

"landscape edging Las Vegas","Unlock sustainable benefits through landscape edging Las Vegas.
"landscape curbing Las Vegas","Open the door to landscape curbing Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape curbing Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Expert Landscaping Services in Las Vegas Nevada. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape drainage Las Vegas","Enhance curb appeal via landscape drainage Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape drainage Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape grading Las Vegas","Embrace the possibilities with landscape grading Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape grading Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape soil Las Vegas","Embark on a journey toward landscape soil Las Vegas. Top Landscaping in Las Vegas Nevada. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape soil Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape mulch Las Vegas","Open the door to landscape mulch Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape mulch Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape rocks Las Vegas","Experience unparalleled value in landscape rocks Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape rocks Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape boulders Las Vegas","Open the door to landscape boulders Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape boulders Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape trees Las Vegas","Immerse yourself in landscape trees Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions.


"landscape shrubs Las Vegas","Combine style and function in landscape shrubs Las Vegas. Nevada Las Vegas Landscaping Services. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape shrubs Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape flowers Las Vegas","Embark on a journey toward landscape flowers Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape flowers Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape turf Las Vegas","Open the door to landscape turf Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape turf Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape lawn care Las Vegas","Embrace the possibilities with landscape lawn care Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape lawn care Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape pest control Las Vegas","Explore a new dimension of landscape pest control Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape pest control Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape fertilization Las Vegas","Achieve remarkable results with landscape fertilization Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape fertilization Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."


"landscape trimming Las Vegas","Immerse yourself in landscape trimming Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape trimming Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape pruning Las Vegas","Embrace the possibilities with landscape pruning Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape pruning Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape clean up Las Vegas","Explore a new dimension of landscape clean up Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape clean up Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape debris removal Las Vegas","Unleash the full beauty of landscape debris removal Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape debris removal Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape design ideas Las Vegas","Combine style and function in landscape design ideas Las Vegas. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape design ideas Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."
"landscape inspiration Las Vegas","Reinvent your exterior with landscape inspiration Las Vegas. Many companies focus on resource-saving techniques, including drip irrigation and drought-resistant plants. Professionals in this region craft visually appealing, water-conscious environments well-suited to desert conditions. By blending native plants, rock formations, and efficient irrigation, you can establish a long-lasting outdoor retreat. Customers can enjoy sustainable, vibrant spaces that also reduce water usage and routine upkeep. Whether you prefer minimalistic rock gardens or lush greenery, skilled experts can tailor designs to your taste. Thoughtful lighting and smart controllers help create an appealing ambiance while maximizing efficiency. Simple additions, like seating areas or decorative pavers, can turn unused corners into welcoming havens. Incorporating region-specific materials leads to seamless integration with the surrounding desert environment. Our proven expertise in landscape inspiration Las Vegas ensures that each project receives a tailored approach. Ultimately, careful planning and professional expertise guarantee outstanding outdoor transformations."

|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2024)
|




Artificial turf is a surface of synthetic fibers made to look like natural grass, used in sports arenas, residential lawns and commercial applications that traditionally use grass. It is much more durable than grass and easily maintained without irrigation or trimming, although periodic cleaning is required. Stadiums that are substantially covered and/or at high latitudes often use artificial turf, as they typically lack enough sunlight for photosynthesis and substitutes for solar radiation are prohibitively expensive and energy-intensive. Disadvantages include increased risk of injury especially when used in athletic competition, as well as health and environmental concerns about the petroleum and toxic chemicals used in its manufacture.
Artificial turf first gained substantial attention in 1966, when ChemGrass was installed in the year-old Astrodome, developed by Monsanto and rebranded as AstroTurf, now a generic trademark (registered to a new owner) for any artificial turf.
The first-generation system of shortpile fibers without infill of the 1960s has largely been replaced by two more. The second features longer fibers and sand infill and the third adds recycled crumb rubber to the sand. Compared to earlier systems, modern artificial turf more closely resembles grass in appearance and is also considered safer for athletic competition. However, it is still not widely considered to be equal to grass. Sports clubs, leagues, unions and individual athletes have frequently spoken out and campaigned against it, while local governments have enacted and enforced laws restricting and/or banning its use.
David Chaney, who moved to Raleigh, North Carolina, in 1960 and later served as Dean of the North Carolina State University College of Textiles, headed the team of Research Triangle Park researchers who created the first notable artificial turf. That accomplishment led Sports Illustrated to declare Chaney as the man "responsible for indoor major league baseball and millions of welcome mats."
Artificial turf was first installed in 1964 on a recreation area at the Moses Brown School in Providence, Rhode Island.[1] The material came to public prominence in 1966, when AstroTurf was installed in the Astrodome in Houston, Texas.[1] The state-of-the-art indoor stadium had attempted to use natural grass during its initial season in 1965, but this failed miserably and the field conditions were grossly inadequate during the second half of the season, with the dead grass painted green. Due to a limited supply of the new artificial grass, only the infield was installed before the Houston Astros' home opener in April 1966; the outfield was installed in early summer during an extended Astros road trip and first used after the All-Star Break in July.
The use of AstroTurf and similar surfaces became widespread in the U.S. and Canada in the early 1970s, installed in both indoor and outdoor stadiums used for baseball and football. More than 11,000 artificial turf playing fields have been installed nationally.[2] More than 1,200 were installed in the U.S. in 2013 alone, according to the industry group the Synthetic Turf Council.[2]


Artificial turf was first used in Major League Baseball in the Houston Astrodome in 1966, replacing the grass field used when the stadium opened a year earlier. Even though the grass was specifically bred for indoor use, the dome's semi-transparent Lucite ceiling panels, which had been painted white to cut down on glare that bothered the players, did not pass enough sunlight to support the grass. For most of the 1965 season, the Astros played on green-painted dirt and dead grass.
The solution was to install a new type of artificial grass on the field, ChemGrass, which became known as AstroTurf. Given its early use, the term astroturf has since been genericized as a term for any artificial turf.[3] Because the supply of AstroTurf was still low, only a limited amount was available for the first home game. There was not enough for the entire outfield, but there was enough to cover the traditional grass portion of the infield. The outfield remained painted dirt until after the All-Star Break. The team was sent on an extended road trip before the break, and on 19 July 1966, the installation of the outfield portion of AstroTurf was completed.
The Chicago White Sox became the first team to install artificial turf in an outdoor stadium, as they used it only in the infield and adjacent foul territory at Comiskey Park from 1969 through 1975.[4] Artificial turf was later installed in other new multi-purpose stadiums such as Pittsburgh's Three Rivers Stadium, Philadelphia's Veterans Stadium, and Cincinnati's Riverfront Stadium. Early AstroTurf baseball fields used the traditional all-dirt path, but starting in 1970 with Cincinnati's Riverfront Stadium,[5] teams began using the "base cutout" layout on the diamond, with the only dirt being on the pitcher's mound, batter's circle, and in a five-sided diamond-shaped "sliding box" around each base. With this layout, a painted arc would indicate where the edge of the outfield grass would normally be, to assist fielders in positioning themselves properly. The last stadium in MLB to use this configuration was Rogers Centre in Toronto, when they switched to an all-dirt infield (but keeping the artificial turf) for the 2016 season.[6][7]

The biggest difference in play on artificial turf was that the ball bounced higher than on real grass and also traveled faster, causing infielders to play farther back than they would normally so that they would have sufficient time to react. The ball also had a truer bounce than on grass so that on long throws fielders could deliberately bounce the ball in front of the player they were throwing to, with the certainty that it would travel in a straight line and not be deflected to the right or left. The biggest impact on the game of "turf", as it came to be called, was on the bodies of the players. The artificial surface, which was generally placed over a concrete base, had much less give to it than a traditional dirt and grass field did, which caused more wear-and-tear on knees, ankles, feet, and the lower back, possibly even shortening the careers of those players who played a significant portion of their games on artificial surfaces. Players also complained that the turf was much hotter than grass, sometimes causing the metal spikes to burn their feet or plastic ones to melt. These factors eventually provoked a number of stadiums, such as the Kansas City Royals' Kauffman Stadium, to switch from artificial turf back to natural grass.
In 2000, St. Petersburg's Tropicana Field became the first MLB field to use a third-generation artificial surface, FieldTurf. All other remaining artificial turf stadiums were either converted to third-generation surfaces or were replaced entirely by new natural grass stadiums. In a span of 13 years, between 1992 and 2005, the National League went from having half of its teams using artificial turf to all of them playing on natural grass. With the replacement of Minneapolis's Hubert H. Humphrey Metrodome by Target Field in 2010, only two MLB stadiums used artificial turf from 2010 through 2018: Tropicana Field and Toronto's Rogers Centre. This number grew to three when the Arizona Diamondbacks switched Chase Field to artificial turf for the 2019 season; the stadium had grass from its opening in 1998 until 2018, but the difficulty of maintaining the grass in the stadium, which has a retractable roof and is located in a desert city, was cited as the reason for the switch.[8] In 2020, Miami's Marlins Park (now loanDepot Park) also switched to artificial turf for similar reasons, while the Texas Rangers' new Globe Life Field was opened with an artificial surface, as it is also a retractable roof ballpark in a hot weather city; this puts the number of teams using synthetic turf in MLB at five as of 2023.
The first professional American football team to play on artificial turf was the Houston Oilers, then part of the American Football League, who moved into the Astrodome in 1968, which had installed AstroTurf two years prior. In 1969, the University of Pennsylvania's Franklin Field in Philadelphia, at the time also home field of the Philadelphia Eagles, switched from grass to AstroTurf, making it the first National Football League stadium to use artificial turf.
In 2002, CenturyLink Field, originally planned to have a natural grass field, was instead surfaced with FieldTurf upon positive reaction from the Seattle Seahawks when they played on the surface at their temporary home of Husky Stadium during the 2000 and 2001 seasons. This would be the first of a leaguewide trend taking place over the next several seasons that would not only result in teams already using artificial surfaces for their fields switching to the new FieldTurf or other similar surfaces but would also see several teams playing on grass adopt a new surface. (The Indianapolis Colts' RCA Dome and the St. Louis Rams' Edward Jones Dome were the last two stadiums in the NFL to replace their first-generation AstroTurf surfaces for next-generation ones after the 2004 season). For example, after a three-year experiment with a natural surface, Giants Stadium went to FieldTurf for 2003, while M&T Bank Stadium added its own artificial surface the same year (it has since been removed and replaced with a natural surface, which the stadium had before installing the turf). Later examples include Paul Brown Stadium (now Paycor Stadium), which went from grass to turf in 2004; Gillette Stadium, which made the switch in 2006;[9] and NRG Stadium, which did so in 2015. As of 2021, 14 NFL fields out of 30 are artificial. NFL players overwhelmingly prefer natural grass over synthetic surfaces, according to a league survey conducted in 2010. When asked, "Which surface do you think is more likely to shorten your career?", 90% responded artificial turf.[10] When players were asked "Is the Turf versus Grass debate overblown or a real concern"[11] in an anonymous player survey, 83% believe it is a real concern while 12.3% believe it is overblown.
Following receiver Odell Beckham Jr.'s injury during Super Bowl LVI, other NFL players started calling for turf to be banned since the site of the game, SoFi Stadium, was a turf field.[12]
Arena football is played indoors on the older short-pile artificial turf.
The first professional Canadian football stadium to use artificial turf was Empire Stadium in Vancouver, British Columbia, then home of the Canadian Football League's BC Lions, which installed 3M TartanTurf in 1970. Today, eight of the nine stadiums in the CFL currently use artificial turf, largely because of the harsh weather conditions in the latter-half of the season. The only one that does not is BMO Field in Toronto, which initially had an artificial pitch and has been shared by the CFL's Toronto Argonauts since 2016 (part of the endzones at that stadium are covered with artificial turf).[13] The first stadium to use the next-generation surface was Ottawa's Frank Clair Stadium (now TD Place Stadium), which the Ottawa Renegades used when they began play in 2002. The Saskatchewan Roughriders' Taylor Field was the only major professional sports venue in North America to use a second-generation artificial playing surface, Omniturf, which was used from 1988 to 2000, followed by AstroTurf from 2000 to 2007 and FieldTurf from 2007 to its 2016 closure.[14]
Some cricket pitches are made of synthetic grass[15] or of a hybrid of mostly natural and some artificial grass, with these "hybrid pitches" having been implemented across several parts of the United Kingdom[16] and Australia.[17] The first synthetic turf cricket field in the USA was opened in Fremont, California in 2016.[18]
The introduction of synthetic surfaces has significantly changed the sport of field hockey. Since being introduced in the 1970s, competitions in western countries are now mostly played on artificial surfaces. This has increased the speed of the game considerably and changed the shape of hockey sticks to allow for different techniques, such as reverse stick trapping and hitting.
Field hockey artificial turf differs from artificial turf for other sports, in that it does not try to reproduce a grass feel, being made of shorter fibers. This allows the improvement in speed brought by earlier artificial turfs to be retained. This development is problematic for areas which cannot afford to build an extra artificial field for hockey alone. The International Hockey Federation and manufacturers are driving research in order to produce new fields that will be suitable for a variety of sports.
The use of artificial turf in conjunction with changes in the game's rules (e.g., the removal of offside, introduction of rolling substitutes and the self-pass, and to the interpretation of obstruction) have contributed significantly to change the nature of the game, greatly increasing the speed and intensity of play as well as placing far greater demands on the conditioning of the players.


