constitute about 6.4% of the entire state's population.[71]
Mining booms drew many Greek and Eastern European immigrants to Nevada.[72] In the early twentieth century, Greeks, Slavs, Danes, Japanese, Italians, and Basques poured into Nevada.[73] Chileans were found in the state as early as 1870.[74] During the mid-1800s, a significant number of European immigrants, mainly from Ireland, England and Germany, arrived in the state with the intention of capitalizing on the thriving mining sector in the region.[75]
Native American tribes in Nevada are the Northern and Southern Paiute, Western Shoshone, Goshute, Hualapai, Washoe, and Ute tribes.[76]
Whites remain the largest racial or ethnic group in Nevada.[77] Hispanics are the fastest growing ethnic group in Nevada.[78] There is a growing Mexican and Central American population in Nevada. Many of Nevada's Latino immigrants are from Mexico, Guatemala and El Salvador.[79] Nevada also has a growing multiracial population.[80]
The top countries of origin for immigrants in Nevada were Mexico (39.5 percent of immigrants), the Philippines (14.3 percent), El Salvador (5.2 percent), China (3.1 percent), and Cuba (3 percent).[81]
The majority of people in Nevada are of white (European) ancestry. A small portion trace their ancestry to Basque people recruited as sheepherders. Hispanics in Nevada are mainly of Mexican and Cuban heritage. Latinos comprise about one-fourth of Nevada's residents and are concentrated in the southeast in Nevada. African Americans live mainly in the Las Vegas and Reno area and constitute less than one-tenth of the population. Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes live on several reservations in the state and make up a small fraction of Nevada's population.[82]
The most common ancestries in Nevada include Mexican, German, Irish, English, Italian and Asian.[83]
Nevada is the third most diverse state in the country, behind only Hawaii and California.[84][85]
Note: Births within the table do not add up, due to Hispanics being counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.
| Race | 2013[86] | 2014[87] | 2015[88] | 2016[89] | 2017[90] | 2018[91] | 2019[92] | 2020[93] | 2021[94] | 2022[95] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 27,293 (77.9%) | 27,638 (77.1%) | 27,648 (76.2%) | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Non-Hispanic White | 14,951 (42.7%) | 15,151 (42.2%) | 14,937 (41.2%) | 13,918 (38.4%) | 13,171 (36.8%) | 13,021 (36.5%) | 12,479 (35.6%) | 11,602 (34.5%) | 11,800 (35.0%) | 10,961 (33.0%) |
| Black | 4,215 (12.0%) | 4,603 (12.8%) | 4,803 (13.2%) | 4,205 (11.6%) | 4,471 (12.5%) | 4,564 (12.8%) | 4,514 (12.9%) | 4,533 (13.5%) | 4,457 (13.2%) | 4,334 (13.1%) |
| Asian | 3,097 (8.8%) | 3,145 (8.8%) | 3,337 (9.2%) | 2,666 (7.3%) | 2,685 (7.5%) | 2,613 (7.3%) | 2,587 (7.4%) | 2,467 (7.3%) | 2,372 (7.0%) | 2,548 (7.7%) |
| Pacific Islander | ... | ... | ... | 308 (0.8%) | 322 (0.9%) | 340 (1.0%) | 372 (1.1%) | 358 (1.1%) | 331 (1.0%) | 358 (1.1%) |
| American Indian | 425 (1.2%) | 475 (1.3%) | 510 (1.4%) | 303 (0.8%) | 305 (0.9%) | 280 (0.8%) | 277 (0.8%) | 234 (0.7%) | 239 (0.7%) | 218 (0.7%) |
| Hispanic (of any race) | 12,718 (36.3%) | 13,006 (36.3%) | 13,225 (36.4%) | 13,391 (36.9%) | 13,176 (36.8%) | 13,307 (37.3%) | 13,238 (37.7%) | 12,763 (37.9%) | 12,842 (38.1%) | 13,019 (39.2%) |
| Total Nevada | 35,030 (100%) | 35,861 (100%) | 36,298 (100%) | 36,260 (100%) | 35,756 (100%) | 35,682 (100%) | 35,072 (100%) | 33,653 (100%) | 33,686 (100%) | 33,193 (100%) |



A small percentage of Nevada's population lives in rural areas. The culture of these places differs significantly from major metropolitan areas. People in these rural counties tend to be native Nevada residents, unlike in the Las Vegas and Reno areas, where the vast majority of the population was born in another state. The rural population is also less diverse in terms of race and ethnicity. Mining plays an important role in the economies of the rural counties, with tourism being less prominent.[96] Ranching also has a long tradition in rural Nevada.[97]
| Rank | Place | Per capita income | County | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Crystal Bay | $180,334 | Washoe | |
| 2 | Glenbrook | $102,963 | Douglas | |
| 3 | Zephyr Cove | $94,920 | Douglas | |
| 4 | Genoa | $86,185 | Douglas | |
| 5 | Incline Village | $74,294 | Washoe | |
| 6 | Kingsbury | $68,215 | Douglas | |
| 7 | Round Hill Village | $67,659 | Douglas | |
| 8 | East Valley | $67,169 | Douglas | |
| 9 | Summerlin South | $65,633 | Clark | |
| 10 | Mount Charleston | $57,583 | Clark | |
Church attendance in Nevada is among the lowest of all U.S. states. In a 2009 Gallup poll only 30% of Nevadans said they attended church weekly or almost weekly, compared to 42% of all Americans (only four states were found to have a lower attendance rate than Nevada's).[99] In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 67% of the population were Christian,[100] reflecting a 1% increase in religiosity from 2014's separate Pew study.[101]
Major religious affiliations of the people of Nevada were, according to the Pew Research Center in 2014: Protestant 35%, Irreligious 28%, Roman Catholic 25%, Latter-day Saints 4%, Jewish 2%, Hindu less than 1%, Buddhist 0.5% and Muslim around 0.2%. Parts of Nevada (in the eastern parts of the state) are situated in the Mormon Corridor.