Some association football clubs in Europe installed synthetic surfaces in the 1980s, which were called "plastic pitches" (often derisively) in countries such as England. There, four professional club venues had adopted them; Queens Park Rangers's Loftus Road (1981–1988), Luton Town's Kenilworth Road (1985–1991), Oldham Athletic's Boundary Park (1986–1991) and Preston North End's Deepdale (1986–1994). QPR had been the first team to install an artificial pitch at their stadium in 1981, but were the first to remove it when they did so in 1988. Artificial pitches were banned from top-flight (then First Division) football in 1991, forcing Oldham Athletic to remove their artificial pitch after their promotion to the First Division in 1991, while then top-flight Luton Town also removed their artificial pitch at the same time. The last Football League team to have an artificial pitch in England was Preston North End, who removed their pitch in 1994 after eight years in use. Artificial pitches were banned from the top four divisions from 1995.
Artificial turf gained a bad reputation[neutrality is disputed] globally, with fans and especially with players. The first-generation artificial turf surfaces were carpet-like in their look and feel, and thus, a far harder surface than grass and soon became known[by whom?] as an unforgiving playing surface that was prone to cause more injuries, and in particular, more serious joint injuries, than would comparatively be suffered on a grass surface. This turf was also regarded as aesthetically unappealing to many fans[weasel words].
In 1981, London football club Queens Park Rangers dug up its grass pitch and installed an artificial one. Others followed, and by the mid-1980s there were four artificial surfaces in operation in the English league. They soon became a national joke: the ball pinged round like it was made of rubber, the players kept losing their footing, and anyone who fell over risked carpet burns. Unsurprisingly, fans complained that the football was awful to watch and, one by one, the clubs returned to natural grass.[19]
In the 1990s, many North American soccer clubs also removed their artificial surfaces and re-installed grass, while others moved to new stadiums with state-of-the-art grass surfaces that were designed to withstand cold temperatures where the climate demanded it. The use of artificial turf was later banned by FIFA, UEFA and by many domestic football associations, though, in recent years,[when?] both governing bodies have expressed resurrected interest in the use of artificial surfaces in competition, provided that they are FIFA Recommended. UEFA has now been heavily involved in programs to test artificial turf, with tests made in several grounds meeting with FIFA approval. A team of UEFA, FIFA and German company Polytan conducted tests in the Stadion Salzburg Wals-Siezenheim in Salzburg, Austria which had matches played on it in UEFA Euro 2008. It is the second FIFA 2 Star approved artificial turf in a European domestic top flight, after Dutch club Heracles Almelo received the FIFA certificate in August 2005.[20] The tests were approved.[21]
FIFA originally launched its FIFA Quality Concept in February 2001. UEFA announced that starting from the 2005–06 season, approved artificial surfaces were to be permitted in their competitions.
A full international fixture for the 2008 European Championships was played on 17 October 2007 between England and Russia on an artificial surface, which was installed to counteract adverse weather conditions, at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow.[22][23] It was one of the first full international games to be played on such a surface approved by FIFA and UEFA. The latter ordered the 2008 European Champions League final hosted in the same stadium in May 2008 to place on grass, so a temporary natural grass field was installed just for the final.
UEFA stressed that artificial turf should only be considered an option where climatic conditions necessitate.[24] One Desso "hybrid grass" product incorporates both natural grass and artificial elements.[25]
In June 2009, following a match played at Estadio Ricardo Saprissa in Costa Rica, American national team manager Bob Bradley called on FIFA to "have some courage" and ban artificial surfaces.
FIFA designated a star system for artificial turf fields that have undergone a series of tests that examine quality and performance based on a two star system.[26] Recommended two-star fields may be used for FIFA Final Round Competitions as well as for UEFA Europa League and Champions League matches.[27] There are currently 130 FIFA Recommended 2-Star installations in the world.[28]
In 2009, FIFA launched the Preferred Producer Initiative to improve the quality of artificial football turf at each stage of the life cycle (manufacturing, installation and maintenance).[29] Currently, there are five manufacturers that were selected by FIFA: Act Global, Limonta, Desso, GreenFields, and Edel Grass. These firms have made quality guarantees directly to FIFA and have agreed to increased research and development.
In 2010, Estadio Omnilife with an artificial turf opened in Guadalajara to be the new home of Chivas, one of the most popular teams in Mexico. The owner of Chivas, Jorge Vergara, defended the reasoning behind using artificial turf because the stadium was designed to be "environment friendly and as such, having grass would result [in] using too much water."[30] Some players criticized the field, saying its harder surface caused many injuries. When Johan Cruyff became the adviser of the team, he recommended the switch to natural grass, which the team did in 2012.[31]
In November 2011, it was reported that a number of English football clubs were interested in using artificial pitches again on economic grounds.[32] As of January 2020, artificial pitches are not permitted in the Premier League or Football League but are permitted in the National League and lower divisions. Bromley are an example of an English football club who currently use a third-generation artificial pitch.[33] In 2018, Sutton United were close to achieving promotion to the Football League and the debate in England about artificial pitches resurfaced again. It was reported that, if Sutton won promotion, they would subsequently be demoted two leagues if they refused to replace their pitch with natural grass.[34] After Harrogate Town's promotion to the Football League in 2020, the club was obliged to install a natural grass pitch at Wetherby Road;[35] and after winning promotion in 2021 Sutton Utd were also obliged to tear up their artificial pitch and replace it with grass, at a cost of more than £500,000.[36] Artificial pitches are permitted in all rounds of the FA Cup competition.
The 2015 FIFA Women's World Cup took place entirely on artificial surfaces, as the event was played in Canada, where almost all of the country's stadiums use artificial turf due to climate issues. This plan garnered criticism from players and fans, some believing the artificial surfaces make players more susceptible to injuries. Over fifty of the female athletes protested against the use of artificial turf on the basis of gender discrimination.[37][38] Australia winger Caitlin Foord said that after playing 90 minutes there was no difference to her post-match recovery – a view shared by the rest of the squad. The squad spent much time preparing on the surface and had no problems with its use in Winnipeg. "We've been training on [artificial] turf pretty much all year so I think we're kind of used to it in that way ... I think grass or turf you can still pull up sore after a game so it's definitely about getting the recovery in and getting it right", Foord said.[39] A lawsuit was filed on 1 October 2014 in an Ontario tribunal court by a group of women's international soccer players against FIFA and the Canadian Soccer Association and specifically points out that in 1994 FIFA spent $2 million to plant natural grass over artificial turf in New Jersey and Detroit.[40] Various celebrities showed their support for the women soccer players in defense of their lawsuit, including actor Tom Hanks, NBA player Kobe Bryant and U.S. men's soccer team keeper Tim Howard. Even with the possibility of boycotts, FIFA's head of women's competitions, Tatjana Haenni, made it clear that "we play on artificial turf and there's no Plan B."[41][42]
The first stadium to use artificial turf in Brazil was Atlético Paranaense's Arena da Baixada in 2016. In 2020, the administration of Allianz Parque, home of Sociedade Esportiva Palmeiras, started the implementation of the second artificial pitch in the country.[43]
Rugby union also uses artificial surfaces at a professional level. Infill fields are used by English Premiership Rugby teams Gloucester, Newcastle Falcons, Saracens F.C. and the now defunct Worcester Warriors, as well as United Rugby Championship teams Cardiff, Edinburgh and Glasgow Warriors. Some fields, including Twickenham Stadium, have incorporated a hybrid field, with grass and synthetic fibers used on the surface. This allows for the field to be much more hard wearing, making it less susceptible to weather conditions and frequent use.
Carpet has been used as a surface for indoor tennis courts for decades, though the first carpets used were more similar to home carpets than a synthetic grass. After the introduction of AstroTurf, it came to be used for tennis courts, both indoor and outdoor, though only a small minority of courts use the surface.[44][45] Both infill and non-infill versions are used, and are typically considered medium-fast to fast surfaces under the International Tennis Federation's classification scheme.[44] A distinct form found in tennis is an "artificial clay" surface,[44] which seeks to simulate a clay court by using a very short pile carpet with an infill of the same loose aggregate used for clay courts that rises above the carpet fibers.[44]
Tennis courts such as Wimbledon are considering using an artificial hybrid grass to replace their natural lawn courts. Such systems incorporate synthetic fibers into natural grass to create a more durable surface on which to play.[46] Such hybrid surfaces are currently used for some association football stadiums, including Wembley Stadium.
Synthetic turf can also be used in the golf industry, such as on driving ranges, putting greens and even in some circumstances tee boxes. For low budget courses, particularly those catering to casual golfers, synthetic putting greens offer the advantage of being a relatively cheap alternative to installing and maintaining grass greens, but are much more similar to real grass in appearance and feel compared to sand greens which are the traditional alternative surface. Because of the vast areas of golf courses and the damage from clubs during shots, it is not feasible to surface fairways with artificial turf.
Artificial grass is used to line the perimeter of some sections of some motor circuits, and offers less grip than some other surfaces.[47] It can pose an obstacle to drivers if it gets caught on their car.[48]

Since the early 1990s, the use of synthetic grass in the more arid western states of the United States has moved beyond athletic fields to residential and commercial landscaping.[49] New water saving programs, as of 2019, which grant rebates for turf removal, do not accept artificial turf as replacement and require a minimum of plants.[50][51]
The use of artificial grass for convenience sometimes faces opposition: Legislation frequently seeks to preserve natural gardens and fully water permeable surfaces, therefore restricting the use of hardscape and plantless areas, including artificial turf. In several locations in different countries, homeowners have been fined, ordered to remove artificial turf and/or had to defend themselves in courts. Many of these restrictions can be found in local bylaws and ordinances. These not always applied in a consistent manner,[52][53][54] especially in municipalities that utilize a complaint-based model for enforcing local laws.
Sunlight reflections from nearby windows can cause artificial turf to melt. This can be avoided by adding perforated vinyl privacy window film adhesive to the outside of the window causing the reflection.
Artificial turf has been used at airports.[55] Here it provides several advantages over natural turf – it does not support wildlife, it has high visual contrast with runways in all seasons, it reduces foreign object damage (FOD) since the surface has no rocks or clumps, and it drains well.[56]
Some artificial turf systems allow for the integration of fiber-optic fibers into the turf. This would allow for runway lighting to be embedded in artificial landing surfaces for aircraft (or lighting or advertisements to be directly embedded in a playing surface).[57]
Artificial turf is commonly used for tanks containing octopusses, in particular the Giant Pacific octopus since it is a reliable way to prevent the octopusses from escaping their tank, as they prevent the suction cups on the tentacles from getting a tight seal.[58]
The first major academic review of the environmental and health risks and benefits of artificial turf was published in 2014;[59] it was followed by extensive research on possible risks to human health, but holistic analyses of the environmental footprint of artificial turf compared with natural turf only began to emerge in the 2020s,[60][61] and frameworks to support informed policymaking were still lacking.[62][63] Evaluating the relative environmental footprints of natural and artificial turf is complex, with outcomes depending on a wide range of factors, including (to give the example of a sports field):[59]
Artificial turf has been shown to contribute to global warming by absorbing significantly more radiation than living turf and, to a lesser extent, by displacing living plants that could sequester carbon dioxide through photosynthesis;[64] a study at New Mexico State University found that in that environment, water-cooling of artificial turf can demand as much water as natural turf.[65] However, a 2022 study that used real-world data to model a ten-year-life-cycle environmental footprint for a new natural-turf soccer field compared with an artificial-turf field found that the natural-turf field contributed twice as much to global warming as the artificial one (largely due to a more resource-intensive construction phase), while finding that the artificial turf would likely cause more pollution of other kinds. It promoted improvements to usual practice such as the substitution of cork for rubber in artificial pitches and more drought-resistant grasses and electric mowing in natural ones.[60] In 2021, a Zurich University of Applied Sciences study for the city of Zurich, using local data on extant pitches, found that, per hour of use, natural turf had the lowest environmental footprint, followed by artificial turf with no infill, and then artificial turf using an infill (e.g. granulated rubber). However, because it could tolerate more hours of use, unfilled artificial turf often had the lowest environmental footprint in practice, by reducing the total number of pitches required. The study recommended optimising the use of existing pitches before building new ones, and choosing the best surface for the likely intensity of use.[61] Another suggestion is the introduction of green roofs to offset the conversion of grassland to artificial turf.[66]
Contrary to popular belief, artificial turf is not maintenance free. It requires regular maintenance, such as raking and patching, to keep it functional and safe.[67]
Some artificial turf uses infill such as silicon sand, but most uses granulated rubber, referred to as "crumb rubber". Granulated rubber can be made from recycled car tires and may carry heavy metals, PFAS chemicals, and other chemicals of environmental concern. The synthetic fibers of artificial turf are also subject to degradation. Thus chemicals from artificial turfs leach into the environment, and artificial turf is a source of microplastics pollution and rubber pollution in air, fresh-water, sea and soil environments.[68][69][70][71][72][73][59][excessive citations] In Norway, Sweden, and at least some other places, the rubber granulate from artificial turf infill constitutes the second largest source of microplastics in the environment after the tire and road wear particles that make up a large portion of the fine road debris.[74][75][76] As early as 2007, Environment and Human Health, Inc., a lobby-group, proposed a moratorium on the use of ground-up rubber tires in fields and playgrounds based on health concerns;[77] in September 2022, the European Commission made a draft proposal to restrict the use of microplastic granules as infill in sports fields.[78]
What is less clear is how likely this pollution is in practice to harm humans or other organisms and whether these environmental costs outweigh the benefits of artificial turf, with many scientific papers and government agencies (such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency) calling for more research.[2] A 2018 study published in Water, Air, & Soil Pollution analyzed the chemicals found in samples of tire crumbs, some used to install school athletic fields, and identified 92 chemicals only about half of which had ever been studied for their health effects and some of which are known to be carcinogenic or irritants. It stated "caution would argue against use of these materials where human exposure is likely, and this is especially true for playgrounds and athletic playing fields where young people may be affected".[79] Conversely, a 2017 study in Sports Medicine argued that "regular physical activity during adolescence and early adulthood helps prevent cancer later in life. Restricting the use or availability of all-weather year-round synthetic fields and thereby potentially reducing exercise could, in the long run, actually increase cancer incidence, as well as cardiovascular disease and other chronic illnesses."[80]
The possibility that carcinogenic substances in artificial turf could increase risks of human cancer (the artificial turf–cancer hypothesis) gained a particularly high profile in the first decades of the twenty-first century and attracted extensive study, with scientific reports around 2020 finding cancer-risks in modern artificial turf negligible.[81][82][83][84] But concerns have extended to other human-health risks, such as endocrine disruption that might affect early puberty, obesity, and children's attention spans.[85][86][87][88] Potential harm to fish[70] and earthworm[89] populations has also been shown.
A study for the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection analyzed lead and other metals in dust kicked into the air by physical activity on five artificial turf fields. The results suggest that even low levels of activity on the field can cause particulate matter containing these chemicals to get into the air where it can be inhaled and be harmful. The authors state that since no level of lead exposure is considered safe for children, "only a comprehensive mandated testing of fields can provide assurance that no health hazard on these fields exists from lead or other metals used in their construction and maintenance."[90]
A number of health and safety concerns have been raised about artificial turf.[2] Friction between skin and older generations of artificial turf can cause abrasions and/or burns to a much greater extent than natural grass.[91] Artificial turf tends to retain heat from the sun and can be much hotter than natural grass with prolonged exposure to the sun.[92]
There is some evidence that periodic disinfection of artificial turf is required as pathogens are not broken down by natural processes in the same manner as natural grass. Despite this, a 2006 study suggests certain microbial life is less active in artificial turf.[91]
There is evidence showing higher rates of player injury on artificial turf. By November 1971, the injury toll on first-generation artificial turf had reached a threshold that resulted in congressional hearings by the House subcommittee on commerce and finance.[93][94][95] In a study performed by the National Football League Injury and Safety Panel, published in the October 2012 issue of the American Journal of Sports Medicine, Elliott B. Hershman et al. reviewed injury data from NFL games played between 2000 and 2009, finding that "the injury rate of knee sprains as a whole was 22% higher on FieldTurf than on natural grass. While MCL sprains did not occur at a rate significantly higher than on grass, rates of ACL sprains were 67% higher on FieldTurf."[96] Metatarsophalangeal joint sprain, known as "turf toe" when the big toe is involved, is named from the injury being associated with playing sports on rigid surfaces such as artificial turf and is a fairly common injury among professional American football players. Artificial turf is a harder surface than grass and does not have much "give" when forces are placed on it.[97]
This sense of the word has come to be frequently used as a generic term for any artificial turf (in the same way that other brand names have been genericized, such as xerox). When used this way, it's often seen in lowercase (astroturf).
It was the first stadium to include dirt sliding pits around each base, something that has become standard in every turf baseball field built since.
cite web: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)In 1988, the Roughriders replaced the first artificial turf with a new type of system called OmniTurf. Unlike AstroTurf, OmniTurf was an inlay turf system, which relied on 300 tons of sand to hold it in place (rather than the traditional glued-down system). Over the years, a number of problems occurred with this system and it eventually became necessary to replace it prior to its usable age being reached.
The major concerns stem from the infill material that is typically derived from scrap tires. Tire rubber crumb contains a range of organic contaminants and heavy metals that can volatilize into the air and/or leach into the percolating rainwater, thereby posing a potential risk to the environment and human health.
Microplastics are increasingly seen as an environmental problem of global proportions. While the focus to date has been on microplastics in the ocean and their effects on marine life, microplastics in soils have largely been overlooked. Researchers are concerned about the lack of knowledge regarding potential consequences of microplastics in agricultural landscapes from application of sewage sludge.
researchers have ranked the sources of microplastic particles by size. The amount of microplastic particles emitted by traffic is estimated to 13 500 tonnes per year. Artificial turf ranks as the second largest source of emissions and is responsible for approximately 2300-3900 tonnes per year.
cite journal: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)cite journal: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)![]() This article incorporates text by National Center for Health Research available under the CC BY-SA 3.0 license. The text and its release have been received by the Wikimedia Volunteer Response Team
This article incorporates text by National Center for Health Research available under the CC BY-SA 3.0 license. The text and its release have been received by the Wikimedia Volunteer Response Team
.
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2016)
|

Landscape design is an independent profession and a design and art tradition, practiced by landscape designers, combining nature and culture. In contemporary practice, landscape design bridges the space between landscape architecture and garden design.[1]
Landscape design focuses on both the integrated master landscape planning of a property and the specific garden design of landscape elements and plants within it. The practical, aesthetic, horticultural, and environmental sustainability are also components of landscape design, which is often divided into hardscape design and softscape design. Landscape designers often collaborate with related disciplines such as architecture, civil engineering, surveying, landscape contracting, and artisan specialties.
Design projects may involve two different professional roles: landscape design and landscape architecture.
There can be a significant overlap of talent and skill between the two roles, depending on the education, licensing, and experience of the professional. Both landscape designers and landscape architects practice landscape design.[2]

The landscape design phase consists of research, gathering ideas, and setting a plan. Design factors include objective qualities such as: climate and microclimates; topography and orientation, site drainage and groundwater recharge; municipal and resource building codes; soils and irrigation; human and vehicular access and circulation; recreational amenities (i.e., sports and water); furnishings and lighting; native plant habitat botany when present; property safety and security; construction detailing; and other measurable considerations.
Design factors also include subjective qualities such as genius loci (the special site qualities to emphasize); client's needs and preferences; desirable plants and elements to retain on site, modify, or replace, and that may be available for borrowed scenery from beyond; artistic composition from perspectives of both looking upon and observing from within; spatial development and definition – using lines, sense of scale, and balance and symmetry; plant palettes; and artistic focal points for enjoyment. There are innumerable other design factors and considerations brought to the complex process of designing a garden that is beautiful, well-functioning, and that thrives over time.
The up-and-coming practice of online landscape design allows professional landscapers to remotely design and plan sites through manipulation of two-dimensional images without ever physically visiting the location. Due to the frequent lack of non-visual, supplementary data such as soil assessments and pH tests, online landscaping necessarily must focus on incorporating only plants which are tolerant across many diverse soil conditions.

Historically, landscape designers trained by apprenticing—such as André Le Nôtre, who apprenticed with his father before designing the Gardens of Versailles—to accomplished masters in the field, with the titular name varying and reputation paramount for a career. The professional section of garden designers in Europe and the Americas went by the name "Landscape Gardener". In the 1890s, the distinct classification of landscape architect was created, with educational and licensing test requirements for using the title legally. Beatrix Farrand, the sole woman in the founding group, refused the title preferring Landscape Gardener. Matching the client and technical needs of a project, and the appropriate practitioner with talent, legal qualifications, and experienced skills, surmounts title nomenclature.[citation needed]
Institutional education in landscape design appeared in the early 20th century. Over time it became available at various levels. Ornamental horticulture programs with design components are offered at community college and universities within schools of agriculture or horticulture, with some beginning to offer garden or landscape design certificates and degrees. Departments of landscape architecture are located within university schools of architecture or environmental design, with undergraduate and graduate degrees offered. Specialties and minors are available in horticultural botany, horticulture, natural resources, landscape engineering, construction management, fine and applied arts, and landscape design history. Traditionally, hand-drawn drawings documented the design and position of features for construction, but Landscape design software is frequently used now.[citation needed]
Other routes of training are through informal apprenticeships with practicing landscape designers, landscape architects, landscape contractors, gardeners, nurseries and garden centers, and docent programs at botanical and public gardens. Since the landscape designer title does not have a college degree or licensing requirements to be used, there is a very wide range of sophistication, aesthetic talent, technical expertise, and specialty strengths to be responsibly matched with specific client and project requirements.[citation needed]
Many landscape designers have an interest and involvement with gardening, personally or professionally. Gardens are dynamic and not static after construction and planting are completed, and so in some ways are "never done". Involvement with landscape management and direction of the ongoing garden direction, evolution, and care depend on the professional's and client's needs and inclinations. As with the other interrelated landscape disciplines, there can be an overlap of services offered under the titles of landscape designer or professional gardener.[2]
|
|
It has been suggested that Southern Nevada be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since February 2025.
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|---|---|
| Nickname(s):
The Silver State (official);
The Sagebrush State; The Battle Born State |
|
| Motto:
All for Our Country
|
|
| Anthem: "Home Means Nevada" | |
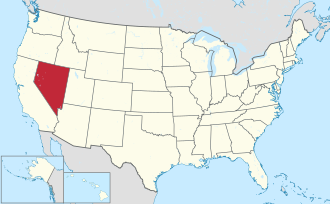
Location of Nevada within the United States
|
|
| Country | United States |
| Before statehood | Nevada Territory, Utah Territory, Arizona Territory |
| Admitted to the Union | October 31, 1864 (36th) |
| Capital | Carson City |
| Largest city | Las Vegas |
| Largest county or equivalent | Clark |
| Largest metro and urban areas | Las Vegas Valley |
| Government
|
|
| • Governor | Joe Lombardo (R) |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Stavros Anthony (R) |
| Legislature | Nevada Legislature |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | Assembly |
| Judiciary | Supreme Court of Nevada |
| U.S. senators | Catherine Cortez Masto (D) Jacky Rosen (D) |
| U.S. House delegation | 3 Democrats 1 Republican (list) |
| Area
|
|
|
• Total
|
110,577 sq mi (286,382 km2) |
| • Land | 109,781.18 sq mi (284,332 km2) |
| • Water | 791 sq mi (2,048 km2) 0.72% |
| • Rank | 7th |
| Dimensions
|
|
| • Length | 492 mi (787 km) |
| • Width | 322 mi (519 km) |
| Elevation
|
5,500 ft (1,680 m) |
| Highest elevation | 13,147 ft (4,007.1 m) |
| Lowest elevation | 481 ft (147 m) |
| Population
(2024)
|
|
|
• Total
|
|
| • Rank | 32nd |
| • Density | 26.8/sq mi (10.3/km2) |
| • Rank | 42nd |
| • Median household income
|
$76,400 (2023)[4] |
| • Income rank
|
24th |
| Demonym | Nevadan |
| Language
|
|
| • Official language | None |
| Time zones | |
| most of state | UTC−08:00 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−07:00 (PDT) |
| West Wendover | UTC−07:00 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−06:00 (MDT) |
| USPS abbreviation |
NV
|
| ISO 3166 code | US-NV |
| Traditional abbreviation | Nev. |
| Latitude | 35° N to 42° N |
| Longitude | 114°ÃƒÆ’ƒÂ¢Ã¢â€šÂ¬Ã… 2′ W to 120° W |
| Website | nv |
| List of state symbols | |
|---|---|
| Song | Home Means Nevada |
| Living insignia | |
| Bird | Mountain bluebird (Sialia currucoides) |
| Fish | Lahontan cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii henshawi) |
| Flower | Sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata) |
| Grass | Indian Rice Grass |
| Insect | Vivid Dancer Damselfly (Argia vivida) |
| Mammal | Desert bighorn sheep |
| Reptile | Desert tortoise (Gopherus agassizii) |
| Tree | Bristlecone pine, Single-leaf Piñon (Pinus monophylla) |
| Inanimate insignia | |
| Color(s) | Silver, Blue |
| Fossil | Ichthyosaur (Shonisaurus popularis) |
| Gemstone | Virgin Valley Black Fire Opal |
| Mineral | Silver |
| Rock | Sandstone |
| Soil | Orovada series |
| Other | Element: Neon |
| State route marker | |
 |
|
| State quarter | |