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the Roman Catholic Church with 451,070; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 175,149; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 45,535; Buddhist congregations 14,727; Baháʼí Faith 1,723; and Muslim 1,700.[102]
The most common non-English languages spoken in Nevada are Spanish, Tagalog and Chinese.[103] Indigenous languages of Nevada include Northern Paiute, the Southern Paiute, Shoshone, and Washo.[104]
The top seven languages spoken in Nevada according to the U.S. Census data are Spanish, Tagalog, Chinese, Vietnamese, Korean, Amharic, Arabic, and Thai.[105]
Historically what is now Nevada has been inhabited mainly by the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe.[106]
The largest Native American tribes in Nevada according to the 2010 census are listed in the table below:[107]
| Tribal grouping | American Indian and
Alaska Native alone |
AIAN in combination with
one or more other races |
Total AIAN alone or
in any combination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total AIAN population | 32062 | 23883 | 55945 |
| Cherokee | 1824 | 4376 | 6200 |
| Paiute | 4182 | 677 | 4859 |
| Navajo | 1926 | 671 | 2597 |
| Paiute-Shoshone | 2118 | 170 | 2288 |
| Mexican American Indian | 1222 | 708 | 1930 |
| Shoshone | 1388 | 400 | 1788 |
| Choctaw | 597 | 872 | 1469 |
| Apache | 719 | 690 | 1409 |
| Sioux | 702 | 626 | 1328 |
| Blackfeet | 284 | 877 | 1161 |
| Te-Moak Tribes of Western Shoshone | 1011 | 118 | 1129 |
| Washoe | 815 | 130 | 945 |
| Ojibwe | 494 | 338 | 832 |
| Reno-Sparks Indian Colony | 579 | 13 | 592 |
| Iroquois | 228 | 283 | 511 |
| Tribe not specified | 9413 | 10117 | 19530 |






The economy of Nevada is tied to tourism (especially entertainment and gambling related), mining, and cattle ranching. Nevada's industrial outputs are tourism, entertainment, mining, machinery, printing and publishing, food processing, and electric equipment. The Bureau of Economic Analysis[109][110] estimates Nevada's total state product in 2018 was $170 billion.[111] The state's per capita personal income in 2020 was $53,635, ranking 31st in the nation.[112] Nevada's state debt in 2012 was calculated to be $7.5 billion, or $3,100 per taxpayer.[113] As of May 2021, the state's unemployment rate was 7.8%.[114]
In portions of the state outside of the Las Vegas and Reno metropolitan areas mining plays a major economic role. By value, gold is by far the most important mineral mined. In 2022, 4,040,000 troy ounces (126 t) of gold worth $7.3 billion were mined in Nevada, and the state accounted for 4% of world gold production. Other minerals mined in Nevada include construction aggregates, copper, gypsum, diatomite and lithium.[115][116] Despite its rich deposits, the cost of mining in Nevada is generally high, and output is very sensitive to world commodity prices.
Cattle ranching is a major economic activity in rural Nevada.[117] Nevada's agricultural outputs are cattle, hay, alfalfa, dairy products, onions, and potatoes. In 2020, there were an estimated 438,511 head of cattle and 71,699 head of sheep in Nevada.[118] Most of these animals forage on rangeland in the summer, with supplemental feed in the winter. Calves are generally shipped to out-of-state feedlots in the fall to be fattened for the market. Over 90% of Nevada's 653,891 acres (264,620 ha) of cropland is used to grow hay, mostly alfalfa, for livestock feed.[118]
The largest employers in the state, as of the first fiscal quarter of 2011, are the following, according to the Nevada Department of Employment, Training and Rehabilitation:[119]


Amtrak's California Zephyr train uses the Union Pacific's original transcontinental railroad line in daily service from Chicago to Emeryville, California, serving Elko, Winnemucca, and Reno. Las Vegas has had no passenger train service since Amtrak's Desert Wind was discontinued in 1997. Amtrak Thruway buses provide connecting service from Las Vegas to trains at Needles, California, Los Angeles, and Bakersfield, California; and from Stateline, Nevada, to Sacramento, California. There have been a number of proposals to re-introduce service to either Los Angeles or Southern California with the privately run Brightline West having begun construction in 2024.
The Union Pacific Railroad has some railroads in the north and south of Nevada. Greyhound Lines provide some bus service to the state.
Interstate 15 (I-15) passes through the southern tip of the state, serving Las Vegas and other communities. I-215 and I-515 also serve the Las Vegas metropolitan area. I-80 crosses through the northern part of Nevada, roughly following the path of the Humboldt River from Utah in the east and the Truckee River westward through Reno into California. It has a spur route, I-580. Nevada also is served by several U.S. highways: US 6, US 50, US 93, US 95 and US 395. There are also 189 Nevada state routes. Many of Nevada's counties have a system of county routes as well, though many are not signed or paved in rural areas. Nevada is one of a few states in the U.S. that do not have a continuous interstate highway linking its two major population centers – the road connection between the Las Vegas and Reno areas is a combination of several different Interstate and U.S. highways. The Interstate 11 proposed routing may eventually remedy this.[120]
The state is one of just a few in the country to allow semi-trailer trucks with three trailers – what might be called a "road train" in Australia. But American versions are usually smaller, in part because they must ascend and descend some fairly steep mountain passes.
RTC Transit is the public transit system in the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The agency is the largest transit agency in the state and operates a network of bus service across the Las Vegas Valley, including the use of The Deuce, double-decker buses, on the Las Vegas Strip and several outlying routes. RTC RIDE operates a system of local transit bus service throughout the Reno-Sparks metropolitan area. Other transit systems in the state include Carson City's JAC. Most other counties in the state do not have public transportation at all.
Additionally, a 4-mile (6.4 km) monorail system provides public transportation in the Las Vegas area. The Las Vegas Monorail line services several casino properties and the Las Vegas Convention Center on the east side of the Las Vegas Strip, running near Paradise Road, with a possible future extension to Harry Reid International Airport. Several hotels also run their own monorail lines between each other, which are typically several blocks in length.
Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas is the busiest airport serving Nevada. The Reno-Tahoe International Airport (formerly known as the Reno Cannon International Airport) is the other major airport in the state.
| External image | |
|---|---|
Nevada has had a thriving solar energy sector. An independent study in 2013 concluded that solar users created a $36 million net benefit. However, in December 2015, the Public Utility Commission let the state's only power company, NV Energy, charge higher rates and fees to solar panel users, leading to an immediate collapse of rooftop solar panel use.[121]
In December 1987, Congress amended the Nuclear Waste Policy Act to designate Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository as the only site to be characterized as a permanent repository for all of the nation's highly radioactive waste.[122]
In 2018, the National Low Income Housing Coalition calculated the discrepancy between available affordable housing units and renters who earn below the poverty line. In Nevada, only 15 affordable rental homes are available per 100 extremely low income (ELI) households.[123] The shortage extended to a deficit in supply of 71,358 affordable rental homes. This was the largest discrepancy of any state. The most notable catalyst for this shortage was the Great Recession and housing crisis of 2007 and 2008. Since then, housing prices have increased while demand has increased, and supply has struggled to match the increase in demand. In addition, low-income service workers were slowly being pushed out by an influx of tech professionals. In Nevada there is essentially a standard of six-figure income to affordably rent a single-family home.[124] Considering the average salary in Nevada, $54,842 per year, this standard is on average, unaffordable.[125] The disproportionate cost of housing compared to average salary has led to 112,872 renters to be paying more than half of their yearly income towards housing.[126]
The definition of an affordable home is "one that a household can obtain for 30 percent or less of its annual income". So, there is clearly a long way to go in order to close the gap between housing prices and relative income in the state. Renters are looking for solutions to still be able to live in the state in a way that their income can support. As a result, single adults are being forced to split rent with other renters or move residences to farther outside metro areas. One solution being offered is to increase the supply of higher income positions within the state to make things more affordable. However, this would require Nevadans to retrain in new jobs or careers.