Released in 2006
|
|
| Lists of United States state symbols | |
Nevada (/nəˈvædÉ™, -vÉ‘ËÂÂÂÂ-/ ⓘ nÉ™-VAD-É™, -â VAH-;[5][6] Spanish: [neˈβaða]) is a landlocked state in the Western United States.[c] It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the ninth-least densely populated U.S. state. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's population live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area,[7] including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities.[8] Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state.
Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); due to the presidency of Abraham Lincoln, the Union benefited immensely from the support of newly awarded statehood by the infusion of the monetary support of nearly $400 million in silver ore generated at the time by the Comstock Lode.[9] It is also known as the "Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as the "Sage-hen State".[10] The state's name means "snowy" in Spanish, referring to Nevada's small overlap with the Sierra Nevada mountain range; however, the rest of Nevada is largely desert and semi-arid, much of it within the Great Basin. Areas south of the Great Basin are within the Mojave Desert, while Lake Tahoe and the Sierra Nevada lie on the western edge. In 2020, 80.1% of the state's land was managed by various jurisdictions of the U.S. federal government, both civilian and military.[11]
Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes inhabit what is now Nevada. The first Europeans to explore the region were Spanish. They called the region Nevada (snowy) because of the snow which covered the mountains in winter, similar to the Sierra Nevada in Spain. The area formed from mostly Alta California and part of Nuevo México's territory within the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which gained independence as Mexico in 1821. The United States annexed the area in 1848 after its victory in the Mexican–American War, and it was incorporated as part of the New Mexico and Utah Territory in 1850. The discovery of silver at the Comstock Lode in 1859 led to a population boom that became an impetus to the creation of Nevada Territory out of western Utah Territory in 1861. Nevada became the 36th state on October 31, 1864, as the second of two states added to the Union during the Civil War (the first being West Virginia).[12]
Nevada is known for its libertarian laws. In 1940, with a population of just over 110,000 people, Nevada was by far the least-populated state, with less than half the population of the next least-populous state, Wyoming.[13] However, legalized gambling and lenient marriage and divorce laws transformed Nevada into a major tourist destination in the 20th century.[14][15] Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legal, though it is illegal in its most populated regions – Clark County (Las Vegas), Washoe County (Reno) and Carson City (which, as an independent city, is not within the boundaries of any county). The tourism industry remains Nevada's largest employer,[16] with mining continuing as a substantial sector of the economy: Nevada is the fourth-largest producer of gold in the world.[17] It is the driest state. Droughts in Nevada, which are influenced by climate change, have been increasing in frequency and severity,[18] putting a further strain on Nevada's water security.
The name "Nevada" comes from the Spanish adjective nevada ([neˈβaða]), meaning "snow-covered" or "snowy".[19] The state takes its name from the Nevada Territory, which in turn was named for the Sierra Nevada.[20]
Nevadans pronounce the second syllable with the "a" of "apple" (/nəˈvædÉ™/) while some people from outside of the state pronounce it with the "a" of "palm" (/nəˈvÉ‘ËÂÂÂÂdÉ™/).[21] Although the quality, but not the length, of the latter pronunciation is closer to the Spanish pronunciation (Spanish /a/ is open central [ä],[22] whereas American English /É‘ËÂÂÂÂ/ varies from back [É‘ËÂÂÂÂ] to central [äËÂÂÂÂ]),[23] it is not the pronunciation used by Nevadans. State Assemblyman Harry Mortenson proposed a bill to recognize the alternative pronunciation of Nevada,[24] though the bill was not supported by most legislators and never received a vote. The Nevadan pronunciation is the one used by the state legislature. At one time, the state's official tourism organization, TravelNevada, stylized the name of the state as "Nevăda", with a breve over the a indicating the locally preferred pronunciation,[25] which was also available as a license plate design until 2007.[26]
Before the arrival of Europeans, the earliest inhabitants were Indigenous tribes including the Goshute, Southern Paiute, Mohave, and Wašišiw (Washoe people).[27][28]

Francisco Garcés was the first European in the area.[29] Nevada was annexed as a part of the Spanish Empire in the northwestern territory of New Spain. Administratively, the area of Nevada was part of the Commandancy General of the Provincias Internas in the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Nevada became a part of Alta California (Upper California) province in 1804 when the Californias were split. With the Mexican War of Independence won in 1821, the province of Alta California became a territory (state) of Mexico, with a small population.
Jedediah Smith entered the Las Vegas Valley in 1827, Peter Skene Ogden traveled the Humboldt River in 1828, and in 1829 a merchant from Nuevo México named Antonio Armijo streamlined travel along the Old Spanish Trail. Chronicling Armijo's route his scout Raphael Rivera was the first to name Las Vegas, in an 1830 report to governor José Antonio Chaves. Following the suggestions by Rivera of a spring, on the published expedition's map, located in the Las Vegas area John C. Frémont set up camp in Las Vegas Springs in 1844. In 1847, Mormons established the State of Deseret, claiming all of Nevada within the Great Basin and the Colorado watershed. They built the first permanent settlement in what is now Nevada, called Mormon Station (now Genoa), in 1851. Additionally, in June 1855, William Bringhurst and 29 other Mormon missionaries built the first permanent structure, a 150-foot square adobe fort, northeast of downtown Las Vegas, converging on the Spanish and Mormon Roads. The fort remained under Salt Lake City's control until the winter of 1858–1859, and the route remained largely under the control of Salt Lake City and Santa Fe tradespersons.
As such, these pioneers laid the foundation for the emergence of the initial settlements between the Sierra Nevadas and Mojave Desert and within the Las Vegas Valley. The enduring influence of New Mexico and Utah culture has since profoundly impacted Nevada's identity, manifesting through New Mexican cuisine and Mormon foodways or New Mexican and Mormon folk musics, into the fabric of Nevada's own cultural landscape.
As a result of the Mexican–American War and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, Mexico permanently lost Alta California in 1848. The new areas acquired by the United States continued to be administered as territories. As part of the Mexican Cession (1848) and the subsequent California Gold Rush that used Emigrant Trails through the area, the state's area evolved first as part of the Utah Territory and New Mexico Territory, then the Nevada Territory (March 2, 1861; named for the Sierra Nevada).[30]

The first discovery of a major U.S. deposit of silver ore occurred in Comstock Lode under Virginia City, Nevada, in 1859.
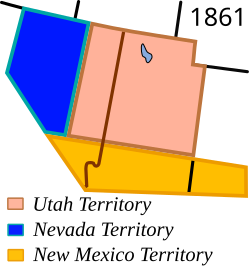
On March 2, 1861, the Nevada Territory separated from the Utah Territory and adopted its current name, shortened from The Sierra Nevada (Spanish for "snow-covered mountain range"). The 1861 southern boundary is commemorated by Nevada Historical Markers 57 and 58 in Lincoln and Nye counties.
Eight days before the presidential election of 1864, Nevada became the 36th state in the Union, despite lacking the minimum 60,000 residents that Congress typically required a potential state to have in order to become a state.[31] At the time, Nevada's population was little more than 40,000.[32] Governor Nye was frustrated that previous attempts to send the constitution via overland mail and by sea had failed by October 24, so on October 26 the full text was sent by telegraph at a cost of $4,303.27[33][d] – the most costly telegraph on file at the time for a single dispatch, equivalent to $86,514.04 in 2024. Finally, the response from Washington came on October 31, 1864: "the pain is over, the child is born, Nevada this day was admitted into the Union". Statehood was rushed to the date of October 31 to help ensure Abraham Lincoln's reelection on November 8 and post-Civil War Republican dominance in Congress,[34] as Nevada's mining-based economy tied it to the more industrialized Union. As it turned out, however, Lincoln and the Republicans won the election handily and did not need Nevada's help.
Nevada is one of only two states to significantly expand its borders after admission to the Union, with the other being Missouri, which acquired additional territory in 1837 due to the Platte Purchase. In 1866 another part of the western Utah Territory was added to Nevada in the eastern part of the state, setting the current eastern boundary. Nevada achieved its current southern boundaries on January 18, 1867, when it absorbed the portion of Pah-Ute County in the Arizona Territory west of the Colorado River, essentially all of present-day Nevada south of the 37th parallel. The transfer was prompted by the discovery of gold in the area, and officials thought Nevada would be better able to oversee the expected population boom. This area includes all of what is now Clark County and the southern-most portions of Esmeralda, Lincoln, and Nye counties.[35]

Mining shaped Nevada's economy for many years (see Silver mining in Nevada). When Mark Twain lived in Nevada during the period described in Roughing It, mining had led to an industry of speculation and immense wealth. Both mining and population temporarily declined in the late 19th century. However, the rich silver strike at Tonopah in 1900, followed by strikes in Goldfield and Rhyolite, created a second mining boom in Nevada and Nevada's population.
Unregulated gambling was commonplace in the early Nevada mining towns but was outlawed in 1909 as part of a nationwide anti-gambling crusade. Because of subsequent declines in mining output and the decline of the agricultural sector during the Great Depression, Nevada again legalized gambling on March 19, 1931, with approval from the legislature. Governor Fred B. Balzar's signature enacted the most liberal divorce laws in the country and open gambling. The reforms came just eight days after the federal government presented the $49 million construction contract for Boulder Dam (now Hoover Dam).[37]
The Nevada Test Site, 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas, was founded on January 11, 1951, for the testing of nuclear weapons. The site consists of about 1,350 square miles (3,500 km2) of the desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear testing at the Nevada Test Site began with a 1 kiloton of TNT (4.2 TJ) nuclear bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. The last atmospheric test was conducted on July 17, 1962, and the underground testing of weapons continued until September 23, 1992. The location is known for having the highest concentration of nuclear-detonated weapons in the U.S.
Over 80% of the state's area is owned by the federal government. This is mainly because homesteads were not permitted in large enough sizes to be viable in the arid conditions that prevail throughout desert Nevada. Instead, early settlers would homestead land surrounding a water source, and then graze livestock on the adjacent public land, which is useless for agriculture without access to water (this pattern of ranching still prevails).
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed in Nevada on March 5, 2020. Because of concerns about coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Nevada governor Steve Sisolak declared a state of emergency on March 12, 2020. Four days later, Nevada reported its first death. On March 17, 2020, Sisolak ordered the closure of non-essential businesses in the state to help prevent the spread of the coronavirus.
Various protests were held against Sisolak's shutdown order beginning in April 2020. Nevada launched the first phase of its reopening on May 9, 2020. Restaurants, retailers, outdoor malls, and hair salons were among the businesses allowed to reopen, but with precautions in place, such as limiting occupancy to 50 percent. A second phase went into effect on May 29, 2020. It allowed for the reopening of state parks and businesses such as bars, gyms, and movie theaters. Casinos began reopening on June 4, 2020.
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2021)
|



Nevada is almost entirely within the Basin and Range Province and is broken up by many north–south mountain ranges. Most of these ranges have endorheic valleys between them.
Much of the northern part of the state is within the Great Basin, a mild desert that experiences hot temperatures in the summer and cold temperatures in the winter. Occasionally, moisture from the Arizona Monsoon will cause summer thunderstorms; Pacific storms may blanket the area with snow. The state's highest recorded temperature was 125 °F (52 °C) in Laughlin (elevation of 605 feet or 184 meters) on June 29, 1994.[38] The coldest recorded temperature was −52 °F (−47 °C) set in San Jacinto in 1972, in the northeastern portion of the state.[38]
The Humboldt River crosses the state from east to west across the northern part of the state, draining into the Humboldt Sink near Lovelock. Several rivers drain from the Sierra Nevada eastward, including the Walker, Truckee, and Carson rivers. All of these rivers are endorheic basins, ending in Walker Lake, Pyramid Lake, and the Carson Sink, respectively. However, not all of Nevada is within the Great Basin. Tributaries of the Snake River drain the far north, while the Colorado River, which also forms much of the boundary with Arizona, drains much of southern Nevada.
The mountain ranges, some of which have peaks above 13,000 feet (4,000 m), harbor lush forests high above desert plains, creating sky islands for endemic species. The valleys are often no lower in elevation than 3,000 feet (910 m), while some in central Nevada are above 6,000 feet (1,800 m).