Education in Nevada is achieved through public and private elementary, middle, and high schools, as well as colleges and universities.
A May 2015 educational reform law expanded school choice options to 450,000 Nevada students who are at up to 185% of the federal poverty level. Education savings accounts (ESAs) are enabled by the new law to help pay the tuition for private schools. Alternatively, families "can use funds in these accounts to also pay for textbooks and tutoring".[127][128]
Approximately 86.9% of Nevada residents have attained at least a high school degree or equivalent, which is below the national average of 88.6%.[129]
Public school districts in Nevada include:
The Nevada Aerospace Hall of Fame provides educational resources and promotes the aerospace and aviation history of the state.[130]

Under the Constitution of the State of Nevada, the powers of the Nevada government are divided among three separate departments: the executive consisting of the governor of Nevada and their cabinet along with the other elected constitutional officers; the legislative consisting of the Nevada Legislature, which includes the Assembly and the Senate; and the judicial consisting of the Supreme Court of Nevada and lower courts.
The governor is the chief magistrate of Nevada,[131] the head of the executive department of the state's government,[131] and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces.[132] The current governor is Joe Lombardo, a Republican. The executive branch also consists of an independently elected lieutenant governor, secretary of state, state treasurer, state controller, and attorney general who function as a check and balance on the power of the governor.[133]
The Nevada Legislature is a bicameral body divided into an Assembly and Senate. Members of the Assembly serve two years, and members of the Senate serve four years. Both houses of the Nevada Legislature enacted term limits starting in 2010, with senators and assemblymen/women who are limited to a maximum of twelve years in each body (by appointment or election which is a lifetime limit) – a provision of the constitution which was upheld by the Supreme Court of Nevada in a unanimous decision. Each session of the legislature meets for a constitutionally mandated 120 days in every odd-numbered year, or longer if the governor calls a special session.
On December 18, 2018, Nevada became the first in the United States with a female majority in its legislature. Women hold nine of the 21 seats in the Nevada Senate, and 23 of the 42 seats in the Nevada Assembly.[134]
The Supreme Court of Nevada is the state supreme court and the head of the Nevada Judiciary. Original jurisdiction is divided between the district courts (with general jurisdiction), and justice courts and municipal courts (both of limited jurisdiction). Appeals from District Courts are made directly to the Nevada Supreme Court, which under a deflective model of jurisdiction, has the discretion to send cases to the Court of Appeals for final resolution.[135]
Incorporated towns in Nevada, known as cities, are given the authority to legislate anything not prohibited by law. A recent movement has begun to permit home rule to incorporate Nevada cities to give them more flexibility and fewer restrictions from the Legislature. Town Boards for unincorporated towns are limited local governments created by either the local county commission, or by referendum, and form a purely advisory role and in no way diminish the responsibilities of the county commission that creates them.

In 1900, Nevada's population was the smallest of all states and was shrinking, as the difficulties of living in a "barren desert" began to outweigh the lure of silver for many early settlers. Historian Lawrence Friedman has explained what happened next:
Nevada, in a burst of ingenuity, built an economy by exploiting its sovereignty. Its strategy was to legalize all sorts of things that were illegal in California ... after the easy divorce came easy marriage and casino gaming. Even prostitution is legal in Nevada, in any county that decides to allow it. Quite a few of them do.[136]
With the advent of air conditioning for summertime use and Southern Nevada's mild winters, the fortunes of the state began to turn around, as it did for Arizona, making these two states the fastest growing in the Union.
Nevada is the only state where prostitution is legal – in a licensed brothel in a county which has specifically voted to permit it. It is illegal in larger jurisdictions such as Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), Washoe County (which contains Reno), and the independent city of Carson City.
Nevada's early reputation as a "divorce haven" arose from the fact that before the no-fault divorce revolution in the 1970s, divorces were difficult to obtain in the United States. Already having legalized gambling and prostitution, Nevada continued the trend of boosting its profile by adopting one of the most liberal divorce statutes in the nation. This resulted in Williams v. North Carolina (1942), 317 U.S. 287 (1942), in which the U.S. Supreme Court ruled North Carolina had to give "full faith and credit" to a Nevada divorce. The Court modified its decision in Williams v. North Carolina (1945), 325 U.S. 226 (1945), by holding a state need not recognize a Nevada divorce unless one of the parties was domiciled there at the time the divorce was granted and the forum state was entitled to make its own determination.
As of 2009, Nevada's divorce rate was above the national average.[137]
Nevada's tax laws are intended to draw new residents and businesses to the state. Nevada has no personal income tax or corporate income tax.[138] Since Nevada does not collect income data it cannot share such information with the federal government, the IRS.[139]
The state sales tax (similar to VAT or GST) in Nevada is variable depending upon the county. The statewide tax rate is 6.85%, with five counties (Elko, Esmeralda, Eureka, Humboldt, and Mineral) charging this amount. Counties may impose additional rates via voter approval or through approval of the state legislature; therefore, the applicable sales tax varies by county from 6.85% to 8.375% (Clark County). Clark County, which includes Las Vegas, imposes four separate county option taxes in addition to the statewide rate: 0.25% for flood control, 0.50% for mass transit, 0.25% for infrastructure, and 0.25% for more law enforcement. In Washoe County, which includes Reno, the sales tax rate is 7.725%, due to county option rates for flood control, the ReTRAC train trench project, and mass transit, and an additional county rate approved under the Local Government Tax Act of 1991.[140] The minimum Nevada sales tax rate changed on July 1, 2009.[141]
The lodging tax rate in unincorporated Clark County, which includes the Las Vegas Strip, is 12%. Within the boundaries of the cities of Las Vegas and Henderson, the lodging tax rate is 13%.
Corporations such as Apple Inc. allegedly have set up investment companies and funds in Nevada to avoid paying taxes.[142]
In 2009, the Nevada Legislature passed a bill creating a domestic partnership registry which enables same-sex couples to enjoy the same rights as married couples. Due to the landmark decision in the case of Obergefell v. Hodges, 576 U.S. 644 (2015), same-sex marriage was outright legalized in the state.
Nevada provides a friendly environment for the formation of corporations, and many (especially California) businesses have incorporated in Nevada to take advantage of the benefits of the Nevada statute. Nevada corporations offer great flexibility to the board of directors and simplify or avoid many of the rules that are cumbersome to business managers in some other states. In addition, Nevada has no franchise tax, although it does require businesses to have a license for which the business has to pay the state.
Similarly, many U.S. states have usury laws limiting the amount of interest a lender can charge, but federal law allows corporations to "import" these laws from their home state. Nevada has no cap on interest rates that may be agreed to in contracts.[143]
Nevada has very liberal alcohol laws. Bars are permitted to remain open 24 hours, with no "last call". Liquor stores, convenience stores and supermarkets may also sell alcohol 24 hours per day and may sell beer, wine and spirits.