The southern third of the state, where the Las Vegas area is situated, is within the Mojave Desert. The area receives less rain in the winter but is closer to the Arizona Monsoon in the summer. The terrain is also lower, mostly below 4,000 feet (1,200 m), creating conditions for hot summer days and cool to chilly winter nights.
Nevada and California have by far the longest diagonal line (in respect to the cardinal directions) as a state boundary at just over 400 miles (640 km). This line begins in Lake Tahoe nearly 4 miles (6.4 km) offshore (in the direction of the boundary), and continues to the Colorado River where the Nevada, California, and Arizona boundaries merge 12 miles (19 km) southwest of the Laughlin Bridge.
The largest mountain range in the southern portion of the state is the Spring Mountain Range, just west of Las Vegas. The state's lowest point is along the Colorado River, south of Laughlin.
Nevada has 172 mountain summits with 2,000 feet (610 m) of prominence. Nevada ranks second, after Alaska, for the greatest number of mountains in the United States, followed by California, Montana, and Washington.[39]

Nevada is the driest state in the United States.[40] It is made up of mostly desert and semi-arid climate regions, and, with the exception of the Las Vegas Valley, the average summer diurnal temperature range approaches 40 °F (22 °C) in much of the state. While winters in northern Nevada are long and fairly cold, the winter season in the southern part of the state tends to be of short duration and mild. Most parts of Nevada receive scarce precipitation during the year. The most rain that falls in the state falls on the east and northeast slopes of the Sierra Nevada.
The average annual rainfall per year is about 7 inches (180 mm); the wettest parts get around 40 inches (1,000 mm). Nevada's highest recorded temperature is 125 °F (52 °C) at Laughlin on June 29, 1994, and the lowest recorded temperature is −50 °F (−46 °C) at San Jacinto on January 8, 1937. Nevada's 125 °F (52 °C) reading is the third highest statewide record high temperature of a U.S. state, just behind Arizona's 128 °F (53 °C) reading and California's 134 °F (57 °C) reading.
| Location | July (°F) | July (°C) | December (°F) | December (°C) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | |
| Las Vegas | 106 | 81 | 41 | 27 | 56 | 38 | 13 | 3 |
| Reno | 92 | 57 | 33 | 14 | 45 | 25 | 7 | –4 |
| Carson City | 89 | 52 | 32 | 11 | 45 | 22 | 7 | –5 |
| Elko | 90 | 50 | 32 | 10 | 37 | 14 | 2 | –9 |
| Fallon | 92 | 54 | 33 | 12 | 45 | 19 | 7 | –7 |
| Winnemucca | 93 | 52 | 34 | 11 | 41 | 17 | 5 | –8 |
| Laughlin | 112 | 80 | 44 | 27 | 65 | 43 | 18 | 6 |
The vegetation of Nevada is diverse and differs by state area. Nevada contains six biotic zones: alpine, sub-alpine, ponderosa pine, pinion-juniper, sagebrush and creosotebush.[42]


Nevada is divided into political jurisdictions designated as counties. Carson City is officially a consolidated municipality, meaning it legally functions as both a city and a county. As of 1919, there were 17 counties in the state, ranging from 146 to 18,159 square miles (380 to 47,030 km2).
Lake County, one of the original nine counties formed in 1861, was renamed Roop County in 1862. Part of the county became Lassen County, California, in 1864, resolving border uncertainty. In 1883, Washoe County annexed the portion that remained in Nevada.[43]
In 1969, Ormsby County was dissolved and the Consolidated Municipality of Carson City was created by the Legislature in its place coterminous with the old boundaries of Ormsby County.
Bullfrog County was formed in 1987 from part of Nye County. After the creation was declared unconstitutional, the county was abolished in 1989.[43]
Humboldt County was designated as a county in 1856 by Utah Territorial Legislature and again in 1861 by the new Nevada Legislature.
Clark County is the most populous county in Nevada, accounting for nearly three-quarters of its residents. Las Vegas, Nevada's most populous city, has been the county seat since the county was created in 1909 from a portion of Lincoln County, Nevada. Before that, it was a part of Arizona Territory. Clark County attracts numerous tourists: An estimated 44 million people visited Clark County in 2014.[44]
Washoe County is the second-most populous county of Nevada. Its county seat is Reno. Washoe County includes the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
Lyon County is the third most populous county. It was one of the nine original counties created in 1861. It was named after Nathaniel Lyon, the first Union General to be killed in the Civil War. Its current county seat is Yerington. Its first county seat was established at Dayton on November 29, 1861.[45]
| County name | County seat | Year founded | 2022 population[46] | Percent of total | Area | Percent of total | Population density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sq mi | km2 | per sq mi | per km2 | ||||||
| Carson City | Carson City | 1861 | 58,130 | 1.83 % | 157 | 410 | 0.14 % | 370.25 | 142.95 |
| Churchill | Fallon | 1861 | 25,843 | 0.81 % | 5,024 | 13,010 | 4.54 % | 5.14 | 1.98 |
| Clark | Las Vegas | 1908 | 2,322,985 | 73.10 % | 8,061 | 20,880 | 7.29 % | 288.18 | 111.27 |
| Douglas | Minden | 1861 | 49,628 | 1.56 % | 738 | 1,910 | 0.67 % | 67.25 | 25.97 |
| Elko | Elko | 1869 | 54,046 | 1.70 % | 17,203 | 44,560 | 15.56 % | 3.14 | 1.21 |
| Esmeralda | Goldfield | 1861 | 744 | 0.02 % | 3,589 | 9,300 | 3.25 % | 0.21 | 0.081 |
| Eureka | Eureka | 1869 | 1,863 | 0.06 % | 4,180 | 10,800 | 3.78 % | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Humboldt | Winnemucca | 1856/1861 | 17,272 | 0.54 % | 9,658 | 25,010 | 8.73 % | 1.79 | 0.69 |
| Lander | Battle Mountain | 1861 | 5,766 | 0.18 % | 5,519 | 14,290 | 4.99 % | 1.04 | 0.40 |
| Lincoln | Pioche | 1867 | 4,482 | 0.14 % | 10,637 | 27,550 | 9.62 % | 0.42 | 0.16 |
| Lyon | Yerington | 1861 | 61,585 | 1.94 % | 2,024 | 5,240 | 1.83 % | 30.43 | 11.75 |
| Mineral | Hawthorne | 1911 | 4,525 | 0.14 % | 3,813 | 9,880 | 3.45 % | 1.19 | 0.46 |
| Nye | Tonopah | 1864 | 54,738 | 1.72 % | 18,199 | 47,140 | 16.46 % | 3.01 | 1.16 |
| Pershing | Lovelock | 1919 | 6,462 | 0.20 % | 6,067 | 15,710 | 5.49 % | 1.07 | 0.41 |
| Storey | Virginia City | 1861 | 4,170 | 0.13 % | 264 | 680 | 0.24 % | 15.80 | 6.10 |
| Washoe | Reno | 1861 | 496,745 | 15.63 % | 6,542 | 16,940 | 5.92 % | 75.93 | 29.32 |
| White Pine | Ely | 1869 | 8,788 | 0.28 % | 8,897 | 23,040 | 8.05 % | 0.99 | 0.38 |
| Totals | Counties: 17 | 3,177,772 | 110,572 | 286,380 | 28.74 | 11.10 | |||
|
Largest cities or towns in Nevada
Source:[47]
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | County | Pop. | ||||||
 Las Vegas  Henderson |
1 | Las Vegas | Clark | 641,903 |  Reno North Las Vegas |
||||
| 2 | Henderson | Clark | 317,610 | ||||||
| 3 | Reno | Washoe | 264,165 | ||||||
| 4 | North Las Vegas | Clark | 262,527 | ||||||
| 5 | Enterprise | Clark | 221,831 | ||||||
| 6 | Spring Valley | Clark | 215,597 | ||||||
| 7 | Sunrise Manor | Clark | 205,618 | ||||||
| 8 | Paradise | Clark | 191,238 | ||||||
| 9 | Sparks | Washoe | 108,445 | ||||||
| 10 | Carson City | Carson City | 58,639 | ||||||





There are 68 designated wilderness areas in Nevada, protecting some 6,579,014 acres (2,662,433 ha) under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service, U.S. Forest Service, and Bureau of Land Management.[48]
The Nevada state parks comprise protected areas managed by the state of Nevada, including state parks, state historic sites, and state recreation areas. There are 24 state park units, including Van Sickle Bi-State Park which opened in July 2011 and is operated in partnership with the adjacent state of California.[49]

| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1860 | 6,857 | — | |
| 1870 | 42,941 | 526.2% | |
| 1880 | 62,266 | 45.0% | |
| 1890 | 47,355 | −23.9% | |
| 1900 | 42,335 | −10.6% | |
| 1910 | 81,875 | 93.4% | |
| 1920 | 77,407 | −5.5% | |
| 1930 | 91,058 | 17.6% | |
| 1940 | 110,247 | 21.1% | |
| 1950 | 160,083 | 45.2% | |
| 1960 | 285,278 | 78.2% | |
| 1970 | 488,738 | 71.3% | |
| 1980 | 800,493 | 63.8% | |
| 1990 | 1,201,833 | 50.1% | |
| 2000 | 1,998,257 | 66.3% | |
| 2010 | 2,700,551 | 35.1% | |
| 2020 | 3,104,614 | 15.0% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 3,267,467 | 5.2% | |
| Source: 1910–2020[50] | |||

The United States Census Bureau determined Nevada had a population of 3,104,614 at the 2020 U.S. census. In 2022, the estimated population of Nevada was 3,177,772, an increase of 73,158 residents (2.36%) since the 2020 census.[51] Nevada had the highest percentage growth in population from 2017 to 2018. At the 2020 census, 6.0% of the state's population were reported as under 5, 22.5% were under 18, and 16.1% were 65 or older. Females made up about 49.8% of the population. 19.1% of the population was reported as foreign-born.
Since the 2020 census, the population of Nevada had a natural increase of 2,374 (the net difference between 42,076 births and 39,702 deaths); and an increase due to net migration of 36,605 (of which 34,280 was due to domestic and 2,325 was due to international migration).[52]
The center of population of Nevada is in southern Nye County.[53] In this county, the unincorporated town of Pahrump, 60 miles (97 km) west of Las Vegas on the California state line, has grown very rapidly from 1980 to 2020. At the 2020 census, the town had 44,738 residents.[54] Las Vegas grew from a gulch of 100 people in 1900 to 10,000 by 1950 to 100,000 by 1970, and was America's fastest-growing city and metropolitan area from 1960 to 2000.
From about the 1940s until 2003, Nevada was the fastest-growing state in the U.S. percentage-wise. Between 1990 and 2000, Nevada's population increased by 66%, while the nation's population increased by 13%. More than two-thirds of the population live in Clark County, which is coextensive with the Las Vegas metropolitan area. Thus, in terms of population, Nevada is one of the most centralized states in the nation.
Henderson and North Las Vegas are among the top 20 fastest-growing U.S. cities with populations over 100,000. The rural community of Mesquite 65 miles (105 km) northeast of Las Vegas was an example of micropolitan growth in the 1990s and 2000s. Other desert towns like Indian Springs and Searchlight on the outskirts of Las Vegas have seen some growth as well.
Since 1950, the rate of population born in Nevada has never peaked above 27 percent, the lowest rate of all states. In 2012, only 25% of Nevadans were born in Nevada.[55]
According to HUD's 2022 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, there were an estimated 7,618 homeless people in Nevada.[56][57]
| Race / Ethnicity | Pop 2000[58] | Pop 2010[59] | Pop 2020[60] | % 2000 | % 2010 | % 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone (NH) | 1,303,001 | 1,462,081 | 1,425,952 | 65.21% | 54.14% | 45.93% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) | 131,509 | 208,058 | 291,960 | 6.58% | 7.70% | 9.40% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) | 21,397 | 23,536 | 23,392 | 1.07% | 0.87% | 0.75% |
| Asian alone (NH) | 88,593 | 191,047 | 265,991 | 4.43% | 7.07% | 8.57% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) | 7,769 | 15,456 | 22,970 | 0.39% | 0.57% | 0.74% |
| Some Other Race alone (NH) | 2,787 | 4,740 | 17,171 | 0.14% | 0.18% | 0.55% |
| Mixed Race/Multi-Racial (NH) | 49,231 | 79,132 | 166,921 | 2.46% | 2.93% | 5.38% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) | 393,970 | 716,501 | 890,257 | 19.72% | 26.53% | 28.68% |
| Total | 1,998,257 | 2,700,551 | 3,104,614 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Race and Ethnicity[61] | Alone | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 45.9% |
|
50.6% |
|
| Hispanic or Latino[e] | — | 28.7% |
|
|
| Multiracial | — | 14.0% |
|
|
| African American (non-Hispanic) | 9.4% |
|
11.1% |
|
| Asian | 8.6% |
|
10.7% |
|
| Native American | 0.8% |
|
2.1% |
|
| Pacific Islander | 0.7% |
|
1.5% |
|
| Other | 0.6% |
|
1.4% |
|
According to the 2022 American Community Survey, 30.3% of Nevada's population were of Hispanic or Latino origin (of any race): Mexican (22%), Cuban (1.5%), Salvadoran (1.5%), Puerto Rican (1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (4.3%).[62] The largest European ancestry groups were: German (8.9%), English (8.1%), Irish (7.2%), and Italian (4.8%).[63] The largest Asian ancestry groups in the state were Filipino (6.4%) and Chinese (1.9%).[64]

| Non-Hispanic White
30–40%
|
In 1980, non-Hispanic whites made up 83.2% of the state's population.[65]
| Racial composition | 1970[65] | 1980 | 1990[65] | 2000[66] | 2010[67] | 2020[68] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 91.7% | 87.5% | 84.3% | 75.2% | 66.2% | 51.2% |
| Black | 5.7% | 6.4% | 6.6% | 6.8% | 8.1% | 9.8% |
| Asian | 0.7% | 1.8% | 3.2% | 4.5% | 7.2% | 8.8% |
| Native | 1.6% | 1.7% | 1.6% | 1.3% | 1.2% | 1.4% |
| Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islander |
– | – | – | 0.4% | 0.6% | 0.8% |
| Other race | 0.3% | 2.7% | 4.4% | 8.0% | 12.0% | 14.0% |
| Two or more races | – | – | – | 3.8% | 4.7% | 14.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino (of any race) | 5.6% | 6.7% | 10.4% | 19.7% | 26.5% | 28.7% |
| Non-Hispanic white | 86.7% | 83.2% | 78.7% | 65.2% | 54.1% | 45.9% |
As of 2011, 63.6% of Nevada's population younger than age 1 were minorities.[69] Las Vegas is a majority-minority city. According to the United States Census Bureau estimates, as of July 1, 2018, non-Hispanic Whites made up 48.7% of Nevada's population.[70]
In Douglas, Mineral, and Pershing counties, a plurality of residents are of Mexican ancestry. In Nye County and Humboldt County, residents are mostly of German ancestry; Washoe County has many Irish Americans. Americans of English descent form pluralities in Lincoln County, Churchill County, Lyon County, White Pine County, and Eureka County.
Asian Americans have lived in the state since at least the 1850s, when the California gold rush brought thousands of Chinese miners to Washoe County. They were followed by a few hundred Japanese farmworkers in the late 19th century. By the late 20th century, many immigrants from China, Japan, Korea, the Philippines, Bangladesh, India, and Vietnam came to the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The city now has a significant Asian American community, with a mostly Chinese and Taiwanese area known as "Chinatown" west of I-15 on Spring Mountain Road. Filipino Americans form the largest Asian American group in the state, with a population of more than 202,000. They comprise 59.8% of the Asian American population in Nevada and constitute about 6.4% of the entire state's population.[71]
Mining booms drew many Greek and Eastern European immigrants to Nevada.[72] In the early twentieth century, Greeks, Slavs, Danes, Japanese, Italians, and Basques poured into Nevada.[73] Chileans were found in the state as early as 1870.[74] During the mid-1800s, a significant number of European immigrants, mainly from Ireland, England and Germany, arrived in the state with the intention of capitalizing on the thriving mining sector in the region.[75]
Native American tribes in Nevada are the Northern and Southern Paiute, Western Shoshone, Goshute, Hualapai, Washoe, and Ute tribes.[76]
Whites remain the largest racial or ethnic group in Nevada.[77] Hispanics are the fastest growing ethnic group in Nevada.[78] There is a growing Mexican and Central American population in Nevada. Many of Nevada's Latino immigrants are from Mexico, Guatemala and El Salvador.[79] Nevada also has a growing multiracial population.[80]
The top countries of origin for immigrants in Nevada were Mexico (39.5 percent of immigrants), the Philippines (14.3 percent), El Salvador (5.2 percent), China (3.1 percent), and Cuba (3 percent).[81]
The majority of people in Nevada are of white (European) ancestry. A small portion trace their ancestry to Basque people recruited as sheepherders. Hispanics in Nevada are mainly of Mexican and Cuban heritage. Latinos comprise about one-fourth of Nevada's residents and are concentrated in the southeast in Nevada. African Americans live mainly in the Las Vegas and Reno area and constitute less than one-tenth of the population. Native Americans of the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes live on several reservations in the state and make up a small fraction of Nevada's population.[82]
The most common ancestries in Nevada include Mexican, German, Irish, English, Italian and Asian.[83]
Nevada is the third most diverse state in the country, behind only Hawaii and California.[84][85]
Note: Births within the table do not add up, due to Hispanics being counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.
| Race | 2013[86] | 2014[87] | 2015[88] | 2016[89] | 2017[90] | 2018[91] | 2019[92] | 2020[93] | 2021[94] | 2022[95] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 27,293 (77.9%) | 27,638 (77.1%) | 27,648 (76.2%) | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| Non-Hispanic White | 14,951 (42.7%) | 15,151 (42.2%) | 14,937 (41.2%) | 13,918 (38.4%) | 13,171 (36.8%) | 13,021 (36.5%) | 12,479 (35.6%) | 11,602 (34.5%) | 11,800 (35.0%) | 10,961 (33.0%) |
| Black | 4,215 (12.0%) | 4,603 (12.8%) | 4,803 (13.2%) | 4,205 (11.6%) | 4,471 (12.5%) | 4,564 (12.8%) | 4,514 (12.9%) | 4,533 (13.5%) | 4,457 (13.2%) | 4,334 (13.1%) |
| Asian | 3,097 (8.8%) | 3,145 (8.8%) | 3,337 (9.2%) | 2,666 (7.3%) | 2,685 (7.5%) | 2,613 (7.3%) | 2,587 (7.4%) | 2,467 (7.3%) | 2,372 (7.0%) | 2,548 (7.7%) |
| Pacific Islander | ... | ... | ... | 308 (0.8%) | 322 (0.9%) | 340 (1.0%) | 372 (1.1%) | 358 (1.1%) | 331 (1.0%) | 358 (1.1%) |
| American Indian | 425 (1.2%) | 475 (1.3%) | 510 (1.4%) | 303 (0.8%) | 305 (0.9%) | 280 (0.8%) | 277 (0.8%) | 234 (0.7%) | 239 (0.7%) | 218 (0.7%) |
| Hispanic (of any race) | 12,718 (36.3%) | 13,006 (36.3%) | 13,225 (36.4%) | 13,391 (36.9%) | 13,176 (36.8%) | 13,307 (37.3%) | 13,238 (37.7%) | 12,763 (37.9%) | 12,842 (38.1%) | 13,019 (39.2%) |
| Total Nevada | 35,030 (100%) | 35,861 (100%) | 36,298 (100%) | 36,260 (100%) | 35,756 (100%) | 35,682 (100%) | 35,072 (100%) | 33,653 (100%) | 33,686 (100%) | 33,193 (100%) |



A small percentage of Nevada's population lives in rural areas. The culture of these places differs significantly from major metropolitan areas. People in these rural counties tend to be native Nevada residents, unlike in the Las Vegas and Reno areas, where the vast majority of the population was born in another state. The rural population is also less diverse in terms of race and ethnicity. Mining plays an important role in the economies of the rural counties, with tourism being less prominent.[96] Ranching also has a long tradition in rural Nevada.[97]
| Rank | Place | Per capita income | County | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Crystal Bay | $180,334 | Washoe | |
| 2 | Glenbrook | $102,963 | Douglas | |
| 3 | Zephyr Cove | $94,920 | Douglas | |
| 4 | Genoa | $86,185 | Douglas | |
| 5 | Incline Village | $74,294 | Washoe | |
| 6 | Kingsbury | $68,215 | Douglas | |
| 7 | Round Hill Village | $67,659 | Douglas | |
| 8 | East Valley | $67,169 | Douglas | |
| 9 | Summerlin South | $65,633 | Clark | |
| 10 | Mount Charleston | $57,583 | Clark | |
Church attendance in Nevada is among the lowest of all U.S. states. In a 2009 Gallup poll only 30% of Nevadans said they attended church weekly or almost weekly, compared to 42% of all Americans (only four states were found to have a lower attendance rate than Nevada's).[99] In 2020, the Public Religion Research Institute determined 67% of the population were Christian,[100] reflecting a 1% increase in religiosity from 2014's separate Pew study.[101]
Major religious affiliations of the people of Nevada were, according to the Pew Research Center in 2014: Protestant 35%, Irreligious 28%, Roman Catholic 25%, Latter-day Saints 4%, Jewish 2%, Hindu less than 1%, Buddhist 0.5% and Muslim around 0.2%. Parts of Nevada (in the eastern parts of the state) are situated in the Mormon Corridor.
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2010 were the Roman Catholic Church with 451,070; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints with 175,149; and the Southern Baptist Convention with 45,535; Buddhist congregations 14,727; Baháʼí Faith 1,723; and Muslim 1,700.[102]
The most common non-English languages spoken in Nevada are Spanish, Tagalog and Chinese.[103] Indigenous languages of Nevada include Northern Paiute, the Southern Paiute, Shoshone, and Washo.[104]
The top seven languages spoken in Nevada according to the U.S. Census data are Spanish, Tagalog, Chinese, Vietnamese, Korean, Amharic, Arabic, and Thai.[105]
Historically what is now Nevada has been inhabited mainly by the Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe.[106]
The largest Native American tribes in Nevada according to the 2010 census are listed in the table below:[107]
| Tribal grouping | American Indian and
Alaska Native alone |
AIAN in combination with
one or more other races |
Total AIAN alone or
in any combination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total AIAN population | 32062 | 23883 | 55945 |
| Cherokee | 1824 | 4376 | 6200 |
| Paiute | 4182 | 677 | 4859 |
| Navajo | 1926 | 671 | 2597 |
| Paiute-Shoshone | 2118 | 170 | 2288 |
| Mexican American Indian | 1222 | 708 | 1930 |
| Shoshone | 1388 | 400 | 1788 |
| Choctaw | 597 | 872 | 1469 |
| Apache | 719 | 690 | 1409 |
| Sioux | 702 | 626 | 1328 |
| Blackfeet | 284 | 877 | 1161 |
| Te-Moak Tribes of Western Shoshone | 1011 | 118 | 1129 |
| Washoe | 815 | 130 | 945 |
| Ojibwe | 494 | 338 | 832 |
| Reno-Sparks Indian Colony | 579 | 13 | 592 |
| Iroquois | 228 | 283 | 511 |
| Tribe not specified | 9413 | 10117 | 19530 |






The economy of Nevada is tied to tourism (especially entertainment and gambling related), mining, and cattle ranching. Nevada's industrial outputs are tourism, entertainment, mining, machinery, printing and publishing, food processing, and electric equipment. The Bureau of Economic Analysis[109][110] estimates Nevada's total state product in 2018 was $170 billion.[111] The state's per capita personal income in 2020 was $53,635, ranking 31st in the nation.[112] Nevada's state debt in 2012 was calculated to be $7.5 billion, or $3,100 per taxpayer.[113] As of May 2021, the state's unemployment rate was 7.8%.[114]
In portions of the state outside of the Las Vegas and Reno metropolitan areas mining plays a major economic role. By value, gold is by far the most important mineral mined. In 2022, 4,040,000 troy ounces (126 t) of gold worth $7.3 billion were mined in Nevada, and the state accounted for 4% of world gold production. Other minerals mined in Nevada include construction aggregates, copper, gypsum, diatomite and lithium.[115][116] Despite its rich deposits, the cost of mining in Nevada is generally high, and output is very sensitive to world commodity prices.
Cattle ranching is a major economic activity in rural Nevada.[117] Nevada's agricultural outputs are cattle, hay, alfalfa, dairy products, onions, and potatoes. In 2020, there were an estimated 438,511 head of cattle and 71,699 head of sheep in Nevada.[118] Most of these animals forage on rangeland in the summer, with supplemental feed in the winter. Calves are generally shipped to out-of-state feedlots in the fall to be fattened for the market. Over 90% of Nevada's 653,891 acres (264,620 ha) of cropland is used to grow hay, mostly alfalfa, for livestock feed.[118]
The largest employers in the state, as of the first fiscal quarter of 2011, are the following, according to the Nevada Department of Employment, Training and Rehabilitation:[119]