In 2016, Nevada voters approved Question 2, which legalized the possession, transportation and cultivation of personal use amounts of marijuana for adults age 21 years and older, and authorized the creation of a regulated market for the sale of marijuana to adults age 21 years and older through state-licensed retail outlets.[144] Nevada voters had previously approved medical marijuana in 2000, but rejected marijuana legalization in a similar referendum in 2006. Marijuana in all forms remains illegal under federal law.
Aside from cannabis legalization, non-alcohol drug laws are a notable exception to Nevada's otherwise libertarian principles. It is notable for having the harshest penalties for drug offenders in the country. Nevada remains the only state to still use mandatory minimum sentencing guidelines for possession of drugs.[145]
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) reported, in their Behavioral Health Barometer for Nevada, published in 2014, changes to substance abuse patterns and addiction across the southwestern state.[146] Between 2012 and 2013, adolescents in Nevada abused illicit substances at a slightly higher percentage than nationally. 10.2 percent of Nevada's adolescents abused illicit drugs compared to 9.2 percent across the United States. Between 2009 and 2013, 11.7 percent of all adolescents in the state reported abusing illicit, intoxicating substances in the month prior to the survey; this represents 25,000 adolescents.
Nevada voters enacted a smoking ban ("The Nevada Clean Indoor Air Act") in November 2006 which became effective on December 8, 2006. It outlaws smoking in most workplaces and public places. Smoking is permitted in bars, but only if the bar serves no food, or the bar is inside a larger casino. Smoking is also permitted in casinos, certain hotel rooms, tobacco shops, and brothels.[147] However, some businesses do not obey this law and the government tends not to enforce it.[148] In 2011, smoking restrictions in Nevada were relaxed for certain places which allow only people 21 or older inside.[149]
In 2006, the crime rate in Nevada was about 24% higher than the national average rate, though crime has since decreased. Property crimes accounted for about 85% of the total crime rate in Nevada, which was 21% higher than the national rate. The remaining 20.3% were violent crimes.[150] A complete listing of crime data in the state for 2013 can be found here:[151]
| Party | Total voters | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | 616,656 | 29.42% | |
| Republican | 616,882 | 29.43% | |
| Independent American | 94,604 | 4.51% | |
| Libertarian | 16,202 | 0.77% | |
| Other parties | 48,727 | 2.33% | |
| Nonpartisan | 703,085 | 33.54% | |
| Total | 2,096,156 | 100.00% | |

Due to heavy growth in the southern portion of the state, there is a noticeable divide between the politics of northern and southern Nevada. Historically, northern Nevada has been very Republican. The more rural counties of the north are among the most conservative regions of the state. Carson City, the state's capital, is a Republican-leaning swing city/county. Washoe County, home to Reno, has historically been strongly Republican, but now has become a fairly balanced swing county, like the state as a whole. Clark County, home to Las Vegas, has been a stronghold for the Democratic Party since it was founded in 1909, having voted Republican only six times and once for a third-party candidate, although in recent times becoming more competitive, most notably in the 2024 Presidential Election where the Democratic Party's margin of victory was only 2.63 percentage points to Republicans.[153] Clark and Washoe counties have long dominated the state's politics. Between them, they cast 87% of Nevada's vote, and elect a substantial majority of the state legislature. The last Republican to carry Clark County was George H. W. Bush in 1988, and the last Republican to carry Washoe County was George W. Bush in 2004. The great majority of the state's elected officials are from either Las Vegas or Reno.[154] Donald Trump was able to carry Nevada with a statewide majority in 2024, despite losing both Clark and Washoe.
In 2014, Republican Adam Laxalt, despite losing both Clark and Washoe counties, was elected Attorney General. However, he had lost Clark County only by 5.6% and Washoe County by 1.4%, attributable to lower turnout in these counties.[155]

Nevada has been won by the winner of nearly every presidential election since its first in 1864, only being carried by the defeated candidate eight times since statehood, most of which were before 1900. Since 1912 Nevada has been carried by the presidential victor the most out of any state (27 of 29 elections), the only exceptions being 1976 when it voted for Gerald Ford over Jimmy Carter and 2016 when the state was carried by Hillary Clinton over Donald Trump. This gives the state status as a political bellwether. It was one of only three states won by John F. Kennedy in the American West in the election of 1960, albeit narrowly.[156] The state's U.S. Senators are Democrats Catherine Cortez Masto and Jacky Rosen. The Governorship is held by Joe Lombardo, a Republican.
Nevada is the only U.S. state to have a none of the above option available on its ballots. Officially called None of These Candidates, the option was first added to the ballot in 1975 and is used in all statewide elections, including president, US Senate and all state constitutional positions. In the event "None of These Candidates" receives a plurality of votes in the election, the candidate with the next-highest total is elected.[157]
In a 2020 study, Nevada was ranked as the 23rd on the "Cost of Voting Index", which is a measure of "the ease of voting across the United States."[158]
Resort areas like Las Vegas, Reno, Lake Tahoe, and Laughlin attract visitors from around the nation and world. In fiscal year 2022 Nevada casinos (not counting those with annual revenue under a million dollars) brought in US$10.7 billion in gaming revenue and another US$15.7 billion in non-gaming revenue.[159]
Nevada has by far the most hotel rooms per capita in the United States. According to the American Hotel and Lodging Association, there were 187,301 rooms in 584 hotels (of 15 or more rooms). The state is ranked just below California, Texas, Florida, and New York in the total number of rooms, but those states have much larger populations. Nevada has one hotel room for every 14 residents, far above the national average of one hotel room per 67 residents.[160]
Prostitution is legal in parts of Nevada in licensed brothels, but only counties with populations under 400,000 have the option to legalize it. Although prostitution is not a major part of the Nevada economy, employing roughly 300 women as independent contractors, it is a very visible endeavor. Of the 14 counties permitted to legalize prostitution under state law, eight have chosen to legalize brothels. State law prohibits prostitution in Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), and Washoe County (which contains Reno). However, prostitution is legal in Storey County, which is part of the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
The Las Vegas Valley is home to the Vegas Golden Knights of the National Hockey League who began to play in the 2017–18 NHL season at T-Mobile Arena on the Las Vegas Strip in Paradise, the Las Vegas Raiders of the National Football League who began play at Allegiant Stadium in Paradise in 2020 after moving from Oakland, California, and the Las Vegas Aces of the WNBA who began playing in 2018 at Mandalay Bay Events Center after relocating from San Antonio. The Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball plan to move to Las Vegas by 2027.[161][162]
Nevada takes pride in college sports, most notably its college football. College teams in the state include the Nevada Wolf Pack (representing the University of Nevada, Reno) and the UNLV Rebels (representing the University of Nevada, Las Vegas), both in the Mountain West Conference (MW).
UNLV is most remembered for its men's basketball program, which experienced its height of supremacy in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Coached by Jerry Tarkanian, the Runnin' Rebels became one of the most elite programs in the country. In 1990, UNLV won the Men's Division I Championship by defeating Duke 103–73, which set tournament records for most points scored by a team and largest margin of victory in the national title game.