Amtrak's California Zephyr train uses the Union Pacific's original transcontinental railroad line in daily service from Chicago to Emeryville, California, serving Elko, Winnemucca, and Reno. Las Vegas has had no passenger train service since Amtrak's Desert Wind was discontinued in 1997. Amtrak Thruway buses provide connecting service from Las Vegas to trains at Needles, California, Los Angeles, and Bakersfield, California; and from Stateline, Nevada, to Sacramento, California. There have been a number of proposals to re-introduce service to either Los Angeles or Southern California with the privately run Brightline West having begun construction in 2024.
The Union Pacific Railroad has some railroads in the north and south of Nevada. Greyhound Lines provide some bus service to the state.
Interstate 15 (I-15) passes through the southern tip of the state, serving Las Vegas and other communities. I-215 and I-515 also serve the Las Vegas metropolitan area. I-80 crosses through the northern part of Nevada, roughly following the path of the Humboldt River from Utah in the east and the Truckee River westward through Reno into California. It has a spur route, I-580. Nevada also is served by several U.S. highways: US 6, US 50, US 93, US 95 and US 395. There are also 189 Nevada state routes. Many of Nevada's counties have a system of county routes as well, though many are not signed or paved in rural areas. Nevada is one of a few states in the U.S. that do not have a continuous interstate highway linking its two major population centers – the road connection between the Las Vegas and Reno areas is a combination of several different Interstate and U.S. highways. The Interstate 11 proposed routing may eventually remedy this.[120]
The state is one of just a few in the country to allow semi-trailer trucks with three trailers – what might be called a "road train" in Australia. But American versions are usually smaller, in part because they must ascend and descend some fairly steep mountain passes.
RTC Transit is the public transit system in the Las Vegas metropolitan area. The agency is the largest transit agency in the state and operates a network of bus service across the Las Vegas Valley, including the use of The Deuce, double-decker buses, on the Las Vegas Strip and several outlying routes. RTC RIDE operates a system of local transit bus service throughout the Reno-Sparks metropolitan area. Other transit systems in the state include Carson City's JAC. Most other counties in the state do not have public transportation at all.
Additionally, a 4-mile (6.4 km) monorail system provides public transportation in the Las Vegas area. The Las Vegas Monorail line services several casino properties and the Las Vegas Convention Center on the east side of the Las Vegas Strip, running near Paradise Road, with a possible future extension to Harry Reid International Airport. Several hotels also run their own monorail lines between each other, which are typically several blocks in length.
Harry Reid International Airport in Las Vegas is the busiest airport serving Nevada. The Reno-Tahoe International Airport (formerly known as the Reno Cannon International Airport) is the other major airport in the state.
| External image | |
|---|---|
Nevada has had a thriving solar energy sector. An independent study in 2013 concluded that solar users created a $36 million net benefit. However, in December 2015, the Public Utility Commission let the state's only power company, NV Energy, charge higher rates and fees to solar panel users, leading to an immediate collapse of rooftop solar panel use.[121]
In December 1987, Congress amended the Nuclear Waste Policy Act to designate Yucca Mountain nuclear waste repository as the only site to be characterized as a permanent repository for all of the nation's highly radioactive waste.[122]
In 2018, the National Low Income Housing Coalition calculated the discrepancy between available affordable housing units and renters who earn below the poverty line. In Nevada, only 15 affordable rental homes are available per 100 extremely low income (ELI) households.[123] The shortage extended to a deficit in supply of 71,358 affordable rental homes. This was the largest discrepancy of any state. The most notable catalyst for this shortage was the Great Recession and housing crisis of 2007 and 2008. Since then, housing prices have increased while demand has increased, and supply has struggled to match the increase in demand. In addition, low-income service workers were slowly being pushed out by an influx of tech professionals. In Nevada there is essentially a standard of six-figure income to affordably rent a single-family home.[124] Considering the average salary in Nevada, $54,842 per year, this standard is on average, unaffordable.[125] The disproportionate cost of housing compared to average salary has led to 112,872 renters to be paying more than half of their yearly income towards housing.[126]
The definition of an affordable home is "one that a household can obtain for 30 percent or less of its annual income". So, there is clearly a long way to go in order to close the gap between housing prices and relative income in the state. Renters are looking for solutions to still be able to live in the state in a way that their income can support. As a result, single adults are being forced to split rent with other renters or move residences to farther outside metro areas. One solution being offered is to increase the supply of higher income positions within the state to make things more affordable. However, this would require Nevadans to retrain in new jobs or careers.
Education in Nevada is achieved through public and private elementary, middle, and high schools, as well as colleges and universities.
A May 2015 educational reform law expanded school choice options to 450,000 Nevada students who are at up to 185% of the federal poverty level. Education savings accounts (ESAs) are enabled by the new law to help pay the tuition for private schools. Alternatively, families "can use funds in these accounts to also pay for textbooks and tutoring".[127][128]
Approximately 86.9% of Nevada residents have attained at least a high school degree or equivalent, which is below the national average of 88.6%.[129]
Public school districts in Nevada include:
The Nevada Aerospace Hall of Fame provides educational resources and promotes the aerospace and aviation history of the state.[130]

Under the Constitution of the State of Nevada, the powers of the Nevada government are divided among three separate departments: the executive consisting of the governor of Nevada and their cabinet along with the other elected constitutional officers; the legislative consisting of the Nevada Legislature, which includes the Assembly and the Senate; and the judicial consisting of the Supreme Court of Nevada and lower courts.
The governor is the chief magistrate of Nevada,[131] the head of the executive department of the state's government,[131] and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces.[132] The current governor is Joe Lombardo, a Republican. The executive branch also consists of an independently elected lieutenant governor, secretary of state, state treasurer, state controller, and attorney general who function as a check and balance on the power of the governor.[133]
The Nevada Legislature is a bicameral body divided into an Assembly and Senate. Members of the Assembly serve two years, and members of the Senate serve four years. Both houses of the Nevada Legislature enacted term limits starting in 2010, with senators and assemblymen/women who are limited to a maximum of twelve years in each body (by appointment or election which is a lifetime limit) – a provision of the constitution which was upheld by the Supreme Court of Nevada in a unanimous decision. Each session of the legislature meets for a constitutionally mandated 120 days in every odd-numbered year, or longer if the governor calls a special session.
On December 18, 2018, Nevada became the first in the United States with a female majority in its legislature. Women hold nine of the 21 seats in the Nevada Senate, and 23 of the 42 seats in the Nevada Assembly.[134]
The Supreme Court of Nevada is the state supreme court and the head of the Nevada Judiciary. Original jurisdiction is divided between the district courts (with general jurisdiction), and justice courts and municipal courts (both of limited jurisdiction). Appeals from District Courts are made directly to the Nevada Supreme Court, which under a deflective model of jurisdiction, has the discretion to send cases to the Court of Appeals for final resolution.[135]
Incorporated towns in Nevada, known as cities, are given the authority to legislate anything not prohibited by law. A recent movement has begun to permit home rule to incorporate Nevada cities to give them more flexibility and fewer restrictions from the Legislature. Town Boards for unincorporated towns are limited local governments created by either the local county commission, or by referendum, and form a purely advisory role and in no way diminish the responsibilities of the county commission that creates them.

In 1900, Nevada's population was the smallest of all states and was shrinking, as the difficulties of living in a "barren desert" began to outweigh the lure of silver for many early settlers. Historian Lawrence Friedman has explained what happened next:
Nevada, in a burst of ingenuity, built an economy by exploiting its sovereignty. Its strategy was to legalize all sorts of things that were illegal in California ... after the easy divorce came easy marriage and casino gaming. Even prostitution is legal in Nevada, in any county that decides to allow it. Quite a few of them do.[136]
With the advent of air conditioning for summertime use and Southern Nevada's mild winters, the fortunes of the state began to turn around, as it did for Arizona, making these two states the fastest growing in the Union.
Nevada is the only state where prostitution is legal – in a licensed brothel in a county which has specifically voted to permit it. It is illegal in larger jurisdictions such as Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), Washoe County (which contains Reno), and the independent city of Carson City.
Nevada's early reputation as a "divorce haven" arose from the fact that before the no-fault divorce revolution in the 1970s, divorces were difficult to obtain in the United States. Already having legalized gambling and prostitution, Nevada continued the trend of boosting its profile by adopting one of the most liberal divorce statutes in the nation. This resulted in Williams v. North Carolina (1942), 317 U.S. 287 (1942), in which the U.S. Supreme Court ruled North Carolina had to give "full faith and credit" to a Nevada divorce. The Court modified its decision in Williams v. North Carolina (1945), 325 U.S. 226 (1945), by holding a state need not recognize a Nevada divorce unless one of the parties was domiciled there at the time the divorce was granted and the forum state was entitled to make its own determination.
As of 2009, Nevada's divorce rate was above the national average.[137]
Nevada's tax laws are intended to draw new residents and businesses to the state. Nevada has no personal income tax or corporate income tax.[138] Since Nevada does not collect income data it cannot share such information with the federal government, the IRS.[139]
The state sales tax (similar to VAT or GST) in Nevada is variable depending upon the county. The statewide tax rate is 6.85%, with five counties (Elko, Esmeralda, Eureka, Humboldt, and Mineral) charging this amount. Counties may impose additional rates via voter approval or through approval of the state legislature; therefore, the applicable sales tax varies by county from 6.85% to 8.375% (Clark County). Clark County, which includes Las Vegas, imposes four separate county option taxes in addition to the statewide rate: 0.25% for flood control, 0.50% for mass transit, 0.25% for infrastructure, and 0.25% for more law enforcement. In Washoe County, which includes Reno, the sales tax rate is 7.725%, due to county option rates for flood control, the ReTRAC train trench project, and mass transit, and an additional county rate approved under the Local Government Tax Act of 1991.[140] The minimum Nevada sales tax rate changed on July 1, 2009.[141]
The lodging tax rate in unincorporated Clark County, which includes the Las Vegas Strip, is 12%. Within the boundaries of the cities of Las Vegas and Henderson, the lodging tax rate is 13%.
Corporations such as Apple Inc. allegedly have set up investment companies and funds in Nevada to avoid paying taxes.[142]
In 2009, the Nevada Legislature passed a bill creating a domestic partnership registry which enables same-sex couples to enjoy the same rights as married couples. Due to the landmark decision in the case of Obergefell v. Hodges, 576 U.S. 644 (2015), same-sex marriage was outright legalized in the state.
Nevada provides a friendly environment for the formation of corporations, and many (especially California) businesses have incorporated in Nevada to take advantage of the benefits of the Nevada statute. Nevada corporations offer great flexibility to the board of directors and simplify or avoid many of the rules that are cumbersome to business managers in some other states. In addition, Nevada has no franchise tax, although it does require businesses to have a license for which the business has to pay the state.
Similarly, many U.S. states have usury laws limiting the amount of interest a lender can charge, but federal law allows corporations to "import" these laws from their home state. Nevada has no cap on interest rates that may be agreed to in contracts.[143]
Nevada has very liberal alcohol laws. Bars are permitted to remain open 24 hours, with no "last call". Liquor stores, convenience stores and supermarkets may also sell alcohol 24 hours per day and may sell beer, wine and spirits.
In 2016, Nevada voters approved Question 2, which legalized the possession, transportation and cultivation of personal use amounts of marijuana for adults age 21 years and older, and authorized the creation of a regulated market for the sale of marijuana to adults age 21 years and older through state-licensed retail outlets.[144] Nevada voters had previously approved medical marijuana in 2000, but rejected marijuana legalization in a similar referendum in 2006. Marijuana in all forms remains illegal under federal law.
Aside from cannabis legalization, non-alcohol drug laws are a notable exception to Nevada's otherwise libertarian principles. It is notable for having the harshest penalties for drug offenders in the country. Nevada remains the only state to still use mandatory minimum sentencing guidelines for possession of drugs.[145]
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) reported, in their Behavioral Health Barometer for Nevada, published in 2014, changes to substance abuse patterns and addiction across the southwestern state.[146] Between 2012 and 2013, adolescents in Nevada abused illicit substances at a slightly higher percentage than nationally. 10.2 percent of Nevada's adolescents abused illicit drugs compared to 9.2 percent across the United States. Between 2009 and 2013, 11.7 percent of all adolescents in the state reported abusing illicit, intoxicating substances in the month prior to the survey; this represents 25,000 adolescents.
Nevada voters enacted a smoking ban ("The Nevada Clean Indoor Air Act") in November 2006 which became effective on December 8, 2006. It outlaws smoking in most workplaces and public places. Smoking is permitted in bars, but only if the bar serves no food, or the bar is inside a larger casino. Smoking is also permitted in casinos, certain hotel rooms, tobacco shops, and brothels.[147] However, some businesses do not obey this law and the government tends not to enforce it.[148] In 2011, smoking restrictions in Nevada were relaxed for certain places which allow only people 21 or older inside.[149]
In 2006, the crime rate in Nevada was about 24% higher than the national average rate, though crime has since decreased. Property crimes accounted for about 85% of the total crime rate in Nevada, which was 21% higher than the national rate. The remaining 20.3% were violent crimes.[150] A complete listing of crime data in the state for 2013 can be found here:[151]
| Party | Total voters | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | 616,656 | 29.42% | |
| Republican | 616,882 | 29.43% | |
| Independent American | 94,604 | 4.51% | |
| Libertarian | 16,202 | 0.77% | |
| Other parties | 48,727 | 2.33% | |
| Nonpartisan | 703,085 | 33.54% | |
| Total | 2,096,156 | 100.00% | |

Due to heavy growth in the southern portion of the state, there is a noticeable divide between the politics of northern and southern Nevada. Historically, northern Nevada has been very Republican. The more rural counties of the north are among the most conservative regions of the state. Carson City, the state's capital, is a Republican-leaning swing city/county. Washoe County, home to Reno, has historically been strongly Republican, but now has become a fairly balanced swing county, like the state as a whole. Clark County, home to Las Vegas, has been a stronghold for the Democratic Party since it was founded in 1909, having voted Republican only six times and once for a third-party candidate, although in recent times becoming more competitive, most notably in the 2024 Presidential Election where the Democratic Party's margin of victory was only 2.63 percentage points to Republicans.[153] Clark and Washoe counties have long dominated the state's politics. Between them, they cast 87% of Nevada's vote, and elect a substantial majority of the state legislature. The last Republican to carry Clark County was George H. W. Bush in 1988, and the last Republican to carry Washoe County was George W. Bush in 2004. The great majority of the state's elected officials are from either Las Vegas or Reno.[154] Donald Trump was able to carry Nevada with a statewide majority in 2024, despite losing both Clark and Washoe.
In 2014, Republican Adam Laxalt, despite losing both Clark and Washoe counties, was elected Attorney General. However, he had lost Clark County only by 5.6% and Washoe County by 1.4%, attributable to lower turnout in these counties.[155]

Nevada has been won by the winner of nearly every presidential election since its first in 1864, only being carried by the defeated candidate eight times since statehood, most of which were before 1900. Since 1912 Nevada has been carried by the presidential victor the most out of any state (27 of 29 elections), the only exceptions being 1976 when it voted for Gerald Ford over Jimmy Carter and 2016 when the state was carried by Hillary Clinton over Donald Trump. This gives the state status as a political bellwether. It was one of only three states won by John F. Kennedy in the American West in the election of 1960, albeit narrowly.[156] The state's U.S. Senators are Democrats Catherine Cortez Masto and Jacky Rosen. The Governorship is held by Joe Lombardo, a Republican.
Nevada is the only U.S. state to have a none of the above option available on its ballots. Officially called None of These Candidates, the option was first added to the ballot in 1975 and is used in all statewide elections, including president, US Senate and all state constitutional positions. In the event "None of These Candidates" receives a plurality of votes in the election, the candidate with the next-highest total is elected.[157]
In a 2020 study, Nevada was ranked as the 23rd on the "Cost of Voting Index", which is a measure of "the ease of voting across the United States."[158]
Resort areas like Las Vegas, Reno, Lake Tahoe, and Laughlin attract visitors from around the nation and world. In fiscal year 2022 Nevada casinos (not counting those with annual revenue under a million dollars) brought in US$10.7 billion in gaming revenue and another US$15.7 billion in non-gaming revenue.[159]
Nevada has by far the most hotel rooms per capita in the United States. According to the American Hotel and Lodging Association, there were 187,301 rooms in 584 hotels (of 15 or more rooms). The state is ranked just below California, Texas, Florida, and New York in the total number of rooms, but those states have much larger populations. Nevada has one hotel room for every 14 residents, far above the national average of one hotel room per 67 residents.[160]
Prostitution is legal in parts of Nevada in licensed brothels, but only counties with populations under 400,000 have the option to legalize it. Although prostitution is not a major part of the Nevada economy, employing roughly 300 women as independent contractors, it is a very visible endeavor. Of the 14 counties permitted to legalize prostitution under state law, eight have chosen to legalize brothels. State law prohibits prostitution in Clark County (which contains Las Vegas), and Washoe County (which contains Reno). However, prostitution is legal in Storey County, which is part of the Reno–Sparks metropolitan area.
The Las Vegas Valley is home to the Vegas Golden Knights of the National Hockey League who began to play in the 2017–18 NHL season at T-Mobile Arena on the Las Vegas Strip in Paradise, the Las Vegas Raiders of the National Football League who began play at Allegiant Stadium in Paradise in 2020 after moving from Oakland, California, and the Las Vegas Aces of the WNBA who began playing in 2018 at Mandalay Bay Events Center after relocating from San Antonio. The Oakland Athletics of Major League Baseball plan to move to Las Vegas by 2027.[161][162]
Nevada takes pride in college sports, most notably its college football. College teams in the state include the Nevada Wolf Pack (representing the University of Nevada, Reno) and the UNLV Rebels (representing the University of Nevada, Las Vegas), both in the Mountain West Conference (MW).
UNLV is most remembered for its men's basketball program, which experienced its height of supremacy in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Coached by Jerry Tarkanian, the Runnin' Rebels became one of the most elite programs in the country. In 1990, UNLV won the Men's Division I Championship by defeating Duke 103–73, which set tournament records for most points scored by a team and largest margin of victory in the national title game.
In 1991, UNLV finished the regular season undefeated, a feat that would not be matched in Division I men's basketball for more than 20 years. Forward Larry Johnson won several awards, including the Naismith Award. UNLV reached the Final Four yet again, but lost their national semifinal against Duke 79–77. The Runnin' Rebels were the Associated Press pre-season No. 1 back to back (1989–90, 1990–91). North Carolina is the only other team to accomplish that (2007–08, 2008–09).
The state's involvement in major-college sports is not limited to its local schools. In the 21st century, the Las Vegas area has become a significant regional center for college basketball conference tournaments. The MW, West Coast Conference, and Western Athletic Conference all hold their men's and women's tournaments in the area, and the Pac-12 holds its men's tournament there as well. The Big Sky Conference, after decades of holding its men's and women's conference tournaments at campus sites, began holding both tournaments in Reno in 2016.
Las Vegas has hosted several professional boxing matches, most recently at the MGM Grand Garden Arena with bouts such as Mike Tyson vs. Evander Holyfield, Evander Holyfield vs. Mike Tyson II, Oscar De La Hoya vs. Floyd Mayweather Jr. and Oscar De La Hoya vs. Manny Pacquiao and at the newer T-Mobile Arena with Canelo Álvarez vs. Amir Khan.
Along with significant rises in popularity in mixed martial arts (MMA), a number of fight leagues such as the UFC have taken interest in Las Vegas as a primary event location due to the number of suitable host venues. The Mandalay Bay Events Center and MGM Grand Garden Arena are among some of the more popular venues for fighting events such as MMA and have hosted several UFC and other MMA title fights. The city has held the most UFC events with 86 events.
The state is also home to the Las Vegas Motor Speedway, which hosts NASCAR's Pennzoil 400 and South Point 400. Two venues in the immediate Las Vegas area host major annual events in rodeo. The Thomas & Mack Center, built for UNLV men's basketball, hosts the National Finals Rodeo. The PBR World Finals, operated by the bull riding-only Professional Bull Riders, was also held at the Thomas & Mack Center before moving to T-Mobile Arena in 2016.
The state is also home to famous tennis player, Andre Agassi, and current baseball superstar Bryce Harper.
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Raiders | Football | NFL | Allegiant Stadium (65,000) | 2020 | 3[f] |
| Vegas Golden Knights | Ice hockey | NHL | T-Mobile Arena (17,500) | 2017 | 1 |
| Las Vegas Aces | Women's basketball | WNBA | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 2018 | 2 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas Aviators | Baseball | MiLB (AAA–PCL) | Las Vegas Ballpark (10,000) | 1983 | 2 |
| Reno Aces | Greater Nevada Field (9,013) | 2009 | 2 | ||
| Vegas Royals | Basketball | ABA | 0 | ||
| Henderson Silver Knights | Ice hockey | AHL | Dollar Loan Center (5,567) | 2020 | 0 |
| Tahoe Knight Monsters | ECHL | Tahoe Blue Event Center (5,000) | 2024 | 0 | |
| Las Vegas Lights FC | Soccer | USLC | Cashman Field (9,334) | 2018 | 0 |
| Nevada Storm | Women's football | WFA | Damonte Ranch High School (N/A) Fernley High School (N/A) Galena High School (N/A) |
2008 | 0 |
| Sin City Trojans | Desert Pines High School (N/A) | 0 | |||
| Vegas Knight Hawks | Indoor football | IFL | Dollar Loan Center (6,019) | 2021 | 0 |
| Las Vegas Desert Dogs | Box lacrosse | NLL | Michelob Ultra Arena (12,000) | 0 |
| Team | Sport | League | Venue (capacity) | Established | Titles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reno Ice Raiders | Ice hockey | MWHL | Reno Ice | 2015 | 0 |
| Vegas Jesters | City National Arena (600) | 2012 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Thunderbirds | USPHL | 2019 | 0 | ||
| Las Vegas Legends | Soccer | NPSL | Peter Johann Memorial Field (2,500) | 2021 | 0 |
| Nevada Coyotes FC | UPSL | Rio Vista Sports Complex (N/A) | 2016 | 0 |
| School | Team | League | Division | Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) | UNLV Rebels | NCAA | NCAA Division I | Mountain West |
| University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) | Nevada Wolf Pack | |||
| College of Southern Nevada (CSN) | CSN Coyotes | NJCAA | NJCAA Division I | Scenic West |
| Western Nevada College (WNC) | WNC Wildcats |

Several United States Navy ships have been named USS Nevada in honor of the state. They include:
Area 51 is near Groom Lake, a dry salt lake bed. The much smaller Creech Air Force Base is in Indian Springs, Nevada; Hawthorne Army Depot in Hawthorne; the Tonopah Test Range near Tonopah; and Nellis AFB in the northeast part of the Las Vegas Valley. Naval Air Station Fallon in Fallon; NSAWC, (pronounced "EN-SOCK") in western Nevada. NSAWC consolidated three Command Centers into a single Command Structure under a flag officer on July 11, 1996. The Naval Strike Warfare Center based at NAS Fallon since 1984, was joined with the Navy Fighter Weapons School (TOPGUN) and the Carrier Airborne Early Warning Weapons School, which both moved from NAS Miramar as a result of a Base Realignment and Closure decision in 1993 which transferred that installation back to the Marine Corps as MCAS Miramar. The Seahawk Weapon School was added in 1998 to provide tactical training for Navy helicopters.
These bases host a number of activities including the Joint Unmanned Aerial Systems Center of Excellence, the Naval Strike and Air Warfare Center, Nevada Test and Training Range, Red Flag, the U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds, the United States Air Force Warfare Center, the United States Air Force Weapons School, and the United States Navy Fighter Weapons School.
Workers were great, no problem they did what was required, but the representative of your company mislead me on what was to be done, I showed pictures from a competitor landscaper, representative stated he could bet there , , . price, but since it wasn’t in contract, I was left with uncomplicated backyard , working with owner at present, so he’s been outstanding working on this situation, as amount of rock was way off and the owner did increase the amount substantially to finish the front yard. another landscaper under contract to finish the backyard. Would like to add a comment the manger/owner of Las Vegas yard n block stands behind his words and helped me tremendously on finishing up the backyard,
Eric and team did an amazing job. They worked with me for months while I got HOA approval for the project. Once they began working they were great, going over everything in detail and making sure things were perfect. This project included wall repair, stucco and paint repair, paver and turf installation. Extremely satisfied with this experience.
Chris, the design consultant, Dave the production manager, along with their install team Opulent were affordable, upfront with costs, efficient and professional. Attached are some before and after pictures. Highly recommend their services.
My initial contact was with Ray, whom did an excellent job giving me an estimate on what I wanted done in my small yard and walkway., the guys that came out and did the work were superior. They did an excellent job. I’m very pleased with this company. I will highly recommend them to family and friends, and I will be using them in the near future for other little projects.
We recently had a very positive experience with Rock N Block for our fence replacement. The entire process went smoothly and exceeded our expectations. Harvey and his team were incredibly professional and communicative throughout the project providing much-needed assurance and peace of mind. The crew was punctual and maintained a diligent and respectful attitude that made the experience pleasant. The crew finished the project ahead of schedule, and the quality of their work is impressive; our new wall looks great! We recommend Rock N Block for any fencing needs and look forward to working with them again. Thank you, Harvey and crew, for a job well done!
Workers were great, no problem they did what was required, but the representative of your company mislead me on what was to be done, I showed pictures from a competitor landscaper, representative stated he could bet there , , . price, but since it wasn’t in contract, I was left with uncomplicated backyard , working with owner at present, so he’s been outstanding working on this situation, as amount of rock was way off and the owner did increase the amount substantially to finish the front yard. another landscaper under contract to finish the backyard. Would like to add a comment the manger/owner of Las Vegas yard n block stands behind his words and helped me tremendously on finishing up the backyard,
My initial contact was with Ray, whom did an excellent job giving me an estimate on what I wanted done in my small yard and walkway., the guys that came out and did the work were superior. They did an excellent job. I’m very pleased with this company. I will highly recommend them to family and friends, and I will be using them in the near future for other little projects.
Chris, the design consultant, Dave the production manager, along with their install team Opulent were affordable, upfront with costs, efficient and professional. Attached are some before and after pictures. Highly recommend their services.
Eric and team did an amazing job. They worked with me for months while I got HOA approval for the project. Once they began working they were great, going over everything in detail and making sure things were perfect. This project included wall repair, stucco and paint repair, paver and turf installation. Extremely satisfied with this experience.