In 1991, UNLV finished the regular season undefeated, a feat that would not be matched in Division I men's basketball for more than 20 years. Forward Larry Johnson won several awards, including the Naismith Award. UNLV reached the Final Four yet again, but lost their national semifinal against Duke 79–77. The Runnin' Rebels were the Associated Press pre-season No. 1 back to back (1989–90, 1990–91). North Carolina is the only other team to accomplish that (2007–08, 2008–09).
The state's involvement in major-college sports is not limited to its local schools. In the 21st century, the Las Vegas area has become a significant regional center for college basketball conference tournaments. The MW, West Coast Conference, and Western Athletic Conference all hold their men's and women's tournaments in the area, and the Pac-12 holds its men's tournament there as well. The Big Sky Conference, after decades of holding its men's and women's conference tournaments at campus sites, began holding both tournaments in Reno in 2016.
Las Vegas has hosted several professional boxing matches, most recently at the MGM Grand Garden Arena with bouts such as Mike Tyson vs. Evander Holyfield, Evander Holyfield vs. Mike Tyson II, Oscar De La Hoya vs. Floyd Mayweather Jr. and Oscar De La Hoya vs. Manny Pacquiao and at the newer T-Mobile Arena with Canelo Álvarez vs. Amir Khan.
Along with significant rises in popularity in mixed martial arts (MMA), a number of fight leagues such as the UFC have taken interest in Las Vegas as a primary event location due to the number of suitable host venues. The Mandalay Bay Events Center and MGM Grand Garden Arena are among some of the more popular venues for fighting events such as MMA and have hosted several UFC and other MMA title fights. The city has held the most UFC events with 86 events.
The state is also home to the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, which hosts NASCAR's Pennzoil 400 and South Point 400. Two venues in the immediate Las Vegas area host major annual events in rodeo. The Thomas & Mack Center, built for UNLV men's basketball, hosts the National Finals Rodeo. The PBR World Finals, operated by the bull riding-only Professional Bull Riders, was also held at the Thomas & Mack Center before moving to T-Mobile Arena in 2016.
The state is also home to famous tennis player, Andre Agassi, and current baseball superstar Bryce Harper.
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Raiders | Football | NFL | Allegiant Stadium (65,000) | 2020 | 3[f] |
| Vegas Golden Knights | Ice hockey | NHL | T-Mobile Arena (17,500) | 2017 | 1 |
| Las Vegas Aces | Women's basketball | WNBA | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2018 | 2 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Aviators | Baseball | MiLB (AAA–PCL) | Las Vegas Ballpark (10,000) | 1983 | 2 |
| Reno Aces | Greater Nevada Field (9,013) | 2009 | 2 | ||
| Vegas Royals | Basketball | ABA | 0 | ||
| Henderson Silver Knights | Ice hockey | AHL | Dollar Loan Center (5,567) | 2020 | 0 |
| Tahoe Knight Monsters | ECHL | Tahoe Blue Event Center (5,000) | 2024 | 0 | |
| Las Vegas Lights FC | Soccer | USLC | Cashman Field (9,334) | 2018 | 0 |
| Nevada Storm | Women's football | WFA | Damonte Ranch High School (N/A) Fernley High School (N/A) Galena High School (N/A) |
2008 | 0 |
| Sin City Trojans | Desert Pines High School (N/A) | 0 | |||
| Vegas Knight Hawks | Indoor football | IFL | Dollar Loan Center (6,019) | 2021 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Desert Dogs | Box lacrosse | NLL | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 0 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reno Ice Raiders | Ice hockey | MWHL | Reno Ice | 2015 | 0 |
| Vegas Jesters | City National Arena (600) | 2012 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Thunderbirds | USPHL | 2019 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Legends | Soccer | NPSL | Peter Johann Memorial Field (2,500) | 2021 | 0 |
| Nevada Coyotes FC | UPSL | Rio Vista Sports Complex (N/A) | 2016 | 0 |
| School | Team | League | Division | Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) | UNLV Rebels | NCAA | NCAA Division I | Mountain West |
| University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) | Nevada Wolf Pack | |||
| College of Southern Nevada (CSN) | CSN Coyotes | NJCAA | NJCAA Division I | Scenic West |
| Western Nevada College (WNC) | WNC Wildcats |

Several United States Navy ships have been named USS Nevada in honor of the state. They include:
Area 51 is near Groom Lake, a dry salt lake bed. The much smaller Creech Air Force Base is in Indian Springs, Nevada; Hawthorne Army Depot in Hawthorne; the Tonopah Test Range near Tonopah; and Nellis AFB in the northeast part of the Las Vegas Valley. Naval Air Station Fallon in Fallon; NSAWC, (pronounced "EN-SOCK") in western Nevada. NSAWC consolidated three Command Centers into a single Command Structure under a flag officer on July 11, 1996. The Naval Strike Warfare Center based at NAS Fallon since 1984, was joined with the Navy Fighter Weapons School (TOPGUN) and the Carrier Airborne Early Warning Weapons School, which both moved from NAS Miramar as a result of a Base Realignment and Closure decision in 1993 which transferred that installation back to the Marine Corps as MCAS Miramar. The Seahawk Weapon School was added in 1998 to provide tactical training for Navy helicopters.
These bases host a number of activities including the Joint Unmanned Aerial Systems Center of Excellence, the Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center, Nevada Test and Training Range, Red Flag, the U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds, the United States Air Force Warfare Center, the United States Air Force Weapons School, and the United States Navy Fighter Weapons School.

Landscape architecture is the design of outdoor areas, landmarks, and structures to achieve environmental, social-behavioural, or aesthetic outcomes.[2] It involves the systematic design and general engineering of various structures for construction and human use, investigation of existing social, ecological, and soil conditions and processes in the landscape, and the design of other interventions that will produce desired outcomes.
The scope of the profession is broad and can be subdivided into several sub-categories including professional or licensed landscape architects who are regulated by governmental agencies and possess the expertise to design a wide range of structures and landforms for human use; landscape design which is not a licensed profession; site planning; stormwater management; erosion control; environmental restoration; public realm, parks, recreation and urban planning; visual resource management; green infrastructure planning and provision; and private estate and residence landscape master planning and design; all at varying scales of design, planning and management. A practitioner in the profession of landscape architecture may be called a landscape architect; however, in jurisdictions where professional licenses are required it is often only those who possess a landscape architect license who can be called a landscape architect.
Modern landscape architecture is a multi-disciplinary field, incorporating aspects of urban design, architecture, geography, ecology, civil engineering, structural engineering, horticulture, environmental psychology, industrial design, soil sciences, botany, and fine arts. The activities of a landscape architect can range from the creation of public parks and parkways to site planning for campuses and corporate office parks; from the design of residential estates to the design of civil infrastructure; and from the management of large wilderness areas to reclamation of degraded landscapes such as mines or landfills. Landscape architects work on structures and external spaces in the landscape aspect of the design – large or small, urban, suburban and rural, and with "hard" (built) and "soft" (planted) materials, while integrating ecological sustainability.
The most valuable contribution can be made at the first stage of a project to generate ideas with technical understanding and creative flair for the design, organization, and use of spaces. The landscape architect can conceive the overall concept and prepare the master plan, from which detailed design drawings and technical specifications are prepared. They can also review proposals to authorize and supervise contracts for the construction work. Other skills include preparing design impact assessments, conducting environmental assessments and audits, and serving as an expert witness at inquiries on land use issues. The majority of their time will most likely be spent inside an office building designing and preparing models for clients.[citation needed]

For the period before 1800, the history of landscape gardening (later called landscape architecture) is largely that of master planning and garden design for manor houses, palaces and royal properties. An example is the extensive work by André Le Nôtre for King Louis XIV of France on the Gardens of Versailles. The first person to write of making a landscape was Joseph Addison in 1712. The term landscape architecture was invented by Gilbert Laing Meason in 1828, and John Claudius Loudon (1783–1843) was instrumental in the adoption of the term landscape architecture by the modern profession. He took up the term from Meason and gave it publicity in his Encyclopedias and in his 1840 book on the Landscape Gardening and Landscape Architecture of the Late Humphry Repton.[6]
John Claudius Loudon was an established and influential horticultural journalist and Scottish landscape architect whose writings were instrumental in shaping Victorian taste in gardens, public parks, and architecture.[7] In the Landscape Gardening and Landscape Architecture of the Late Humphry Repton, Loudon describes two distinct styles of landscape gardening existing at the beginning of the 19th century: geometric and natural.[6] Loudon wrote that each style reflected a different stage of society. The geometric style was “most striking and pleasing,” displaying wealth and taste in an “early state of society” and in “countries where the general scenery was wild, irregular, and natural, and man, comparatively, uncultivated and unrefined.”[6] The natural style was used in “modern times” and in countries where “society is in a higher state of cultivation," displaying wealth and taste through the sacrifice of profitable lands to make room for such designs. [6]
The prominent English landscape designer Humphry Repton (1752-1818) echoed similar ideas in his work and design ideas. In his writings on the use of delineated spaces (e.g. courtyards, terrace walls, fences), Repton states that while the motive for defense no longer exists, the features are still useful in separating "the gardens, which belong to man, and the forest, or desert, which belongs to the wild denizens."[6] Repton refers to Indigenous peoples as "uncivilized human beings, against whom some decided line of defense was absolutely necessary.”[6]
The practice of landscape architecture spread from the Old to the New World. The term "landscape architect" was used as a professional title by Frederick Law Olmsted in the United States in 1863[citation needed] and Andrew Jackson Downing, another early American landscape designer, was editor of The Horticulturist magazine (1846–52). In 1841 his first book, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America, was published to a great success; it was the first book of its kind published in the United States.[8] During the latter 19th century, the term landscape architect began to be used by professional landscapes designers, and was firmly established after Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. and Beatrix Jones (later Farrand) with others founded the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA) in 1899. IFLA was founded at Cambridge, England, in 1948 with Sir Geoffrey Jellicoe as its first president, representing 15 countries from Europe and North America. Later, in 1978, IFLA's Headquarters were established in Versailles.[9][10][11]


The variety of the professional tasks that landscape architects collaborate on is very broad, but some examples of project types include:[12]
Landscape managers use their knowledge of landscape processes to advise on the long-term care and development of the landscape. They often work in forestry, nature conservation and agriculture.[citation needed]
Landscape scientists have specialist skills such as soil science, hydrology, geomorphology or botany that they relate to the practical problems of landscape work. Their projects can range from site surveys to the ecological assessment of broad areas for planning or management purposes. They may also report on the impact of development or the importance of particular species in a given area.[citation needed]
Landscape planners are concerned with landscape planning for the location, scenic, ecological and recreational aspects of urban, rural, and coastal land use. Their work is embodied in written statements of policy and strategy, and their remit includes master planning for new developments, landscape evaluations and assessments, and preparing countryside management or policy plans. Some may also apply an additional specialism such as landscape archaeology or law to the process of landscape planning.[citation needed]
Green roof (or more specifically, vegetative roof) designers design extensive and intensive roof gardens for stormwater management, evapo-transpirative cooling, sustainable architecture, aesthetics, and habitat creation.[13]

Through the 19th century, urban planning became a focal point and central issue in cities. The combination of the tradition of landscape gardening and the emerging field of urban planning offered landscape architecture an opportunity to serve these needs.[14] In the second half of the century, Frederick Law Olmsted completed a series of parks that continue to have a significant influence on the practices of landscape architecture today. Among these were Central Park in New York City, Prospect Park in Brooklyn, New York and Boston's Emerald Necklace park system. Jens Jensen designed sophisticated and naturalistic urban and regional parks for Chicago, Illinois, and private estates for the Ford family including Fair Lane and Gaukler Point. One of the original eleven founding members of the American Society of Landscape Architects (ASLA), and the only woman, was Beatrix Farrand. She was design consultant for over a dozen universities including: Princeton in Princeton, New Jersey; Yale in New Haven, Connecticut; and the Arnold Arboretum for Harvard in Boston, Massachusetts. Her numerous private estate projects include the landmark Dumbarton Oaks in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C.[15] Since that time, other architects – most notably Ruth Havey and Alden Hopkins – changed certain elements of the Farrand design.[citation needed]
Since this period urban planning has developed into a separate independent profession that has incorporated important contributions from other fields such as civil engineering, architecture and public administration. Urban Planners are qualified to perform tasks independent of landscape architects, and in general, the curriculum of landscape architecture programs do not prepare students to become urban planners.[16]
Landscape architecture continues to develop as a design discipline and to respond to the various movements in architecture and design throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Thomas Church was a mid-century landscape architect significant in the profession. Roberto Burle Marx in Brazil combined the International style and native Brazilian plants and culture for a new aesthetic. Innovation continues today solving challenging problems with contemporary design solutions for master planning, landscapes, and gardens.[citation needed]
Ian McHarg was known for introducing environmental concerns in landscape architecture.[17][18] He popularized a system of analyzing the layers of a site in order to compile a complete understanding of the qualitative attributes of a place. This system became the foundation of today's Geographic Information Systems (GIS). McHarg would give every qualitative aspect of the site a layer, such as the history, hydrology, topography, vegetation, etc. GIS software is ubiquitously used in the landscape architecture profession today to analyze materials in and on the Earth's surface and is similarly used by urban planners, geographers, forestry and natural resources professionals, etc.[citation needed]
European nations enabled the widespread circulation of urban planning strategies by transferring landscaping ideas and practices to overseas colonies. The green belt was a popular landscape practice exported by Britain onto colonial territories such as Haifa (1918-1948).[19] Spatial mechanisms like the green belt, implemented through the Haifa Bay Plan and the British "Grand Model," were used to enforce political control and civic order and extend western ideas of progress and development.[19] The Greater London Regional Planning Committee accepted the green belt concept which formed the basis of the 1938 Green Belt Act. The planning prototype demarcated open spaces, distinguished between city and countryside, limited urban growth, and created zoning divisions.[19] It was used extensively in the British colonies to facilitate British rule through the organized division of landscape and populations. [19]
Indigenous land management practices create constantly changing landscapes through the use of vegetation and natural systems, contrasting with western epistemologies of the discipline that separate ornament from function.[20] The discipline of landscape architecture favors western designs made from structured materials and geometric forms.[20] Landscape architecture history books tend to include projects that contain constructed architectural elements that persist over time, excluding many Indigenous landscape-based designs.[20]
Landscape architecture textbooks often place Indigenous peoples as a prefix to the official start of the discipline. The widely read landscape history text The Landscape of Man (1964) offers a global history of the designed landscape from past to present, featuring African and other Indigenous peoples in its discussions of Paleolithic man between 500,000 and 8,000 BCE in relation to human migration.[20] Indigenous land-management practices are described as archaeological rather than a part of contemporary practice. Gardens in Time (1980) also places Indigenous practice as prehistory at the beginning of the landscape architecture timeline. Authors John and Ray Oldham describe Aborigines of Australia as “survivors of an ancient way of life” who provide an opportunity to examine western Australia as a “meeting place of a prehistoric man.”[20]
In the late 18th century, the landscapes created by aboriginal land and fire management practices appealed to English settlers in Australia.[20] Journals from the period of early white settlement note the landscape resembling parks and popular designs in English landscape gardens of the same period.[20] In England, these designs were considered sophisticated and celebrated for the intentional sacrifice of usable land. In Australia, the park-like condition was used to justify British control, citing its emptiness and lack of productive use as a basis for the dispossession of Aboriginal people. [20]
Landscape Architects are generally required to have university or graduate education from an accredited landscape architecture degree program, which can vary in length and degree title. They learn how to create projects from scratch, such as residential or commercial planting and designing outdoor living spaces[21] they are willing to work with others to get a better outcome for the customers when doing a project; they will have to learn the basics of how to create a project on a manner of time and will require to get your license in a certain state to be allowed to work; students of Landscape Architects will learn how to interact with clients and will learn how to explain a design from scratch when giving the final project.[22]
Landscape architecture has been taught in the University of Manchester since the 1950s. The course in the Manchester School of Architecture enables students to gain various bachelor's and master's degrees, including MLPM(Hons) which is accredited by the Landscape Institute and by the Royal Town Planning Institute.[23]
In many countries, a professional institute, comprising members of the professional community, exists in order to protect the standing of the profession and promote its interests, and sometimes also regulate the practice of landscape architecture. The standard and strength of legal regulations governing landscape architecture practice varies from nation to nation, with some requiring licensure in order to practice; and some having little or no regulation. In Europe, North America, parts of South America, Australia, India, and New Zealand, landscape architecture is a regulated profession.[24]
Since 1889, with the arrival of the French architect and urbanist landscaper Carlos Thays, recommended to recreate the National Capital's parks and public gardens, it was consolidated an apprentice and training program in landscaping that eventually became a regulated profession, currently the leading academic institution is the UBA University of Buenos Aires"UBA Facultad de Arquitectura, Diseño y Urbanismo" (Faculty of Architecture, Design and Urbanism) offering a Bacherlor's degree in Urban Landscaping Design and Planning, the profession itself is regulated by the National Ministry of Urban Planning of Argentina and the Institute of the Buenos Aires Botanical Garden.[citation needed]
The Australian Institute of Landscape Architects (AILA) provides accreditation of university degrees and non-statutory professional registration for landscape architects. Once recognized by AILA, landscape architects use the title 'Registered Landscape Architect' across the six states and territories within Australia.[citation needed]
AILA's system of professional recognition is a national system overseen by the AILA National Office in Canberra. To apply for AILA Registration, an applicant usually needs to satisfy a number of pre-requisites, including university qualification, a minimum number years of practice and a record of professional experience.[25]
Landscape Architecture within Australia covers a broad spectrum of planning, design, management, and research. From specialist design services for government and private sector developments through to specialist professional advice as an expert witness.[citation needed]
In Canada, landscape architecture, like law and medicine, is a self-regulating profession pursuant to provincial statute. For example, Ontario's profession is governed by the Ontario Association of Landscape Architects pursuant to the Ontario Association of Landscape Architects Act. Landscape architects in Ontario, British Columbia, and Alberta must complete the specified components of L.A.R.E (Landscape Architecture Registration Examination) as a prerequisite to full professional standing.
Provincial regulatory bodies are members of a national organization, the Canadian Society of Landscape Architects / L'Association des Architectes Paysagistes du Canada (CSLA-AAPC), and individual membership in the CSLA-AAPC is obtained through joining one of the provincial or territorial components.[26]
ISLA (Indonesia Society of Landscape Architects) is the Indonesian society for professional landscape architects formed on 4 February 1978 and is a member of IFLA APR and IFLA World. The main aim is to increase the dignity of the professional members of landscape architects by increasing their activity role in community service, national and international development. The management of IALI consists of National Administrators who are supported by 20 Regional Administrators (Provincial level) and 3 Branch Managers at city level throughout Indonesia.[citation needed]
Landscape architecture education in Indonesia was held in 18 universities, which graduated D3, Bachelor and Magister graduates. The landscape architecture education incorporate in Association of Indonesian Landscape Architecture Education.[citation needed]
AIAPP (Associazione Italiana Architettura del Paesaggio) is the Italian association of professional landscape architects formed in 1950 and is a member of IFLA and IFLA Europe (formerly known as EFLA). AIAPP is in the process of contesting this new law which has given the Architects' Association the new title of Architects, Landscape Architects, Planners and Conservationists whether or not they have had any training or experience in any of these fields other than Architecture. In Italy, there are several different professions involved in landscape architecture:
The New Zealand Institute of Landscape Architects (NZILA) is the professional body for Landscape Architects in NZ.[27]
In April 2013, NZILA jointly with AILA, hosted the 50th International Federation of Landscape Architects (IFLA) World Congress in Auckland, New Zealand. The World Congress is an international conference where Landscape Architects from all around the globe meet to share ideas around a particular topic.[citation needed]
Within NZ, Members of NZILA when they achieve their professional standing, can use the title Registered Landscape Architect NZILA.[citation needed]
NZILA provides an education policy and an accreditation process to review education programme providers; currently there are three accredited undergraduate Landscape Architecture programmes in New Zealand. Lincoln University also has an accredited masters programme in landscape architecture.[citation needed]
Landscape architecture in Norway was established in 1919 at the Norwegian University of Life Sciences (NMBU) at Ås. The Norwegian School of Landscape Architecture at the Faculty of Landscape and Society is responsible for Europe's oldest landscape architecture education on an academic level. The departments areas include design and design of cities and places, garden art history, landscape engineering, greenery, zone planning, site development, place making and place keeping.[citation needed]
In May 1962, Joane Pim, Ann Sutton, Peter Leutscher and Roelf Botha (considered the forefathers of the profession in South Africa) established the Institute for Landscape Architects, now known as the Institute for Landscape Architecture in South Africa (ILASA).[28] ILASA is a voluntary organisation registered with the South African Council for the Landscape Architectural Profession (SACLAP).[29] It consists of three regional bodies, namely, Gauteng, KwaZula-Natal and the Western Cape. ILASA's mission is to advance the profession of landscape architecture and uphold high standards of professional service to its members, and to represent the profession of landscape architecture in any matter which may affect the interests of the members of the institute. ILASA holds the country's membership with The International Federation of Landscape Architects (IFLA).[30]
In South Africa, the profession is regulated by SACLAP, established as a statutory council in terms of Section 2 of the South African Council for the Landscape Architectural Profession Act – Act 45 of 2000. The Council evolved out of the Board of Control for Landscape Architects (BOCLASA), which functioned under the Council of Architects in terms of The Architectural Act, Act 73 of 1970. SACLAP's mission is to establish, direct, sustain and ensure a high level of professional responsibilities and ethical conduct within the art and science of landscape architecture with honesty, dignity and integrity in the broad interest of public health, safety and welfare of the community.[citation needed]
After completion of an accredited under-graduate and/or post-graduate qualification in landscape architecture at either the University of Cape Town or the University of Pretoria, or landscape technology at the Cape Peninsula University of Technology, professional registration is attained via a mandatory mentored candidacy period (minimum of two years) and sitting of the professional registration exam. After successfully completing the exam, the individual is entitled to the status of Professional Landscape Architect or Professional Landscape Technologist.[citation needed]
Architects Sweden, Sveriges Arkitekter, is the collective trade union and professional organisation for all architects, including landscape architects, in Sweden. The professional body is a member of IFLA (International Federation of Landscape Architects) as well as IFLA Europe.
As a landscape architect, anyone can become a member of Architects Sweden if they have a national or international university degree that is approved by the association. If the degree is from within the European Union, Architects Sweden approves Landscape architect educations listed by IFLA Europe. For educations outside the EU, the association makes an assessment on a statement from the Swedish Council for Higher Education (UHR).
The UK's professional body is the Landscape Institute (LI). It is a chartered body that accredits landscape professionals and university courses. At present there are fifteen accredited programmes in the UK. Membership of the LI is available to students, academics and professionals, and there are over 3,000 professionally qualified members.[citation needed]
The Institute provides services to assist members including support and promotion of the work of landscape architects; information and guidance to the public and industry about the specific expertise offered by those in the profession; and training and educational advice to students and professionals looking to build upon their experience.[citation needed]
In 2008, the LI launched a major recruitment drive entitled "I want to be a Landscape Architect" to encourage the study of Landscape Architecture. The campaign aimed to raise the profile of landscape architecture and highlight its valuable role in building sustainable communities and fighting climate change.[31]
As of July 2018, the "I want to be a Landscape Architect" initiative was replaced by a brand new careers campaign entitled #ChooseLandscape, which aims to raise awareness of landscape as a profession; improve and increase access to landscape education; and inspire young people to choose landscape as a career.[32] This new campaign includes other landscape-related professions such as landscape management, landscape planning, landscape science and urban design.[33]

In the United States, landscape architecture is regulated by individual state governments. For a landscape architect, obtaining licensure requires advanced education and work experience, plus passage of the national examination called the Landscape Architect Registration Examination (L.A.R.E.). Licensing is overseen at the national level by the Council of Landscape Architectural Registration Boards (CLARB). Several states require passage of a state exam as well.
Landscape architecture has been identified as an above-average growth profession by the US Bureau of Labor Statistics and was listed in U.S. News & World Report's list of Best Jobs to Have in 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 and 2010.[34] The national trade association for United States landscape architects is the American Society of Landscape Architects. Frederick Law Olmsted, who designed Central Park in New York City, is known as the "father of American landscape architecture".[35]
There are important distinctions between planners and allied professionals and between planning and related fields. Planners approach problems comprehensively, have a long-range perspective, and deal with unique place-based issues. Although people in related professions (e.g., law, architecture, landscape architecture, engineering, real estate development, etc.) and disciplines (humanities, psychology, etc.) often work with planners, they do not necessarily have the same knowledge base, skillset, and approach.
Workers were great, no problem they did what was required, but the representative of your company mislead me on what was to be done, I showed pictures from a competitor landscaper, representative stated he could bet there , , . price, but since it wasn’t in contract, I was left with uncomplicated backyard , working with owner at present, so he’s been outstanding working on this situation, as amount of rock was way off and the owner did increase the amount substantially to finish the front yard. another landscaper under contract to finish the backyard. Would like to add a comment the manger/owner of Las Vegas yard n block stands behind his words and helped me tremendously on finishing up the backyard,
Eric and team did an amazing job. They worked with me for months while I got HOA approval for the project. Once they began working they were great, going over everything in detail and making sure things were perfect. This project included wall repair, stucco and paint repair, paver and turf installation. Extremely satisfied with this experience.
Chris, the design consultant, Dave the production manager, along with their install team Opulent were affordable, upfront with costs, efficient and professional. Attached are some before and after pictures. Highly recommend their services.
My initial contact was with Ray, whom did an excellent job giving me an estimate on what I wanted done in my small yard and walkway., the guys that came out and did the work were superior. They did an excellent job. I’m very pleased with this company. I will highly recommend them to family and friends, and I will be using them in the near future for other little projects.
We recently had a very positive experience with Rock N Block for our fence replacement. The entire process went smoothly and exceeded our expectations. Harvey and his team were incredibly professional and communicative throughout the project providing much-needed assurance and peace of mind. The crew was punctual and maintained a diligent and respectful attitude that made the experience pleasant. The crew finished the project ahead of schedule, and the quality of their work is impressive; our new wall looks great! We recommend Rock N Block for any fencing needs and look forward to working with them again. Thank you, Harvey and crew, for a job well done!
Workers were great, no problem they did what was required, but the representative of your company mislead me on what was to be done, I showed pictures from a competitor landscaper, representative stated he could bet there , , . price, but since it wasn’t in contract, I was left with uncomplicated backyard , working with owner at present, so he’s been outstanding working on this situation, as amount of rock was way off and the owner did increase the amount substantially to finish the front yard. another landscaper under contract to finish the backyard. Would like to add a comment the manger/owner of Las Vegas yard n block stands behind his words and helped me tremendously on finishing up the backyard,
My initial contact was with Ray, whom did an excellent job giving me an estimate on what I wanted done in my small yard and walkway., the guys that came out and did the work were superior. They did an excellent job. I’m very pleased with this company. I will highly recommend them to family and friends, and I will be using them in the near future for other little projects.
Chris, the design consultant, Dave the production manager, along with their install team Opulent were affordable, upfront with costs, efficient and professional. Attached are some before and after pictures. Highly recommend their services.
Eric and team did an amazing job. They worked with me for months while I got HOA approval for the project. Once they began working they were great, going over everything in detail and making sure things were perfect. This project included wall repair, stucco and paint repair, paver and turf installation. Extremely satisfied with this experience.